
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to protect against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.

A pawnbroker is an individual or business that offers secured loans to people, with items of personal property used as collateral. The items having been pawned to the broker are themselves called pledges or pawns, or simply the collateral. While many items can be pawned, pawnshops typically accept jewelry, musical instruments, home audio equipment, computers, video game systems, coins, gold, silver, televisions, cameras, power tools, firearms, and other relatively valuable items as collateral.

Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Commercial debt is generally subject to contractual terms regarding the amount and timing of repayments of principal and interest. Loans, bonds, notes, and mortgages are all types of debt. In financial accounting, debt is a type of financial transaction, as distinct from equity.
Credit risk is the possibility of losing a lender holds due to a risk of default on a debt that may arise from a borrower failing to make required payments. In the first resort, the risk is that of the lender and includes lost principal and interest, disruption to cash flows, and increased collection costs. The loss may be complete or partial. In an efficient market, higher levels of credit risk will be associated with higher borrowing costs. Because of this, measures of borrowing costs such as yield spreads can be used to infer credit risk levels based on assessments by market participants.
A credit score is a number that provides a comparative estimate of an individual's creditworthiness based on an analysis of their credit report. It is an inexpensive and main alternative to other forms of consumer loan underwriting.

Experian is a multinational data analytics and consumer credit reporting company headquartered in Dublin, Ireland. Experian collects and aggregates information on over 1 billion people and businesses including 235 million individual U.S. consumers and more than 25 million U.S. businesses. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. Experian is a partner in USPS address validation. It is one of the "Big Three" credit-reporting agencies, alongside TransUnion and Equifax.
Underwriting (UW) services are provided by some large financial institutions, such as banks, insurance companies and investment houses, whereby they guarantee payment in case of damage or financial loss and accept the financial risk for liability arising from such guarantee. An underwriting arrangement may be created in a number of situations including insurance, issues of security in a public offering, and bank lending, among others. The person or institution that agrees to sell a minimum number of securities of the company for commission is called the underwriter.
A credit history is a record of a borrower's responsible repayment of debts. A credit report is a record of the borrower's credit history from a number of sources, including banks, credit card companies, collection agencies, and governments. A borrower's credit score is the result of a mathematical algorithm applied to a credit report and other sources of information to predict future delinquency.
A credit bureau is a data collection agency that gathers account information from various creditors and provides that information to a consumer reporting agency in the United States, a credit reference agency in the United Kingdom, a credit reporting body in Australia, a credit information company (CIC) in India, a Special Accessing Entity in the Philippines, and also to private lenders. It is not the same as a credit rating agency.
A credit score is a numerical expression based on a level analysis of a person's credit files, to represent the creditworthiness of an individual. A credit score is primarily based on a credit report, information typically sourced from credit bureaus.
Debt settlement is a settlement negotiated with a debtor's unsecured creditor. Commonly, creditors agree to forgive a large part of the debt: perhaps around half, though results can vary widely. When settlements are finalized, the terms are put in writing. It is common that the debtor makes one lump-sum payment in exchange for the creditor agreeing that the debt is now cancelled and the matter closed. Some settlements are paid out over a number of months. In either case, as long as the debtor does what is agreed in the negotiation, no outstanding debt will appear on the former debtor's credit report.
The following article is based on UK market; other countries may differ.
Probability of default (PD) is a financial term describing the likelihood of a default over a particular time horizon. It provides an estimate of the likelihood that a borrower will be unable to meet its debt obligations.
A credit score is a numerical expression representing the creditworthiness of an individual. A credit score is primarily based on a credit report, information typically sourced from credit bureaus.
An identity score is a system for detecting identity theft. Identity scores are increasingly being adopted as a means to prevent fraud in business and as a tool to verify and correct public records.
Credit analysis is the method by which one calculates the creditworthiness of a business or organization. In other words, It is the evaluation of the ability of a company to honor its financial obligations. The audited financial statements of a large company might be analyzed when it issues or has issued bonds. Or, a bank may analyze the financial statements of a small business before making or renewing a commercial loan. The term refers to either case, whether the business is large or small. A credit analyst is the finance professional undertaking this role.
FreeCreditScore.com, FreeCreditReport.com and Credit.com are websites owned by Experian Consumer Direct, a subsidiary of the credit bureau Experian. The sites offer users their personal credit reports from Experian on the condition that they sign up for Experian's Triple Advantage credit monitoring program for a fee. The credit report also comes with the user's PLUS credit score. The membership may be canceled with no charge within 7 days of signup by contacting the call center.
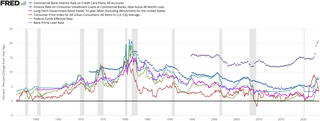
Car finance refers to the various financial products which allow someone to acquire a car, including car loans and leases.
Loan modification is the systematic alteration of mortgage loan agreements that help those having problems making the payments by reducing interest rates, monthly payments or principal balances. Lending institutions could make one or more of these changes to relieve financial pressure on borrowers to prevent the condition of foreclosure. Loan modifications have been practiced in the United States since the 1930s. During the Great Depression, loan modification programs took place at the state level in an effort to reduce levels of loan foreclosures.
Business credit reports are reports that show the credit history of a business. They are usually created by credit bureaus when a credit grantor reports information related to a business credit account. These reports are typically used during the decision-making process to decide whether or not to grant credit to a business. They are similar to consumer credit reports but focus specifically on the business sector.




