Related Research Articles

A floppy disk or floppy diskette is an obsolete type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device.

A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box.
Universal Disk Format (UDF) is an open, vendor-neutral file system for computer data storage for a broad range of media. In practice, it has been most widely used for DVDs and newer optical disc formats, supplanting ISO 9660. Due to its design, it is very well suited to incremental updates on both recordable and (re)writable optical media. UDF was developed and maintained by the Optical Storage Technology Association (OSTA).
RAID is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This was in contrast to the previous concept of highly reliable mainframe disk drives referred to as "single large expensive disk" (SLED).

The ST-506 and ST-412 were early hard disk drive products introduced by Seagate in 1980 and 1981 respectively, that later became construed as hard disk drive interfaces: the ST-506 disk interface and the ST-412 disk interface. Compared to the ST-506 precursor, the ST-412 implemented a refinement to the seek speed, and increased the drive capacity from 5 MB to 10 MB, but was otherwise highly similar.
Mount Rainier (MRW) is a format for writable optical discs which provides the packet writing and defect management. Its goal is the replacement of the floppy disk. It is named after Mount Rainier, a volcano near Seattle, Washington, United States.

A USB flash drive is a data storage device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface. It is typically removable, rewritable and much smaller than an optical disc. Most weigh less than 30 g (1 oz). Since first appearing on the market in late 2000, as with virtually all other computer memory devices, storage capacities have risen while prices have dropped. As of March 2016, flash drives with anywhere from 8 to 256 gigabytes (GB) were frequently sold, while 512 GB and 1 terabyte (TB) units were less frequent. As of 2018, 2 TB flash drives were the largest available in terms of storage capacity. Some allow up to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on the exact type of memory chip used, and are thought to physically last between 10 and 100 years under normal circumstances.
S.M.A.R.T. is a monitoring system included in computer hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and eMMC drives. Its primary function is to detect and report various indicators of drive reliability with the intent of anticipating imminent hardware failures.

Data corruption refers to errors in computer data that occur during writing, reading, storage, transmission, or processing, which introduce unintended changes to the original data. Computer, transmission, and storage systems use a number of measures to provide end-to-end data integrity, or lack of errors.
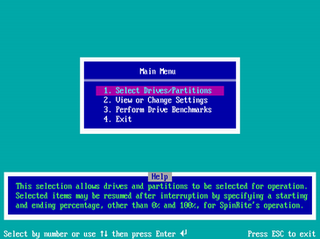
SpinRite is a computer program for scanning magnetic data storage devices such as hard disks, recovering data from them and refreshing their surfaces. The first version was released in 1987 by Steve Gibson. Version 6.0, still current and available as of June 2022, was released in 2004. SpinRite is run from a bootable medium on a PC-compatible computer, allowing it to scan a computer's hard drive and file system. It does not depend upon the operating system installed on the computer.
Micropolis Corporation was a disk drive company located in Chatsworth, California and founded in 1976. Micropolis initially manufactured high capacity hard-sectored 5.25-inch floppy drives and controllers, later manufacturing hard drives using SCSI and ESDI interfaces.

A hard disk drive failure occurs when a hard disk drive malfunctions and the stored information cannot be accessed with a properly configured computer.
A bad sector in computing is a disk sector on a disk storage unit that is permanently damaged. Upon taking damage, all information stored on that sector is lost. When a bad sector is found and marked, the operating system like Windows or Linux will skip it in the future.
The host protected area (HPA) is an area of a hard drive or solid-state drive that is not normally visible to an operating system. It was first introduced in the ATA-4 standard CXV (T13) in 2001.
In computing, error recovery control (ERC) is a feature of hard disks which allow a system administrator to configure the amount of time a drive's firmware is allowed to spend recovering from a read or write error. Limiting the recovery time allows for improved error handling in hardware or software RAID environments. In some cases, there is a conflict as to whether error handling should be undertaken by the hard drive or by the RAID implementation, which leads to drives being marked as unusable and significant performance degradation, when this could otherwise have been avoided.
badblocks is a Linux utility to check for bad sectors on a disk drive. It can create a text file with list of these sectors that can be used with other programs, like mkfs, so that they are not used in the future and thus do not cause corruption of data. It is part of the e2fsprogs project, and a port is available for BSD operating systems.
Data erasure is a software-based method of overwriting the data that aims to completely destroy all electronic data residing on a hard disk drive or other digital media by using zeros and ones to overwrite data onto all sectors of the device in an irreversible process. By overwriting the data on the storage device, the data is rendered irrecoverable and achieves data sanitization.

The Macintosh External Disk Drive is the original model in a series of external 3+1⁄2-inch floppy disk drives manufactured and sold by Apple Computer exclusively for the Macintosh series of computers introduced in January 1984. Later, Apple would unify their external drives to work cross-platform between the Macintosh and Apple II product lines, dropping the name "Macintosh" from the drives. Though Apple had been producing external floppy disk drives prior to 1984, they were exclusively developed for the Apple II, III and Lisa computers using the industry standard 5+1⁄4-inch flexible disk format. The Macintosh external drives were the first to widely introduce Sony's new 3+1⁄2-inch rigid disk standard commercially and throughout their product line. Apple produced only one external 3+1⁄2-inch drive exclusively for use with the Apple II series called the Apple UniDisk 3.5.
The floppy disk is a data storage and transfer medium that was ubiquitous from the mid-1970s well into the 2000s. Besides the 3½-inch and 5¼-inch formats used in IBM PC compatible systems, or the 8-inch format that preceded them, many proprietary floppy disk formats were developed, either using a different disk design or special layout and encoding methods for the data held on the disk.
References
- ↑ "Hard disk defect management Definition from PC Magazine Encyclopedia". www.pcmag.com. Archived from the original on 2009-08-27.
- ↑ "Method and controller for defect tracking in a redundant array - US Patent 5974544 Description". Archived from the original on 2011-06-12. Retrieved 2010-03-17.