
Advertising is a marketing communication that employs an openly sponsored, non-personal message to promote or sell a product, service or idea. Sponsors of advertising are typically businesses wishing to promote their products or services. Advertising is differentiated from public relations in that an advertiser pays for and has control over the message. It differs from personal selling in that the message is non-personal, i.e., not directed to a particular individual. Advertising is communicated through various mass media, including traditional media such as newspapers, magazines, television, radio, outdoor advertising or direct mail; and new media such as search results, blogs, social media, websites or text messages. The actual presentation of the message in a medium is referred to as an advertisement, or "ad" or advert for short.
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a way of measuring economic variables in different countries so that irrelevant exchange rate variations do not distort comparisons. Purchasing power exchange rates are such that it would cost exactly the same number of, for example, US dollars to buy euros and then buy a basket of goods in the market as it would cost to purchase the same goods directly with dollars. The purchasing power exchange rate used in this conversion equals the ratio of the currencies' respective purchasing powers.

Sex in advertising is the use of sex appeal in advertising to help sell a particular product or service. According to research, sexually appealing imagery does not need to pertain to the product or service in question. A few examples of sexually appealing imagery include nudity, pin-up models, and muscular men. "Sex sells" became a controversial issue, with techniques for enlarging and titillating the audience challenging conventional moral standards.
In economics and marketing, product differentiation is the process of distinguishing a product or service from others, to make it more attractive to a particular target market. This involves differentiating it from competitors' products as well as a firm's own products. The concept was proposed by Edward Chamberlin in his 1933 The Theory of Monopolistic Competition.
An advertorial is an advertisement in the form of editorial content. The term "advertorial" is a blend of the words "advertisement" and "editorial." Merriam-Webster dates the origin of the word to 1946.

In economics, a luxury good is a good for which demand increases more than proportionally as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a greater proportion of overall spending.
False advertising is the use of false, misleading, or unproven information to advertise products to consumers. The advertising frequently does not disclose its source. One form of false advertising is to claim that a product has a health benefit or contains vitamins or minerals that it in fact does not. Many governments use regulations to control false advertising. A false advertisement can further be classified as deceptive if the advertiser deliberately misleads the consumer, as opposed to making an honest mistake.

An advertising campaign is a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme which make up an integrated marketing communication (IMC). An IMC is a platform in which a group of people can group their ideas, beliefs, and concepts into one large media base. Advertising campaigns utilize diverse media channels over a particular time frame and target identified audiences.

Bespoke tailoring is clothing made to an individual buyer's specifications by a tailor.
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) advertising usually refers to the marketing of pharmaceutical products but also applies to the direct marketing of medical devices, consumer diagnostics and sometimes financial services. Avenues for DTC advertising include TV, print, radio and other mass and social media. This form of advertising is directed toward patients, rather than healthcare professionals. The objective of direct-to-consumer advertising by a pharmaceutical company is to promote a particular medication to the patient directly.
Digital marketing is the marketing of products or services using digital technologies, mainly on the Internet, but also including mobile phones, display advertising, and any other digital medium.
In advertising, a hard sell is an advertisement or campaign that uses a more direct, forceful, and overt sales message. This approach is the diametric counterpart of a soft sell.
Comparison is a feature in the morphology or syntax of some languages, whereby adjectives and adverbs are inflected or modified to indicate the relative degree of the property defined by the adjective or adverb. The comparative expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality, quantity, or degree; the superlative is the form of an adverb or adjective that is the greatest degree of a given descriptor.
Comparative advertising or advertising war is an advertisement in which a particular product, or service, specifically mentions a competitor by name for the express purpose of showing why the competitor is inferior to the product naming it. Also referred to as "knocking copy", it is loosely defined as advertising where “the advertised brand is explicitly compared with one or more competing brands and the comparison is obvious to the audience.”
Media planning is generally outsourced to entails sourcing and selecting optimal media platforms for a client's brand or product to use. The job of media planning is to determine the best combination of media to achieve the objectives.
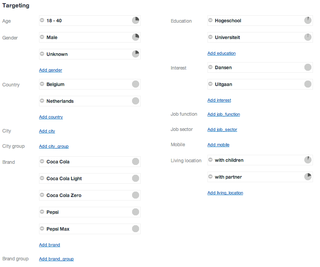
Targeted advertising is a form of online advertising that uses sophisticated methods to target the most receptive audiences with certain traits, based on the product or person the advertiser is promoting. These traits can either be demographic which are focused on race, economic status, sex, age, the level of education, income level and employment or they can be psychographic focused which are based on the consumer's values, personality, attitudes, opinions, lifestyles and interests. They can also be behavioral variables, such as browser history, purchase history, and other recent activity. Targeted advertising is focused on certain traits and the consumers who are likely to have a strong preference will receive the message instead of those who have no interest and whose preferences do not match a product's attribute. This eliminates wastage.
Advertising to children is the act of marketing or advertising products or services to children as defined by national legislation and advertising standards. It is often the subject of debate, relating to the alleged influence on little children's consumption. Laws concerning such advertisements have largely evolved in recent years such as the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) in the United States. In most countries, advertising to small children is framed by a mix of legislation and advertising self-regulation.

x265 is a library for encoding video into the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC/H.265) video compression format that was developed and standardized by the ISO/IEC MPEG and ITU-T VCEG. x265 is offered under either version 2 of the GNU General Public License (GPL) or a commercial license, similar to the x264 project.
In marketing and microeconomics, customer switching or consumer switching describes "customers/consumers abandoning a product or service in favor of a competitor". Assuming constant price, product or service quality, counteracting this behaviour in order to achieve maximal customer retention is the business of marketing, public relations and advertising. Brand switching—as opposed to brand loyalty is the outcome of customer switching behaviour.







