Disfranchisement, also disenfranchisement or voter disqualification, is the restriction of suffrage of a person or group of people, or a practice that has the effect of preventing a person exercising the right to vote. Disfranchisement can also refer to the revocation of power or control of a particular individual, community or being to the natural amenity they have; that is to deprive of a franchise, of a legal right, of some privilege or inherent immunity. Disfranchisement may be accomplished explicitly by law or implicitly through requirements applied in a discriminatory fashion, through intimidation, or by placing unreasonable requirements on voters for registration or voting. High barriers to entry to the political competition can disenfranchise political movements.

Parole is a form of early release of a prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated parole officers, or else they may be rearrested and returned to prison.
In the United States, habitual offender laws have been implemented since at least 1952, and are part of the United States Justice Department's Anti-Violence Strategy. These laws require a person who is convicted of an offense and who has one or two other previous serious convictions to serve a mandatory life sentence in prison, with or without parole depending on the jurisdiction. The purpose of the laws is to drastically increase the punishment of those who continue to commit offenses after being convicted of one or two serious crimes.

Incarceration in the United States is one of the primary means of punishment for crime in the United States. In 2023, over five million people are under supervision by the criminal justice system, with nearly two million people incarcerated in state or federal prisons and local jails. The United States has the largest known prison population in the world. Prison populations grew dramatically beginning in the 1970s, but began a decline around 2009, dropping 25% by year-end 2021.

Recidivism is the act of a person repeating an undesirable behavior after they have experienced negative consequences of that behavior, or have been trained to extinguish it. Recidivism is also used to refer to the percentage of former prisoners who are rearrested for a similar offense.

Prison reform is the attempt to improve conditions inside prisons, improve the effectiveness of a penal system, or implement alternatives to incarceration. It also focuses on ensuring the reinstatement of those whose lives are impacted by crimes.

The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) is a United States federal law enforcement agency within the U.S. Department of Justice that operates U.S. federal prisons and is responsible for the care, custody, and control of federal prisoners.
A military prison is a prison operated by a military. Military prisons are used variously to house prisoners of war, unlawful combatants, those whose freedom is deemed a national security risk by the military or national authorities, and members of the military found guilty of a serious crime. There are two types: penal and confinement-oriented, where captured enemy combatants are confined for military reasons until hostilities cease. Most militaries have some sort of military police unit operating at the divisional level or below to perform many of the same functions as civilian police, from traffic-control to the arrest of violent offenders and the supervision of detainees and prisoners of war.

Incapacitation in the context of criminal sentencing philosophy is one of the functions of punishment. It involves capital punishment, sending an offender to prison, or possibly restricting their freedom in the community, to protect society and prevent that person from committing further crimes. Incarceration, as the primary mechanism for incapacitation, is also used as to try to deter future offending.

The United States Medical Center for Federal Prisoners is a United States federal prison in Springfield, Missouri which provides medical, mental health, and dental services to male offenders. It is operated by the Federal Bureau of Prisons, a division of the United States Department of Justice.

The Federal Correctional Institution, Terre Haute is a medium-security United States federal prison for male inmates in Indiana. It is part of the Federal Correctional Complex, Terre Haute and is operated by the Federal Bureau of Prisons, a division of the United States Department of Justice. The facility also has an adjacent satellite prison camp for minimum-security male offenders.
In the United States, life imprisonment is amongst the most severe punishments provided by law, depending on the state, and second only to the death penalty. According to a 2013 study, 1 of every 2,000 inhabitants of the U.S. were imprisoned for life as of 2012.
Red Onion State Prison (ROSP) is a supermax state prison located in unincorporated Wise County, Virginia, near Pound. Operated by the Virginia Department of Corrections (VADOC), it houses about 800 inmates. The prison opened in August 1998.
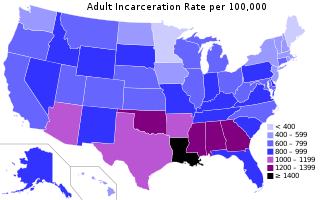
According to the latest available data at the World Prison Brief on May 7, 2023, the United States has the sixth highest incarceration rate in the world, at 531 people per 100,000. Between 2019 and 2020, the United States saw a significant drop in the total number of incarcerations. State and federal prison and local jail incarcerations dropped by 14% from 2.1 million in 2019 to 1.8 million in mid-2020. In 2018, the United States had the highest incarceration rate in the world.

A prison, also known as a jail, gaol, penitentiary, detention center, correction center, correctional facility, or remand center, is a facility where people are confined against their will and denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state, generally as punishment for various crimes. Authorities most commonly use prisons within a criminal-justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those who have pled or been found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment.
Indefinite imprisonment or indeterminate imprisonment is the imposition of a sentence of imprisonment with no definite period of time set during sentencing. It was imposed by certain nations in the past, before the drafting of the United Nations Convention against Torture (CAT). The length of an indefinite imprisonment was determined during imprisonment based on the inmate's conduct. The inmate could have been returned to society or be kept in prison for life.
Prison overcrowding is a social phenomenon occurring when the demand for space in prisons in a jurisdiction exceeds the capacity for prisoners. The issues associated with prison overcrowding are not new, and have been brewing for many years. During the United States' War on Drugs, the states were left responsible for solving the prison overcrowding issue with a limited amount of money. Moreover, federal prison populations may increase if states adhere to federal policies, such as mandatory minimum sentences. On the other hand, the Justice Department provides billions of dollars a year for state and local law enforcement to ensure they follow the policies set forth by the federal government concerning U.S. prisons. Prison overcrowding has affected some states more than others, but overall, the risks of overcrowding are substantial and there are solutions to this problem.
Prisons in India are overcrowded and eight of out ten prisoners in Indian jails await trial. There are 1319 prisons in India as of 2021. Currently, there are about 1400 prisons. After the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of prisoners increased 13 per cent from 2020 to 2021, making over 80 per cent of the prisons overcrowded. After the Supreme Court order, a number of prisoners were release in 2020 to decongest the jails reducing the overall prison occupancy in 20 states and two Union Territories to a little over 93 per cent. However, the occupancy rate increased to 130 per cent again by 2021. About 63 unnatural deaths took place in Indian prisons. Among the major states, Tamil Nadu is the only state which has less than 100 per cent occupancy followed by Karnataka.

Penal labor in the United States is a multi-billion-dollar industry. Annually, incarcerated workers provide at least $9 billion in services to the prison system and produce more than $2 billion in goods. The industry underwent many transitions throughout the late 19th and early and mid 20th centuries. Legislation such as the Hawes-Cooper Act of 1929 placed limitations on the trade of prison-made goods. Federal establishment of the Federal Prison Industries (FPI) in 1934 revitalized the prison labor system following the Great Depression. Increases in prison labor participation began in 1979 with the formation of the Prison Industry Enhancement Certification Program (PIECP). The PIECP is a federal program first authorized under the Justice System Improvement Act of 1979. Approved by Congress in 1990 for indefinite continuation, the program legalizes the transportation of prison-made goods across state lines and allows prison inmates to earn market wages in private sector jobs that can go towards tax deductions, victim compensation, family support, and room and board.

Proposition 36, also titled A Change in the "Three Strikes Law" Initiative, was a California ballot measure that was passed in November 2012 to modify California's Three Strikes Law. The latter law punishes habitual offenders by establishing sentence escalation for crimes that were classified as "strikes", and requires a mandatory minimum sentence of 25 to life for a "third-strike offense."








