Related Research Articles

The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is 8,900 km (5,530 mi) long, 200 to 700 km wide, and has an average height of about 4,000 m (13,123 ft). The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina.

Minera Escondida is a mining company that operates two open pit copper mines in the Atacama Desert, 170 km southeast of Antofagasta in northern Chile. It is currently the highest producing copper mine in the world. Its 2007 production of 1.483 million tons of the metal was worth US$10.12 billion, mainly as metal in concentrate, but some as cathode, and was 9.5% of world output and 26% of Chilean production, according to the US Geological Survey's preliminary estimates of 2007 world mine output.
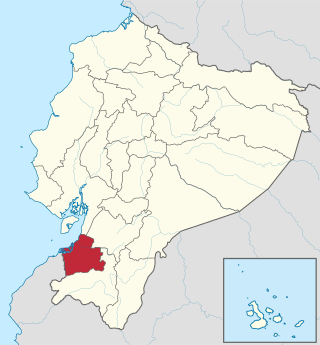
El Oro is the southernmost of Ecuador's coastal provinces. It was named for its historically important gold production. Today it is one of the world's major exporters of bananas. The capital is Machala.

Chuquicamata is the largest open pit copper mine in terms of excavated volume in the world. It is located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama, at 2,850 m (9,350 ft) above sea level. It is 215 km (134 mi) northeast of Antofagasta and 1,240 km (770 mi) north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 tons annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of 850 metres (2,790 ft) makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world, after Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, United States.

Rancagua is a city and commune in central Chile and part of the Rancagua conurbation. It is the capital of the Cachapoal Province and of the O'Higgins Region, located 87 km (54 mi) south of the national capital of Santiago.

Moquegua is a city in southern Peru, located in the Department of Moquegua, of which it is the capital. It is also capital of Mariscal Nieto Province and Moquegua District. It is located 1144 kilometers south of the capital city of Lima.

Copiapó is a city and commune in northern Chile, located about 65 kilometers east of the coastal town of Caldera. Founded on December 8, 1744, it is the capital of Copiapó Province and Atacama Region.

El Salvador is a mining town in the commune of Diego de Almagro, Chañaral Province, Atacama Region, Chile. Located at an elevation of more than 2,400 meters in the foothills of the Andes and in the middle of the Atacama Desert, it has a population of approximately 7,000 inhabitants. At its peak, El Salvador once had a population of 34,000 inhabitants.

Metallurgy in pre-Columbian America is the extraction, purification and alloying of metals and metal crafting by Indigenous peoples of the Americas prior to European contact in the late 15th century. Indigenous Americans had been using native metals from ancient times, with recent finds of gold artifacts in the Andean region dated to 2155–1936 BCE, and North American copper finds being dated to approximately 5000 BCE. The metal would have been found in nature without the need for smelting, and shaped into the desired form using hot and cold hammering without chemical alteration or alloying. To date "no one has found evidence that points to the use of melting, smelting and casting in prehistoric eastern North America."

Mining in the United Kingdom produces a wide variety of fossil fuels, metals, and industrial minerals due to its complex geology. In 2013, there were over 2,000 active mines, quarries, and offshore drilling sites on the continental land mass of the United Kingdom producing £34bn of minerals and employing 36,000 people.
Estadio Huachipato-CAP Acero, known until 2015 as Estadio CAP, is a football stadium located in Talcahuano, Chile. Inaugurated in 2009, it is the home field of Huachipato, replacing Estadio Las Higueras, which was demolished in 2008. The stadium capacity is 10,500 people (all-seated).

The Mantos Blancos mine is a large copper mine located in northern Chile in Antofagasta Region. Mantos Blancos represents one of the largest copper reserves in Chile and in the world having estimated reserves of 500 million tonnes of ore grading 1% copper.

Mapuche silverwork is one of the best known aspects of Mapuche material culture. The adornments have been subject to changes in fashion but some designs have resisted change.

Inca rule in Chile was brief, it lasted from the 1470s to the 1530s when the Inca Empire was absorbed by Spain. The main settlements of the Inca Empire in Chile lay along the Aconcagua, Mapocho and Maipo rivers. Quillota in Aconcagua Valley was likely the Incas' foremost settlement. The bulk of the people conquered by the Incas in Central Chile were Diaguitas and part of the Promaucae. Incas appear to have distinguished between a "province of Chile" and a "province of Copayapo" neighboring it to the north. In Aconcagua Valley the Incas settled people from the areas of Arequipa and possibly also the Lake Titicaca.
Sierra Gorda Mine in Chile is a copper and molybdenum open pit mine which started production on October 1, 2014. The mine is located 2 km north-west of the village of Sierra Gorda in the Antofagasta Province of northern Chile.

Potrerillos is a ghost town in the interior of Atacama Region, Chile. Potrerillos became established as mining camp in the 1920s by Andes Copper Mining Company.
During most of Chile's history, from 1500 to the present, mining has been an important economic activity. 16th century mining was oriented towards the exploitation of gold placer deposits using encomienda labour. After a period of decline in the 17th century mining resurged in the 18th and early 19th century this time revolving chiefly around silver. In the 1870s silver mining declined sharply. Chile took over the highly lucrative saltpetre mining districts of Peru and Bolivia in the War of the Pacific (1879–83). In the first half of the 20th century copper mining overshadowed the declining saltpetre mining.

Szenicsite is a copper hydroxy molybdate mineral, named after husband and wife Terry and Marissa Szenics, American mineral collectors who found the first specimens. When it was first discovered in Atacama, Chile, it was thought to be lindgrenite. The occurrence appeared in an isolated area, which was about one cubic meter in size. The mineral occurred in cavities of copper bearing powellite and matrix rich molybdenite. These cavities were filled with a material resembling clay. Outside of the zone the szenicsite crystals grew, copper levels seemed to decrease, and the mineralization changed to lindgrenite. Moving further from the zone, the minerals growing seemed to be lacking copper, and consisted of powellite blebs in the ore. Szenicsite was approved by the IMA in 1993.
Tres Puntas is silver deposit and mine in Chile's Atacama Region. It is located 80 km north of the regional capital Copiapó. Tres Puntas was discovered in 1848 sparking the largest silver rush in Chile since Chañarcillo was discovered in 1832. The deposit was discovered by Miguel Osorio but came to be owned by Apolinario Soto.
References
- ↑ "Inca de Oro mine" (PDF). smedg.org.au. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-03. Retrieved 2013-07-26.
26°45′20″S69°54′16″W / 26.75556°S 69.90444°W