Inkberry is a common name for several unrelated plants:

Plants are mainly multicellular, predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, plants were treated as one of two kingdoms including all living things that were not animals, and all algae and fungi were treated as plants. However, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes. By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae, a group that includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, mosses and the green algae, but excludes the red and brown algae.
- Any plant in the genus Phytolacca (pokeweeds)
- Especially Phytolacca americana (American Pokeweed)
- Dianella nigra (Turutu in Māori, New Zealand blueberry)
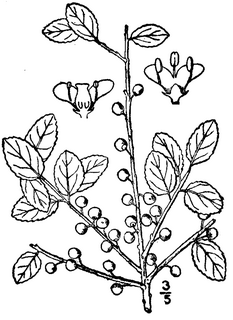
- Ilex glabra (Evergreen Winterberry)
- Ilex verticillata (American Winterberry)
- Scaevola plumieri (Beachberry), species of Scaevola (plant)
A genus is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, as well as viruses, in biology. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

Phytolacca is a genus of perennial plants native to North America, South America and East Asia. Some members of the genus are known as pokeweeds or similar names such as pokebush, pokeberry, pokeroot or poke sallet. Other names for species of Phytolacca include inkberry and ombú. The generic name is derived from the Greek word φυτόν (phyton), meaning "plant," and the Latin word lacca, a red dye. Phytolaccatoxin and phytolaccigenin are present in many species which are poisonous to mammals if not cooked properly. However, the berries are eaten by birds, which are not affected by the toxin because the small seeds with very hard outer shells remain intact in the digestive system and are eliminated whole.

Phytolacca americana, also known as American pokeweed, pokeweed, poke sallet, or poke salad, is a poisonous, herbaceous perennial plant in the pokeweed family Phytolaccaceae growing up to 8 ft (2.4m) in height. It has simple leaves on green to red or purplish stems and a large white taproot. The flowers are green to white, followed by purple to almost black berries which are a food source for songbirds such as gray catbird, northern mockingbird, northern cardinal, and brown thrasher, as well as other birds and some small animals.
| This page is an index of articles on plant species (or higher taxonomic groups) with the same common name (vernacular name). If an internal link led you here, you may wish to edit the linking article so that it links directly to the intended article. |