India's telecommunication network is the second largest in the world by number of telephone users with 1179.49 million subscribers as on 31 January 2021. It has one of the lowest call tariffs in the world enabled by mega telecom operators and hyper-competition among them. India has the world's second-largest Internet user-base with 747.41 million broadband internet subscribers in the country.
Communications in Indonesia has a complex history due to the need to reach an extended archipelago of over 17,500 islands. The once important non-electronic communication methods of the past have given way to a considerable telecommunications infrastructure in contemporary Indonesia.

The nation of Japan currently possesses one of the most advanced communication networks in the world. For example, by 2008 the Japanese government's Internal Affairs and Communications Ministry stated that about 75 million people used mobile phones to access the Internet, said total accounting for about 82% of individual Internet users.
The People's Republic of China possesses a diversified communications system that links all parts of the country by Internet, telephone, telegraph, radio, and television. The country is served by an extensive system of automatic telephone exchanges connected by modern networks of fiber-optic cable, coaxial cable, microwave radio relay, and a domestic satellite system; cellular telephone service is widely available, expanding rapidly, and includes roaming service to foreign countries. Fiber to the x infrastructure has been expanded rapidly in recent years.
Telecommunications in Tanzania include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet available in mainland Tanzania and the semiautonomous Zanzibar archipelago.
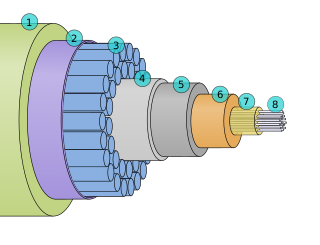
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the sea bed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables laid beginning in the 1850s carried telegraphy traffic, establishing the first instant telecommunications links between continents, such as the first transatlantic telegraph cable which became operational on 16 August 1858.
Discovery Channel is an American cable channel owned by Warner Bros. Discovery, a publicly traded company run by CEO David Zaslav. As of June 2012, Discovery Channel was the third most widely distributed subscription channel in the United States, behind now-sibling channel TBS and The Weather Channel; it is available in 409 million households worldwide, through its U.S. flagship channel and its various owned or licensed television channels internationally.
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it crosses the conventional boundary between the UHF and SHF bands at 3.0 GHz. The S band is used by airport surveillance radar for air traffic control, weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those satellites used by NASA to communicate with the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station. The 10 cm radar short-band ranges roughly from 1.55 to 5.2 GHz. The S band also contains the 2.4–2.483 GHz ISM band, widely used for low power unlicensed microwave devices such as cordless phones, wireless headphones (Bluetooth), wireless networking (WiFi), garage door openers, keyless vehicle locks, baby monitors as well as for medical diathermy machines and microwave ovens. India's regional satellite navigation network (IRNSS) broadcasts on 2.483778 to 2.500278 GHz.

Reliance Communications Limited (RCOM) was an Indian mobile network provider headquartered in Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra that offered voice and 2G and 3G and 4G data services. In February 2019, the company filed for bankruptcy as it was unable to sell assets to repay its debt. It has an estimated debt of ₹500 billion against assets worth ₹180 billion.
The television industry in India is very diverse and produces thousands of programs in many of the Indian languages. More than half of all Indian households own a television. As of 2016, the country had over 857 channels of which 184 were pay channels. National channels operate in Hindi and English, in addition to regional channels in several languages including Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Bengali, Marathi, Odia, Punjabi, Assamese, Gujarati, Urdu, Bhojpuri, Kashmiri, Konkani and Haryanvi, among others. The Hindi, Telugu and Tamil language television industries are by far the largest television industries in India.
Cogeco Inc. is a Canadian telecommunications and media company. Its corporate offices are located at 1 Place Ville-Marie in Montreal, Quebec. The company is structured into three strategic business units (SBU); Cogeco Connexion, Breezeline, and Cogeco Media. The company provides a range of telecommunication products and services including cable television, radio and television broadcasting, telephony, and Internet services in Ontario and Quebec in Canada, and in eleven states along the east coast of the United States.

Cable & Wireless plc was a British telecommunications company. In the mid-1980s, it became the first company in the UK to offer an alternative telephone service to British Telecom. The company later offered cable TV to its customers, but it sold its cable assets to NTL in 2000. It remained a significant player in the UK telecoms market and in certain overseas markets, especially in the former British colonies of the Caribbean, where it was formerly the monopoly incumbent. It was also the main supplier of communication in the British South Atlantic, including Saint Helena and the Falkland Islands. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

Disney Star Asianet is an Indian media conglomerate company based in Kerala headquartered in Kochi owned by The Walt Disney Company India, which is wholly owned by The Walt Disney Company. Disney Star Asianet operates Asianet, Asianet HD, Asianet Plus, Asianet Middle East, Asianet Movies, Asianet Movies HD, Star Vijay, Vijay Super, Vijay Takkar, Vijay International, Star Suvarna, Suvarna Plus.

Asianet News is an Indian Malayalam language free to air news channel. owned by Jupiter Entertainment Ventures. The channel is based in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. Asianet News is currently one of the market leaders in the Malayalam television news sector.
The Indian Telecommunications Service, widely known as ITS, and earlier known as 'Telegraph Engineering Service Class I' is one of the gazetted central engineering services officer under Group 'A' of the executive branch of the Government of India. The appointment to this service is done through Combined Engineering Services Exam held every year by Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) of India. The service was created to meet the technological needs of the government in areas related to telecommunications. The Department of Telecommunications (DOT) had been managed for years by the officers of this permanent cadre, called the Indian Telecommunications Service (ITS).The officers of ITS work under restrictions and rules of Central Engineering Services (Conduct) rules.

Asianet is an Indian Malayalam language general entertainment pay television channel owned by The Walt Disney Company India. a wholly owned by The Walt Disney Company. The channel is headquartered in Kochi. Asianet HD is the first general entertainment HD television channel in Malayalam.
Cable & Wireless Communications Ltd operating as C&W Communications is a telecommunications company which has operations in the Caribbean and Central America. It is owned by Liberty Latin America and is headquartered in London.

SUN GroupPrivate Limited is an Indian media conglomerate, based in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It was founded by Kalanithi Maran in 1992. Sun Group besides television media has 48 FM Radio Stations, two Daily Newspapers, five Magazines, a DTH satellite service & an IPL franchise.

Asianet Satellite Communications Private Limited, is an Indian multi system operator (MSO). It is the largest cable network services company in Kerala since its inception in 1993. It is a market leader in South India, it is ranked among the top 20 ISP's in India by TRAI. It is also one of the fastest growing ISPs in India. Asianet Satellite Communications have no connections to Asianet, Asianet Plus, Asianet Movies.

HFCL is an Indian telecom company incorporated in 1987. It has been in operation into various segments of manufacturing, Research & Development and turnkey solutions.









