Related Research Articles

Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard and brittle transition metal. Chromium is the main additive in stainless steel, to which it adds anti-corrosive properties. Chromium is also highly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, with almost 90% of infrared light being reflected. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, chrōma, meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored.

Tanning is the process of treating skins and hides of animals to produce leather. A tannery is the place where the skins are processed.
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) is a professional association of industrial hygienists and practitioners of related professions, with headquarters in Cincinnati, Ohio. One of its goals is to advance worker protection by providing timely, objective, scientific information to occupational and environmental health professionals.

The National Research Council is the primary national research and technology organization (RTO) of the Government of Canada, in science and technology research and development. The Minister of Innovation, Science, and Economic Development is responsible for the National Research Council.
Bioremediation is a process used to treat contaminated media, including water, soil and subsurface material, by altering environmental conditions to stimulate growth of microorganisms and degrade the target pollutants. In many cases, bioremediation is less expensive and more sustainable than other remediation alternatives. Biological treatment is a similar approach used to treat wastes including wastewater, industrial waste and solid waste.

Chrome plating, often referred to simply as chrome, is a technique of electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. The chromed layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, ease cleaning procedures, or increase surface hardness. Sometimes, a less expensive imitator of chrome may be used for aesthetic purposes.

The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Its current director is John Howard.

Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, CrO2−
4. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, Cr
2O2−
7. They are oxyanions of chromium in the 6+ oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible.

Occupational hygiene is the anticipation, recognition, evaluation, control, and confirmation of protection from hazards at work that may result in injury, illness, or affect the well being of workers. These hazards or stressors are typically divided into the categories biological, chemical, physical, ergonomic and psychosocial. The risk of a health effect from a given stressor is a function of the hazard multiplied by the exposure to the individual or group. For chemicals, the hazard can be understood by the dose response profile most often based on toxicological studies or models. Occupational hygienists work closely with toxicologists for understanding chemical hazards, physicists for physical hazards, and physicians and microbiologists for biological hazards Environmental and occupational hygienists are considered experts in exposure science and exposure risk management. Depending on an individual's type of job, a hygienist will apply their exposure science expertise for the protection of workers, consumers and/or communities.

Orica Limited is an Australian-based multinational corporation that is one of the world's largest providers of commercial explosives and blasting systems to the mining, quarrying, oil and gas and construction markets, a supplier of sodium cyanide for gold extraction, and a specialist provider of ground support services in mining and tunnelling.
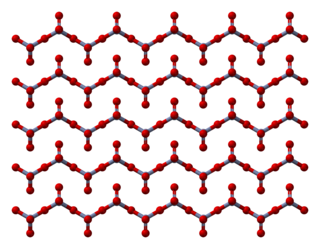
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name. This compound is a dark-purple solid under anhydrous conditions, bright orange when wet and which dissolves in water concomitant with hydrolysis. Millions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly for electroplating. Chromium trioxide is a powerful oxidiser and a carcinogen.

Hexavalent chromium is chromium in any chemical compound that contains the element in the +6 oxidation state. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via hexavalent chromium, specifically the salt sodium dichromate. Approximately 136,000 tonnes of hexavalent chromium were produced in 1985. Hexavalent chromium is likely key to all materials made from chromium.
Paul James Lioy was a United States environmental health scientist born in Passaic, New Jersey, working in the field of exposure science. He was one of the world's leading experts in personal exposure to toxins. He published in the areas of air pollution, airborne and deposited particles, Homeland Security, and Hazardous Wastes. Lioy was a Professor and Division Director at the Department of Environmental and Occupational Health, Rutgers University - School of Public Health. Until 30 June 2015 he was a Professor and Vice Chair of the Department of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, Rutgers University - Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. He was Deputy Director of Government Relations and Director of Exposure Science, at the Rutgers Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Institute in Piscataway, New Jersey.
Chromium toxicity refers to any poisonous toxic effect in an organism or cell that results from exposure to specific forms of chromium—especially hexavalent chromium. Hexavalent chromium and its compounds are toxic when inhaled or ingested. Trivalent chromium is a trace mineral that is essential to human nutrition. There is a hypothetical risk of genotoxicity in humans if large amounts of trivalent chromium were somehow able to enter living cells, but normal metabolism and cell function prevent this.

From 1952 to 1966, Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) dumped about 370 million gallons of chromium-tainted wastewater into unlined wastewater spreading ponds around the town of Hinkley, California, located in the Mojave Desert.

Michael John McGuire is an American environmental engineer and writer whose career has focused on drinking water quality improvement. He has been recognized for his expertise in the control of trace organic and inorganic contaminants and microbial pathogens in water. He is also known for his work in the identification, control and treatment of taste and odor problems in drinking water. He has published numerous articles in professional journals and he has been the co-editor of five books and compilations of articles. He published a book that documented the first continuous disinfection of a drinking water supply in the U.S. He has been active in the American Water Works Association, and he has served as a volunteer and officer in that organization. In 2009, he was elected to the National Academy of Engineering.
Anna Medora Baetjer was an American physiologist and toxicologist, known for her research into the health effects of industrial work on women and for her discovery of the carcinogenic properties of chromium.
Sibte Hasan Zaidi was an Indian pathologist and toxicologist. After his training in pathology at the Hammersmith Hospital in London, United Kingdom, he returned to India to continue experimental toxicology research initially at the Central Drug Research Institute, and then as Founding Director at Industrial Toxicology Research Center (ITRC) in Lucknow (1965-1978). During his later years, he served on national and international committees to increase awareness and set policy to prevent the harmful effects of industrial toxins in people.

Omowunmi "Wunmi" A. Sadik is a Nigerian professor, chemist, and inventor working at Binghamton University. She has developed microelectrode biosensors for detection of drugs and explosives and is working on the development of technologies for recycling metal ions from waste, for use in environmental and industrial applications. In 2012, Sadik co-founded the non-profit Sustainable Nanotechnology Organization.
Dennis J. Paustenbach PhD, CIH, DABT, is an American scientist, businessman, researcher, and author. Dennis is currently President of Paustenbach and Associates, which is a consulting firm who uses risk assessment techniques to characterize occupational and environmental health hazards. He is the founder and former president of ChemRisk, a consulting firm specializing in the use of toxicology and risk assessment to characterize the hazards of chemicals in soil, air, water, food, sediments and consumer products. He was, for about 4 years, a Group Vice-President of Exponent.
References
- ↑ Health Information Resource Database, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, accessed June 29, 2011
- ↑ Council, N.R.; Canada, N.R.C. (1961). Scientific and Technical Societies of the United States and Canada. National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council. p. 219. Retrieved 2014-10-13.
- ↑ Michaels D, Monforton C, Lurie P. (2006). Selected science: an industry campaign to undermine an OSHA hexavalent chromium standard. Environmental Health.