Related Research Articles
Laryngeal cancers are mostly squamous-cell carcinomas, reflecting their origin from the epithelium of the larynx.

Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium. It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most often vaginal bleeding not associated with a menstrual period. Other symptoms include pain with urination, pain during sexual intercourse, or pelvic pain. Endometrial cancer occurs most commonly after menopause.

Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed.

The neck dissection is a surgical procedure for control of neck lymph node metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck. The aim of the procedure is to remove lymph nodes from one side of the neck into which cancer cells may have migrated. Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma into the lymph nodes of the neck reduce survival and is the most important factor in the spread of the disease. The metastases may originate from SCC of the upper aerodigestive tract, including the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx, as well as the thyroid, parotid and posterior scalp.
Lumpectomy is a surgical removal of a discrete portion or "lump" of breast tissue, usually in the treatment of a malignant tumor or breast cancer. It is considered a viable breast conservation therapy, as the amount of tissue removed is limited compared to a full-breast mastectomy, and thus may have physical and emotional advantages over more disfiguring treatment. Sometimes a lumpectomy may be used to either confirm or rule out that cancer has actually been detected. A lumpectomy is usually recommended to patients whose cancer has been detected early and who do not have enlarged tumors. Although a lumpectomy is used to allow for most of the breast to remain intact, the procedure may result in adverse affects that can include sensitivity and result in scar tissue, pain, and possible disfiguration of the breast if the lump taken out is significant. According to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, lumpectomy may be performed for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), invasive ductal carcinoma, or other conditions.

Cystectomy is a medical term for surgical removal of all or part of the urinary bladder. It may also be rarely used to refer to the removal of a cyst. The most common condition warranting removal of the urinary bladder is bladder cancer.

Pelvic exenteration is a radical surgical treatment that removes all organs from a person's pelvic cavity. It is used to treat certain advanced or recurrent cancers. The urinary bladder, urethra, rectum, and anus are removed. In women, the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries and, in some cases, the vulva are removed. In men, the prostate is removed. The procedure leaves the person with a permanent colostomy and urinary diversion.

Radical mastectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of breast, underlying chest muscle, and lymph nodes of the axilla as a treatment for breast cancer. Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women today, and is primarily treated by surgery, particularly during the early twentieth century when the mastectomy was developed with success. However, with the advancement of technology and surgical skills, the extent of mastectomies has been reduced. Less invasive mastectomies are employed today in comparison to those in the past. Nowadays, a combination of radiotherapy and breast conserving mastectomy are employed to optimize treatment.

Radical retropubic prostatectomy is a surgical procedure in which the prostate gland is removed through an incision in the abdomen. It is most often used to treat individuals who have early prostate cancer. Radical retropubic prostatectomy can be performed under general, spinal, or epidural anesthesia and requires blood transfusion less than one-fifth of the time. Radical retropubic prostatectomy is associated with complications such as urinary incontinence and impotence, but these outcomes are related to a combination of individual patient anatomy, surgical technique, and the experience and skill of the surgeon.

Vulvar cancer is a cancer of the vulva, the outer portion of the female genitals. It most commonly affects the labia majora. Less often, the labia minora, clitoris, or vaginal glands are affected. Symptoms include a lump, itchiness, changes in the skin, or bleeding from the vulva.
Gynecologic oncology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on cancers of the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer. As specialists, they have extensive training in the diagnosis and treatment of these cancers.
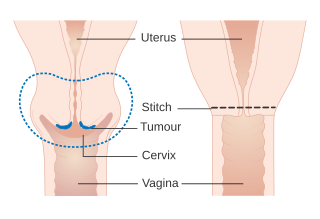
In gynecologic oncology, trachelectomy, also called cervicectomy, is a surgical removal of the uterine cervix. As the uterine body is preserved, this type of surgery is a fertility preserving surgical alternative to a radical hysterectomy and applicable in selected younger women with early cervical cancer.

Breast-conserving surgery (BCS) refers to an operation that aims to remove breast cancer while avoiding a mastectomy. Other terms for this operation include: lumpectomy, wide local excision, segmental resection, tylectomy, and quadrantectomy. BCS has been increasingly accepted as an alternative to mastectomy in specific patients, as it provides tumor removal while maintaining an acceptable cosmetic outcome. This page reviews the history of this operation, important considerations in decision making and patient selection, and the emerging field of oncoplastic breast conservation surgery.

Uterine serous carcinoma is an uncommon form of endometrial cancer that typically arises in postmenopausal women. It is typically diagnosed on endometrial biopsy, prompted by post-menopausal bleeding.
Uterine clear-cell carcinoma (CC) is a rare form of endometrial cancer with distinct morphological features on pathology; it is aggressive and has high recurrence rate. Like uterine papillary serous carcinoma CC does not develop from endometrial hyperplasia and is not hormone sensitive, rather it arises from an atrophic endometrium. Such lesions belong to the type II endometrial cancers.
A lymphocele is a collection of lymphatic fluid within the body not bordered by epithelial lining. It is usually a surgical complication seen after extensive pelvic surgery and is most commonly found in the retroperitoneal space. Spontaneous development is rare.

The Wertheim–Meigs operation is a surgical procedure for the treatment of cervical cancer performed by way of an abdominal incision.
Lymphatogenous metastasis is the spread of cancer from the vulva, clitoris and bartholin glands. As these other more superficial cancers grow deeper into the surrounding tissue, the risk of lymphatogenous metastasis increases. Vulvar cancers spread primarily to the inguinofemoral lymph nodes. From these lymph nodes, cancer can spread to the pelvic lymph nodes.

Bartholin gland carcinoma is an uncommon type of malignancy in the Bartholin gland that accounts for 1% of all vulvar malignant neoplasms. It is most common in women in their mid-60s. The tumor can become large before a woman is aware of symptoms. One of the first symptoms can be dyspareunia. In other instances a woman may find a mass or ulcer in the vulva area. Many clinicians assume that an enlarged Bartholin gland is malignant in postmenopausal woman until proven otherwise. The growth of the tumor can spread to nearby areas such as the ischiorectal fossa and inguinal lymph nodes. Approximately 50% of bartholin gland carcinomas originate from squamous cell carcinomas. Another uncommon characteristic of Bartholin gland malignancies is that the growth of a lesion originates from the three types of epithelial tissue present in the gland: mucinous, transitional, and squamous.
Carcinoma of the tonsil is a type of squamous cell carcinoma. The tonsil is the most common site of squamous cell carcinoma in the oropharynx. It comprises 23.1% of all malignancies of the oropharynx. The tumors frequently present at advanced stages, and around 70% of patients present with metastasis to the cervical lymph nodes. . The most reported complaints include sore throat, otalgia or dysphagia. Some patients may complain of feeling the presence of a lump in the throat. Approximately 20% patients present with a node in the neck as the only symptom.
References
- ↑ Wallwiener, D. & Becker, S. & Beckmann, M. & Brucker, S. & Friese, K. & Isaacson, K. & Jonat, W. & Wattiez, A. (2014). 6.3 Surgical Techniques. Atlas of Gynecologic Surgery. Online textbook, n.p. Retrieved February 3, 2018
- ↑ "What does Inguinofemoral Lymphadenectomy mean? Definition, meaning and sense (The Titi Tudorancea Encyclopedia)". www.tititudorancea.com. Retrieved 2018-02-03.
- ↑ "NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms". National Cancer Institute. Retrieved 2018-02-03.