Related Research Articles

Friedrich Wöhler FRS(For) HonFRSE was a German chemist known for his work in both organic and inorganic chemistry, being the first to isolate the chemical elements beryllium and yttrium in pure metallic form. He was the first to prepare several inorganic compounds, including silane and silicon nitride.
Hafnium is a chemical element; it has symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, though it was not identified until 1922, by Dirk Coster and George de Hevesy. Hafnium is named after Hafnia, the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered.

Lutetium is a chemical element; it has symbol Lu and atomic number 71. It is a silvery white metal, which resists corrosion in dry air, but not in moist air. Lutetium is the last element in the lanthanide series, and it is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements; it can also be classified as the first element of the 6th-period transition metals.

Niobium is a chemical element; it has symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in Earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite. Its name comes from Greek mythology: Niobe, daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, which makes them difficult to distinguish.

Tantalum is a chemical element; it has symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, it is named after Tantalus, a figure in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It is part of the refractory metals group, which are widely used as components of strong high-melting-point alloys. It is a group 5 element, along with vanadium and niobium, and it always occurs in geologic sources together with the chemically similar niobium, mainly in the mineral groups tantalite, columbite and coltan.

Charles Hatchett FRS FRSE was an English mineralogist and analytical chemist who discovered the element niobium, for which he proposed the name "columbium".
A period 5 element is one of the chemical elements in the fifth row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The fifth period contains 18 elements, beginning with rubidium and ending with xenon. As a rule, period 5 elements fill their 5s shells first, then their 4d, and 5p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as rhodium.

Group 3 is the first group of transition metals in the periodic table. This group is closely related to the rare-earth elements. It contains the four elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lutetium (Lu), and lawrencium (Lr). The group is also called the scandium group or scandium family after its lightest member.

Group 5 is a group of elements in the periodic table. Group 5 contains vanadium (V), niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta) and dubnium (Db). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table. This group is sometimes called the vanadium group or vanadium family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.

Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac was a Swiss chemist whose work with atomic weights suggested the possibility of isotopes and the packing fraction of nuclei. His study of the rare earth elements led to his discovery of ytterbium in 1878 and co-discovery of gadolinium in 1880.

Heinrich Rose was a German mineralogist and analytical chemist. He was the brother of the mineralogist Gustav Rose and a son of Valentin Rose. Rose's early works on phosphorescence were noted in the Quarterly Journal of Science in 1821, and on the strength of these works, he was elected privatdozent at the University of Berlin from 1822, then Professor from 1832.
Pelopium was the proposed name for a new element found by the chemist Heinrich Rose in 1845. The name derived from the Greek king and later god Pelops, son of Tantalus. During the analysis of the mineral tantalite, he concluded that it does contain an element similar to niobium and tantalum. The similar reactivity of niobium and tantalum complicated preparation of pure samples and therefore several new elements were proposed, which were later found to be mixtures of niobium and tantalum.

Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta
2O
5. It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. Ta
2O
5 is an inert material with a high refractive index and low absorption, which makes it useful for coatings. It is also extensively used in the production of capacitors, due to its high dielectric constant.

Georges Urbain was a French chemist, a professor of the Sorbonne, a member of the Institut de France, and director of the Institute of Chemistry in Paris. Much of his work focused on the rare earths, isolating and separating elements such as europium and gadolinium, and studying their spectra, their magnetic properties and their atomic masses. He discovered the element lutetium. He also studied the efflorescence of saline hydrates.

Christian Wilhelm Blomstrand was a Swedish mineralogist and chemist. He was a professor at the University of Lund from 1862-1895, where he isolated the element niobium in 1864. He developed an early version of the periodic table and made advances in understanding the chemistry of coordination compounds. Blomstrand published textbooks in chemistry and was well-known internationally for his scientific contributions.
Dianium was the proposed name for a new element found by the mineralogist and poet Wolfgang Franz von Kobell in 1860. The name derived from the Roman goddess Diana. During the analysis of the mineral tantalite and niobite, he concluded that it does contain an element similar to niobium and tantalum. The symbol was Di.

Niobium(V) fluoride, also known as niobium pentafluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula NbF5. It is a colorless solid.
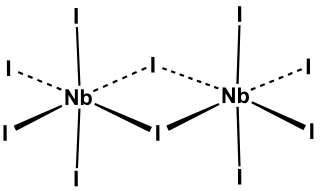
Niobium pentaiodide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2I10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, NbI5. It is a diamagnetic, yellow solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two NbI5 units are joined by a pair of iodide bridges. There is no bond between the Nb centres. Niobium(V) chloride, niobium(V) bromide, tantalum(V) chloride, tantalum(V) bromide, and tantalum(V) iodide, all share this structural motif.
Georg Karl Brauer was a German chemist.
References
- ↑ Hermann, R. (1847). "Untersuchungen über das Ilmenium". Journal für Praktische Chemie. 40: 457–480. doi:10.1002/prac.184704001110.
- 1 2 Marignac, Blomstrand, H. Deville, L. Troost und R. Hermann (1866). "Tantalsäure, Niobsäure, (Ilmensäure) und Titansäure". Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry. 5 (1): 384–389. doi:10.1007/BF01302537. S2CID 97246260.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Gupta, C. K.; Suri, A. K. (1994). Extractive Metallurgy of Niobium. CRC Press. pp. 1–16. ISBN 0-8493-6071-4.
- ↑ Marignac, M. C. (1866). "Recherches sur les combinaisons du niobium". Annales de chimie et de physique (in French). 4 (8): 7–75.
- ↑ Hermann, R. (1871). "Ueber ein einfaches Verfahren zur Trennung der Säuren des Niobiums von denen des Ilmeniums". Zeitschrift für Analytische Chemie. 10: 344–348. doi:10.1007/BF01354144. S2CID 96176382.
- ↑ Hermann [R.] (1846). "On the new Metal Ilmenium". The Chemical Gazette, Or, Journal of Practical Chemistry, in All Its Applications to Pharmacy, Arts and Manufactures. 4 (XCVIII): 449–452.
