
In wireless routing, inter-flow interference refers to the interference between neighboring routers competing for the same busy channel.
The inter-flow interference routing metric is incorporated in MIC [1] and iAWARE [2] wireless routing protocol.

In wireless routing, inter-flow interference refers to the interference between neighboring routers competing for the same busy channel.
The inter-flow interference routing metric is incorporated in MIC [1] and iAWARE [2] wireless routing protocol.
IEEE 802.15 is a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) IEEE 802 standards committee which specifies wireless personal area network (WPAN) standards. There are 10 major areas of development, not all of which are active.

IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet without connecting wires.

A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes.

Wireless community networks (WCNs) or wireless community projects or simply community networks, are non-centralized, self-managed and collaborative networks organized in a grassroots fashion by communities, NGO's and cooperatives in order to provide a viable alternative to municipal wireless networks for consumers.

Wi-Fi or WiFi is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link desktop and laptop computers, tablet computers, smartphones, smart TVs, printers, and smart speakers together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries and airports to provide the public Internet access for mobile devices.
Wireless local loop (WLL), is the use of a wireless communications link as the "last mile / first mile" connection for delivering plain old telephone service (POTS) or Internet access to telecommunications customers. Various types of WLL systems and technologies exist.

Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a family of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options.

A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. It can also be a form of wireless ad hoc network.

The Wi-Fi Alliance is a non-profit organization that owns the Wi-Fi trademark. Manufacturers may use the trademark to brand products certified for Wi-Fi interoperability.

IEEE 802.16 is a series of wireless broadband standards written by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The IEEE Standards Board established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband for wireless metropolitan area networks. The Workgroup is a unit of the IEEE 802 local area network and metropolitan area network standards committee.
A cognitive radio (CR) is a radio that can be programmed and configured dynamically to use the best wireless channels in its vicinity to avoid user interference and congestion. Such a radio automatically detects available channels in wireless spectrum, then accordingly changes its transmission or reception parameters to allow more concurrent wireless communications in a given spectrum band at one location. This process is a form of dynamic spectrum management.
IEEE 802.11p is an approved amendment to the IEEE 802.11 standard to add wireless access in vehicular environments (WAVE), a vehicular communication system. It defines enhancements to 802.11 required to support Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) applications. This includes data exchange between high-speed vehicles and between the vehicles and the roadside infrastructure, so called V2X communication, in the licensed ITS band of 5.9 GHz (5.85–5.925 GHz). IEEE 1609 is a higher layer standard based on the IEEE 802.11p. It is also the basis of a European standard for vehicular communication known as ETSI ITS-G5.
In a hierarchical telecommunications network, the backhaul portion of the network comprises the intermediate links between the core network, or backbone network, and the small subnetworks at the edge of the network.
A wireless ad hoc network (WANET) or mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a pre-existing infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in wireless networks. Instead, each node participates in routing by forwarding data for other nodes, so the determination of which nodes forward data is made dynamically on the basis of network connectivity and the routing algorithm in use.
A wide variety of different wireless data technologies exist, some in direct competition with one another, others designed for specific applications. Wireless technologies can be evaluated by a variety of different metrics of which some are described in this entry.
IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended throughput to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20 MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/s. This specification under the marketing name of Wi-Fi has been implemented all over the world. The 802.11g protocol is now Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard, and Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2012 standard.
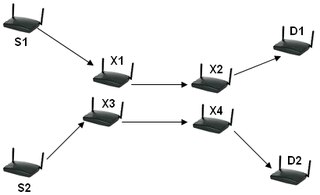
Intra-flow interference is interference between intermediate routers sharing the same flow path.
IEEE 802.11s is a wireless local area network (WLAN) standard and an IEEE 802.11 amendment for mesh networking, defining how wireless devices can interconnect to create a wireless LAN mesh network, which may be used for relatively fixed topologies and wireless ad hoc networks. The IEEE 802.11s task group drew upon volunteers from university and industry to provide specifications and possible design solutions for wireless mesh networking. As a standard, the document was iterated and revised many times prior to finalization.

Victor Bahl is a Technical Fellow and CTO of Azure for Operators at Microsoft. He started networking research at Microsoft. He is known for his research contributions to white space radio data networks, radio signal-strength based indoor positioning systems, multi-radio wireless systems, wireless network virtualization, edge computing, and for bringing wireless links into the datacenter. He is also known for his leadership of the mobile computing community as the co-founder of the ACM Special Interest Group on Mobility of Systems, Users, Data, and Computing (SIGMOBILE). He is the founder of international conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services Conference (MobiSys), and the founder of ACM Mobile Computing and Communications Review, a quarterly scientific journal that publishes peer-reviewed technical papers, opinion columns, and news stories related to wireless communications and mobility. Bahl has received important awards; delivered dozens of keynotes and plenary talks at conferences and workshops; delivered over six dozen distinguished seminars at universities; written over hundred papers with more than 65,000 citations and awarded over 100 US and international patents. He is a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery, IEEE, and American Association for the Advancement of Science.

Zygmunt J. Haas is a professor and distinguished chair in computer science, University of Texas at Dallas (UTD) also the professor emeritus in electrical and computer engineering, Cornell University. His research interests include ad hoc networks, wireless networks, sensor networks, and zone routing protocols.