
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States and fair dealings doctrine in the United Kingdom.

Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets. The modern concept of intellectual property developed in England in the 17th and 18th centuries. The term "intellectual property" began to be used in the 19th century, though it was not until the late 20th century that intellectual property became commonplace in most of the world's legal systems.

A counterfeit is a fake or unauthorized replica of a genuine product, such as money, documents, designer items, or other valuable goods. Counterfeiting generally involves creating an imitation of a genuine item that closely resembles the original to deceive others into believing it is authentic.

Industrial property is one of two subsets of intellectual property, it takes a range of forms, including patents for inventions, industrial designs, trademarks, service marks, layout-designs of integrated circuits, commercial names and designations, geographical indications and protection against unfair competition. In some cases, aspects of intellectual creation, although present, are less clearly defined. The object of industrial property consists of signs conveying information, in particular to consumers, regarding products and services offered on the market. Protection is directed against unauthorized use of such signs that could mislead consumers, and against misleading practices in general.
Intellectual property rights (IPRs) have been acknowledged and protected in China since 1980. China has acceded to the major international conventions on protection of rights to intellectual property. Domestically, protection of intellectual property law has also been established by government legislation, administrative regulations, and decrees in the areas of trademark, copyright, and patent.
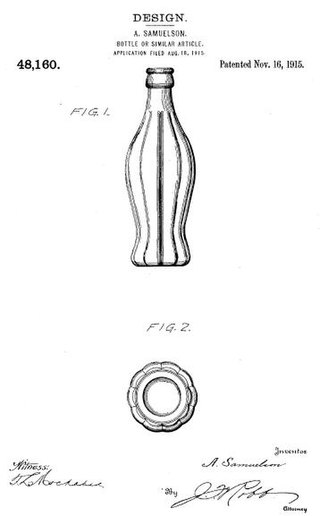
In the United States, a design patent is a form of legal protection granted to the ornamental design of an article of manufacture. Design patents are a type of industrial design right. Ornamental designs of jewelry, furniture, beverage containers and computer icons are examples of objects that are covered by design patents.
The European Union (EU) proposal for a directive on criminal measures aimed at ensuring the enforcement of intellectual property rights (2005/0127/COD) was a proposal from the European Commission for a directive aimed "to supplement Directive 2004/48/EC of 29 April 2004 on the enforcement of intellectual property rights ". The directive was proposed on July 12, 2005 by the Commission of the European Communities.

The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to intellectual property:

An intellectual property (IP) infringement is the infringement or violation of an intellectual property right. There are several types of intellectual property rights, such as copyrights, patents, trademarks, industrial designs, plant breeders rights and trade secrets. Therefore, an intellectual property infringement may for instance be one of the following:
The Prioritizing Resources and Organization for Intellectual Property Act of 2008 is a United States law that increases both civil and criminal penalties for trademark, patent and copyright infringement. The law also establishes a new executive branch office, the Office of the United States Intellectual Property Enforcement Representative (USIPER).

The Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA) is a multilateral treaty for the purpose of establishing international standards for intellectual property rights enforcement that did not enter into force. The agreement aims to establish an international legal framework for targeting counterfeit goods, generic medicines and copyright infringement on the Internet, and would create a new governing body outside existing forums, such as the World Trade Organization, the World Intellectual Property Organization, and the United Nations.

A trademark is a form of intellectual property that consists of a word, phrase, symbol, design, or a combination that identifies a product or service from a particular source and distinguishes it from others. Trademarks can also extend to non-traditional marks like drawings, symbols, 3D shapes like product designs or packaging, sounds, scents, or specific colors used to create a unique identity. For example, Pepsi® is a registered trademark associated with soft drinks, and the distinctive shape of the Coca-Cola® bottle is a registered trademark protecting Coca-Cola's packaging design.

The Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) is an international legal agreement between all the member nations of the World Trade Organization (WTO). It establishes minimum standards for the regulation by national governments of different forms of intellectual property (IP) as applied to nationals of other WTO member nations. TRIPS was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) between 1989 and 1990 and is administered by the WTO.

Copyright infringement is the use of works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, such as the right to reproduce, distribute, display or perform the protected work, or to produce derivative works. The copyright holder is usually the work's creator, or a publisher or other business to whom copyright has been assigned. Copyright holders routinely invoke legal and technological measures to prevent and penalize copyright infringement.
Panama has passed several laws protecting intellectual property in the country.

Iran is a member of the WIPO since 2001 and has acceded to several WIPO intellectual property treaties. Iran joined the Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property in 1959. In December 2003 Iran became a party to the Madrid Agreement and the Madrid Protocol for the International Registration of Marks. In 2005 Iran joined the Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration, which ensures the protection of geographical names associated with products. As at February 2008 Iran had yet to accede to The Hague Agreement for the Protection of Industrial Designs.

The National Intellectual Property Rights Coordination Center (NIPRCC) is a U.S. government center overseen by U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement, a component of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. The NIPRCC coordinates the U.S. government's enforcement of intellectual property laws.
Remedies for copyright infringement in the United States can be either civil or criminal in nature. Criminal remedies for copyright infringement prevent the unauthorized use of copyrighted works by defining certain violations of copyright to be criminal wrongs which are liable to be prosecuted and punished by the state. Unlike civil remedies, which are obtained through private civil actions initiated by the owner of the copyright, criminal remedies are secured by the state which prosecutes the infringing individual or organisation.

The Intellectual Property Agency of Armenia (AIPA) is the patent office of Armenia. The agency works under the supervision of the Ministry of Economy of Armenia and is tasked with granting patent and IP address protections, trademarks, and copyrights for objects of industrial property, inventions and usage patterns, industrial design, and commercial and service marks, among others.
Intellectual property of Ethiopia is managed by the Ethiopian Intellectual Property Office (EIFO), who oversees Intellectual Property Right (IPR) issues. Ethiopia has not signed IPR treaty such as the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) copyright treaty, the Berne Convention for Literary and Artistic Works, the Madrid System for the International Registration of Marks, and the Patent Cooperation Treaty.






