Lebanon is a parliamentary democratic republic within the overall framework of confessionalism, a form of consociationalism in which the highest offices are proportionately reserved for representatives from certain religious communities. The constitution of Lebanon grants the people the right to change their government. However, from the mid-1970s until the parliamentary elections in 1992, the Lebanese Civil War (1975–1990) precluded the exercise of political rights.

The Lebanese Civil War was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 150,000 fatalities and also led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon.
Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism as a set of social practices where daily life is organised on the basis of communal norms and rules that individuals strategically use and transcend. This definition highlights the co-constitutive aspect of sectarianism and people’s agency, as opposed to understanding sectarianism as being fixed and incompatible communal boundaries.
The Taif Agreement, officially known as the National Reconciliation Accord, was reached to provide "the basis for the ending of the civil war and the return to political normalcy in Lebanon". Negotiated in Taif, Saudi Arabia, it was designed to end the 15 year-long Lebanese Civil War, reassert Lebanese government authority in southern Lebanon, which was controlled at the time by the Christian-separatist South Lebanon Army under the occupational hegemony of Israel. Though the agreement set a time frame for withdrawal of Syrian military forces from Lebanon, stipulating that the Syrian occupation end within two years, Syria did not withdraw its forces from the country until 2005. It was signed on 22 October 1989 and ratified by the Lebanese parliament on 5 November, 1989.
The National Pact is an unwritten agreement that laid the foundation of Lebanon as a multiconfessional state following negotiations between the Shia, Sunni, and Maronite leaderships. Erected in the summer of 1943, the National Pact was formed by the then-president Bechara El Khoury and the prime minister Riad Al Solh. Mainly centered around the interests of political elites, the Maronite elite served as a voice for the Christian population of Lebanon while the Sunni elite represented the voice of the Muslim population. The pact also established Lebanon's independence from France.
Confessionalism is a system of government that is a de jure mix of religion and politics. It typically entails distributing political and institutional power proportionally among confessional communities.

Fawaz A. Gerges is a Lebanese-American academic and author with expertise on the Middle East, U.S. foreign policy, international relations, social movements, and relations between the Islamic and Western worlds.
Lebanon–Syria relations were officially established in October 2008 when Syrian President Bashar Al-Assad issued a decree to establish diplomatic relations with Lebanon for the first time since both countries gained independence from France in 1943 (Lebanon) and 1946 (Syria). Lebanon had traditionally been seen by Syria as part of Greater Syria. Following World War I, the League of Nations Mandate partitioned Ottoman Syria under French control, eventually leading to the creation of nation-states Lebanon and Syria.
Mohammed Abu-Nimer is an American expert on conflict resolution and dialogue for peace. He is a full professor at the American University School of International Service in International Peace and Conflict Resolution in Washington, DC, the largest school of international relations in the United States.
Sectarianism can be defined as a practice that is created over a period of time through consistent social, cultural and political habits leading to the formation of group solidarity that is dependent upon practices of inclusion and exclusion. Sectarian discrimination focuses on the exclusion aspect of sectarianism and can be defined as 'hatred arising from attaching importance to perceived differences between subdivisions within a group', for example the different denominations of a religion or the factions of a political belief.

Iraqi nationalism is a form of nationalism that asserts the belief that Iraqis form a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Iraqis of different ethnoreligious groups such as Mesopotamian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Yazidis, Mandeans, Shabaks and Yarsans.

Turkey and the United Arab Emirates share extensive cultural, military and economic ties, but relations have substantially deteriorated since Arab Spring, and later started to recover in the recent years.
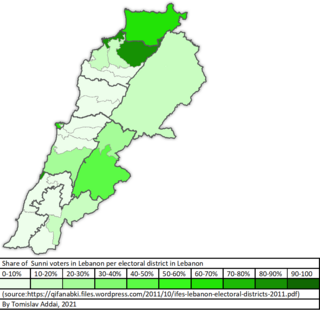
Lebanese Sunni Muslims refers to Lebanese people who are adherents of the Sunni branch of Islam in Lebanon, which is one of the largest denomination in Lebanon tied with Shias. Sunni Islam in Lebanon has a history of more than a millennium. According to a CIA 2018 study, Lebanese Sunni Muslims constitute an estimated 30.6% of Lebanon's population.

Arab nationalism is a political ideology asserting that Arabs constitute a single nation. As a traditional nationalist ideology, it promotes Arab culture and civilization, celebrates Arab history, the Arabic language and Arabic literature. It often also calls for unification of Arab society. It bases itself on the premise that the people of the Arab world — from the Atlantic Ocean to the Arabian Sea — constitute one nation bound together by a common identity: ethnicity, language, culture, history, geography, and politics.

The Arab Winter is a term referring to the resurgence of authoritarianism and Islamic extremism in some Arab countries in the 2010s in the aftermath of the Arab Spring protests. The term "Arab Winter" refers to the events across Arab League countries in the Middle East and North Africa, including the Syrian civil war, the Iraqi insurgency and the subsequent War in Iraq, the Egyptian Crisis, the First Libyan Civil War and the subsequent Second Libyan Civil War, and the Yemeni civil war. Events referred to as the Arab Winter include those in Egypt that led to the removal from office in 2013 of Mohamed Morsi and the subsequent election in 2014 of Abdel Fattah el-Sisi.

The Second Republic is Lebanon's current republican system of government. It was established on 22 October 1989 by Lebanese political leaders and business people under the Taif Agreement.
Fabrice Balanche is a geographer and specialist in the political geography of Syria, Lebanon, Iraq and the Middle East in general.

The 2021 Beirut clashes, also known as the 2021 Beirut massacre, Tayouneh Incident or Mini May 7, occurred in the Tayouneh neighborhood of the Lebanese capital of Beirut on 14 October 2021 between Hezbollah and the Amal Movement, and unidentified gunmen allegedly associated with the Lebanese Forces, and the Lebanese Armed Forces, resulting in the death of seven people and injury of 32 others, and the arrest of nine by the Lebanese Armed Forces. The violence erupted during a protest organized by Hezbollah and its allies against Tarek Bitar, the lead judge probing the 2020 explosion in the city's port, as they accuse him of being partisan. The clashes took place at the Justice Palace, located in Eastern Beirut along the former civil war front line between the Christian and Muslim Shiite areas. The clashes were the worst in the country since the 2008 Lebanon conflict.
Sectarianism in Lebanon refers to the formal and informal organization of Lebanese politics and society along religious lines. It has been formalized and legalized within state and non-state institutions and is inscribed in its constitution. Lebanon recognizes 18 different sects: 67.6% of the population is Muslim, 32.4% is Christian, the majority being Maronites Catholics and Greek Orthodox, while 4.52% is Druze. The foundations of sectarianism in Lebanon date back to the mid-19th century during Ottoman rule. It was subsequently reinforced with the creation of the Republic of Lebanon in 1920 and its 1926 constitution, and in the National Pact of 1943. In 1990, with the Taif Agreement, the constitution was revised but did not structurally change aspects relating to political sectarianism. The dynamic nature of sectarianism in Lebanon has prompted some historians and authors to refer to it as "the sectarian state par excellence" because it is a mixture of religious communities and their myriad sub-divisions, with a constitutional and political order to match.










