Related Research Articles

Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science principles and methods to support legal decision-making in matters of criminal and civil law.

Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially ranged weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets or the like; the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance.

The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (BATFE), commonly referred to as the ATF, is a domestic law enforcement agency within the United States Department of Justice. Its responsibilities include the investigation and prevention of federal offenses involving the unlawful use, manufacture, and possession of firearms and explosives; acts of arson and bombings; and illegal trafficking and tax evasion of alcohol and tobacco products. The ATF also regulates via licensing the sale, possession, and transportation of firearms, ammunition, and explosives in interstate commerce. Many of the ATF's activities are carried out in conjunction with task forces made up of state and local law enforcement officers, such as Project Safe Neighborhoods. The ATF operates a unique fire research laboratory in Beltsville, Maryland, where full-scale mock-ups of criminal arson can be reconstructed. The ATF had 5,285 employees and an annual budget of almost $1.5 billion in 2021. The ATF has received criticism over its handling of the Ruby Ridge siege, the Waco siege and other incidents.

Ballistic gelatin is a testing medium designed to simulate the effects of bullet wounds in animal muscle tissue. It was developed and improved by Martin Fackler and others in the field of wound ballistics. It is calibrated to match pig muscle, which is ballistically similar to human muscle tissue.

The chamber of a firearm is the cavity at the back end of a breechloading weapon's barrel or cylinder, where the ammunition is inserted before being fired. The rear opening of the chamber is the breech, and is sealed by the breechblock or the bolt.

A gunshot is a single discharge of a gun, typically a man-portable firearm, producing a visible flash, a powerful and loud shockwave and often chemical gunshot residue. The term can also refer to a ballistic wound caused by such a discharge.

Gunshot residue (GSR), also known as cartridge discharge residue (CDR), gunfire residue (GFR), or firearm discharge residue (FDR), consists of all of the particles that are expelled from the muzzle of a gun following the discharge of a bullet. It is principally composed of burnt and unburnt particles from the explosive primer, the propellant (gunpowder), stabilisers and other additives. The act of firing a bullet incites a highly pressurised, explosive reaction that is contained within the barrel of the firearm, which expels the bullet. This can cause the bullet, the barrel, or the cartridge to become damaged, meaning gunshot residue may also included metallic particles from the cartridge casing, the bullet jacket, as well as any other dirt or residue contained within the barrel that could have become dislodged.

Microstamping is a proprietary ballistics identification technology. Microscopic markings are engraved onto the tip of the firing pin and onto the breech face of a firearm with a laser. When the gun is fired, these etchings are transferred to the primer by the firing pin and to the cartridge case head by the breech face, using the pressure created when a round is fired. After being fired, if the cases are recovered by police, the microscopic markings imprinted on the cartridges can then be examined by forensic ballistics experts to help trace the firearm to the last registered owner. A California law requiring the use of microstamping technology in all new semiautomatic firearms sold in the state has attracted controversy.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to forensic science:
Calvin Hooker Goddard was a forensic scientist, army officer, academic, researcher and a pioneer in forensic ballistics. He examined the bullet casings in the 1929 St. Valentine's Day Massacre and showed that the guns used were not police issued weapons, leading the investigators to conclude it was a mob hit.

A comparison microscope is a device used to analyze side-by-side specimens. It consists of two microscopes connected by an optical bridge, which results in a split view window enabling two separate objects to be viewed simultaneously. This avoids the observer having to rely on memory when comparing two objects under a conventional microscope.
Automated Firearms Identification refers to the use of computers to automate the process of matching a piece of recovered ballistic evidence, against a database.
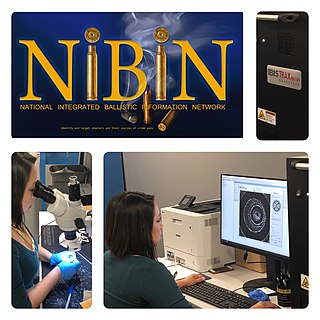
The National Integrated Ballistic Information Network or NIBIN is a specialized computer network in the United States. It contains digital images of recovered pieces of ballistic evidence.

Black Talon is a brand of hollow-point pistol and rifle ammunition introduced in 1991 by Winchester, primarily intended for law enforcement and personal defense use. Black Talon rounds were known for the unique construction of the bullet and its sharp petal shape after expansion following impact with tissue or other wet media. Black Talon ammunition was produced in the following calibers: 9mm Luger, 10mm Auto, .40 S&W, .45 ACP, .357 Magnum, .44 Magnum, .300 Winchester Magnum, .308 Winchester, .338 Winchester Magnum, and .30-06 Springfield.

The National Ballistics Intelligence Service, or NABIS, is a British intelligence service dedicated to managing and providing detailed information regarding firearm-related criminality. The service aims to use its database to store ballistics information about police cases involving firearms, and consequently maintain it for future use and reference. The service operates four facilities to test and analyse firearms evidence to help link it with other cases. These are based in Birmingham, London,Manchester and at Gartcosh in the Scottish Crime Campus in the town.
Gun laws in Maryland regulate the sale, possession, and use of firearms and ammunition in the U.S. state of Maryland.

Precision guided firearms (PGFs) are long-range rifle systems designed to improve the accuracy of shooting at targets at extended ranges through target tracking, heads-up display, and advanced fire control. Inspired by missile lock-on and fighter jet technology, the application of PGF technology to small arms mitigates multiple sources of marksman error including mis-aim, trigger jerk and shot setup miscalculation. PGFs can significantly increase first shot success probability (FSSP) out to extreme ranges of 1,100 meters or more.

Forensic firearm examination is the forensic process of examining the characteristics of firearms or bullets left behind at a crime scene. Specialists in this field try to link bullets to weapons and weapons to individuals. They can raise and record obliterated serial numbers in an attempt to find the registered owner of a weapon and look for fingerprints on a weapon and cartridges.

A privately made firearm, also called a ghost gun or homemade firearm, is a firearm made by a private individual, in contrast to one produced by a corporate or government entity. The term "ghost gun" is used mostly in the United States by gun control advocates, but it is being adopted by gun rights advocates and the firearm industry.

A gun serial number is a unique identifier assigned to a singular firearm.
References
- 1 2 "Nationwide Firearms Database Shot Down by Government-Sponsored Study". Fox News. 6 December 2011.
- ↑ "Officials wary of federal ballistics data budget cuts - News - Virgin Islands Daily News". Archived from the original on 2011-04-21. Retrieved 2011-05-11.
- ↑ "State Police Report Recommends Suspending Ballistics ID System - Baltimore News Story - WBAL Baltimore". Archived from the original on 2012-03-15. Retrieved 2011-05-11.
- 1 2 "OIG Audit Report 05-30".
- ↑ Integrated Ballistics Identification System
- ↑ "N.Y. gun database has yet to lead to prosecutions". NBC News . Archived from the original on 2017-04-10.
- ↑ "Bullet-tracing technology hits bull's-eye". Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. 8 August 1999. p. 10A.
- ↑ Ian Robertson (20 May 2007). "Real-life CSI". Sun Media. Archived from the original on 17 October 2007. Alt URL