| Headquarters | Cleveland , United States |
|---|---|
| Products | Viscose |
Industrial Rayon Corporation, formerly the Industrial Fibre Company, was a company that made viscose in the United States. [1] [2] [3]

| Headquarters | Cleveland , United States |
|---|---|
| Products | Viscose |
Industrial Rayon Corporation, formerly the Industrial Fibre Company, was a company that made viscose in the United States. [1] [2] [3]


Juniata Terrace, a former industrial village, is a borough in Mifflin County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 567 at the 2020 census. Juniata Terrace was added to the National Register of Historic Places as a historic district on May 17, 2024.

Velvet is a type of woven fabric with a dense, even pile that gives it a distinctive soft feel. By extension, the word velvety means "smooth like velvet". Historically, velvet was typically made from silk. Today, velvet can be made from silk, linen, cotton, wool, synthetic fibers, silk-cotton blends, or synthetic-natural fiber blends.

Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated with nitrocellulose lacquer to prevent this.

Rayon, also called viscose and commercialised in some countries as sabra silk or cactus silk, is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. Many types and grades of viscose fibers and films exist. Some imitate the feel and texture of natural fibers such as silk, wool, cotton, and linen. The types that resemble silk are often called artificial silk. It can be woven or knit to make textiles for clothing and other purposes.
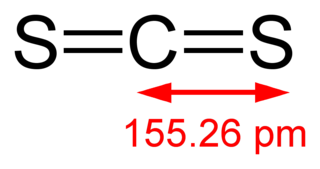
Carbon disulfide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CS2 and structure S=C=S. It is also considered as the anhydride of thiocarbonic acid. It is a colorless, flammable, neurotoxic liquid that is used as a building block in organic synthesis. Pure carbon disulfide has a pleasant, ether- or chloroform-like odor, but commercial samples are usually yellowish and are typically contaminated with foul-smelling impurities.
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants or fur from animals. They are the result of extensive research by scientists to replicate naturally occurring animal and plant fibers. In general, synthetic fibers are created by extruding fiber-forming materials through spinnerets, forming a fiber. These are called synthetic or artificial fibers. The word polymer comes from a Greek prefix "poly" which means "many" and suffix "mer" which means "single units"..

Lyocell is a semi-synthetic fiber used to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. It is a form of regenerated cellulose made by dissolving pulp and dry jet-wet spinning. Unlike rayon made by the more common viscose processes, Lyocell production does not use carbon disulfide, which is toxic to workers and the environment. Lyocell was originally trademarked as Tencel in 1982.
Courtaulds was a United Kingdom-based manufacturer of fabric, clothing, artificial fibres, and chemicals. It was established in 1794 and became the world's leading man-made fibre production company before being broken up in 1990 into Courtaulds plc and Courtaulds Textiles Ltd.

Grasim Industries Limited is an Indian manufacturing company based in Mumbai. Since its inception in 1947 as a textile manufacturer, Grasim has diversified into textile raw materials like viscose staple fiber (VSF) and viscose filament yarn, chemicals and insulators, along with cement and financial services through its subsidiaries UltraTech Cement and Aditya Birla Capital respectively. The company is a part of the Aditya Birla Group.

Artificial silk or art silk is any synthetic fiber which resembles silk, but typically costs less to produce. Frequently, the term artificial silk is just a synonym for rayon. When made out of bamboo viscose it is also sometimes called bamboo silk.

Bamboo textile is any cloth, yarn or clothing made from bamboo fibres. While bamboo was historically used only for structural elements, such as bustles and the ribs of corsets, in recent years various technologies have been developed that allow bamboo fibre to be used for a wide range of textile and fashion applications.
Frank Hastings Griffin was an American chemist and inventor who developed the double-godet, a stretch-spinning process that created rayon from artificial silk. He served as chief chemist, general manager, vice president and as a member of the board of directors for American Viscose Corporation.

American Viscose Corporation was an American division of the British firm Courtaulds, which manufactured rayon and other synthetic fibres. The company operated from 1910 to 1976 when it was renamed Avtex. Avtex closed in 1990.

Vereinigte Glanzstoff-Fabriken was a German manufacturer of artificial fiber founded in 1899 that became one of the leading European producers of rayon.
Matthias Eduard Schweizer was a Swiss chemist who in 1857 invented Schweizer's reagent, in which cellulose can be dissolved to produce artificial silk or rayon. He was one of the pioneers of the synthetic textile industry.

Max Fremery was a German chemist and industrialist. He was one of the founders of the Vereinigte Glanzstoff-Fabriken (VGF) in 1899. VGF became a major manufacturer of artificial fibers.

J. P. Bemberg was a German rayon manufacturer that produced an unusually fine artificial fiber which became known as Bemberg®. J. P. Bemberg came under the control of Vereinigte Glanzstoff-Fabriken and eventually disappeared after a series of mergers and divestitures, but Bemberg™ rayon was still being produced in 2015 by Asahi in Japan,
Thomas F. Mancuso was an American epidemiologist and professor of occupational health at the University of Pittsburgh's School of Public Health between 1962 and 1982, known for conducting long-term studies of the cancer-causing effects of low-level radiation and several chemicals used in industry, including asbestos. He is credited for being the first to understand that beryllium and chromium could cause cancer.

The American Viscose Plant Historic District is an industrial park and historic district located in Roanoke, Virginia. The site is the location of the former American Viscose Corporation rayon processing plant that once employed over 5,000 and for a time was reportedly the largest rayon producing mill in the world. The plant's construction began in 1916 with the building of the first of what became three large processing plants of two spinning units each; the second began construction in 1921 and the third in 1925. With the plant's viability decreased by newer facilities elsewhere and rayon's usage supplanted by nylon and other synthetic fabrics, the factory closed in 1958. The property was purchased by an assortment of Roanoke investors in 1961 and has been operated as an industrial park since.

Cellatex SA is a former French rayon spinning company, founded in 1981 on the basis of a business established in 1902 in Givet, Ardennes (France), and liquidated in 2000.