
In meteorology, an anemometer is a device that measures wind speed and direction. It is a common instrument used in weather stations. The earliest known description of an anemometer was by Italian architect and author Leon Battista Alberti (1404–1472) in 1450.
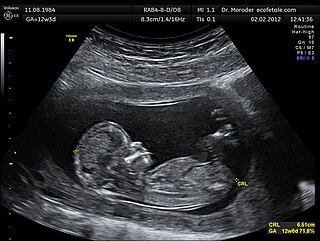
Ultrasound is sound with frequencies greater than 20 kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, including ultrasound. Ultrasonic devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz.
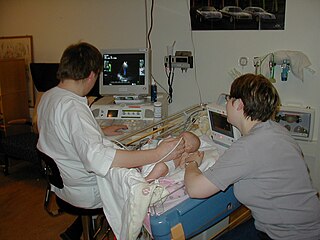
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography.
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured using devices called flowmeters in various ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:

Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), nondestructive inspection (NDI), and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, ultrasonic, and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical imaging, including on echocardiography, medical ultrasonography, and digital radiography.

A fishfinder or sounder (Australia) is an instrument used to locate fish underwater by detecting reflected pulses of sound energy, as in sonar. A modern fishfinder displays measurements of reflected sound on a graphical display, allowing an operator to interpret information to locate schools of fish, underwater debris, and the bottom of body of water. Fishfinder instruments are used both by sport and commercial fishermen. Modern electronics allows a high degree of integration between the fishfinder system, marine radar, compass and GPS navigation systems.
Laser-ultrasonics uses lasers to generate and detect ultrasonic waves. It is a non-contact technique used to measure materials thickness, detect flaws and carry out materials characterization. The basic components of a laser-ultrasonic system are a generation laser, a detection laser and a detector.
Eddy-current testing is one of many electromagnetic testing methods used in nondestructive testing (NDT) making use of electromagnetic induction to detect and characterize surface and sub-surface flaws in conductive materials.
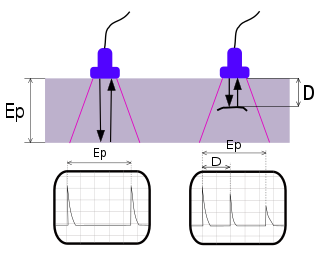
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse-waves with center frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz, and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion.
Level sensors detect the level of liquids and other fluids and fluidized solids, including slurries, granular materials, and powders that exhibit an upper free surface. Substances that flow become essentially horizontal in their containers because of gravity whereas most bulk solids pile at an angle of repose to a peak. The substance to be measured can be inside a container or can be in its natural form. The level measurement can be either continuous or point values. Continuous level sensors measure level within a specified range and determine the exact amount of substance in a certain place, while point-level sensors only indicate whether the substance is above or below the sensing point. Generally the latter detect levels that are excessively high or low.

Phased array ultrasonics (PA) is an advanced method of ultrasonic testing that has applications in medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing. Common applications are to noninvasively examine the heart or to find flaws in manufactured materials such as welds. Single-element probes, known technically as monolithic probes, emit a beam in a fixed direction. To test or interrogate a large volume of material, a conventional probe must be physically scanned to sweep the beam through the area of interest. In contrast, the beam from a phased array probe can be focused and swept electronically without moving the probe. The beam is controllable because a phased array probe is made up of multiple small elements, each of which can be pulsed individually at a computer-calculated timing. The term phased refers to the timing, and the term array refers to the multiple elements. Phased array ultrasonic testing is based on principles of wave physics, which also have applications in fields such as optics and electromagnetic antennae.

Rail inspection is the practice of examining rail tracks for flaws that could lead to catastrophic failures. According to the United States Federal Railroad Administration Office of Safety Analysis, track defects are the second leading cause of accidents on railways in the United States. The leading cause of railway accidents is attributed to human error. The contribution of poor management decisions to rail accidents caused by infrequent or inadequate rail inspection is significant but not reported by the FRA, only the NTSB. Every year, North American railroads spend millions of dollars to inspect the rails for internal and external flaws. Nondestructive testing (NDT) methods are used as preventive measures against track failures and possible derailment.
Tubular NDT is the application of various technologies to detect anomalies such as corrosion and manufacturing defects in metallic tubes. Tubing can be found in such equipment as boilers and heat exchangers. To carry out an examination in situ, a manhole cover is usually removed to allow a technician access to the tubes. Alternatively, a tube bundle may be removed from a heat-exchanger and transported by forklift to a maintenance area for easier access.

Ultrasonic transducers and ultrasonic sensors are devices that generate or sense ultrasound energy. They can be divided into three broad categories: transmitters, receivers and transceivers. Transmitters convert electrical signals into ultrasound, receivers convert ultrasound into electrical signals, and transceivers can both transmit and receive ultrasound.

Electromagnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) is a transducer for non-contact acoustic wave generation and reception in conducting materials. Its effect is based on electromagnetic mechanisms, which do not need direct coupling with the surface of the material. Due to this couplant-free feature, EMATs are particularly useful in harsh, i.e., hot, cold, clean, or dry environments. EMATs are suitable to generate all kinds of waves in metallic and/or magnetostrictive materials. Depending on the design and orientation of coils and magnets, shear horizontal (SH) bulk wave mode, surface wave, plate waves such as SH and Lamb waves, and all sorts of other bulk and guided-wave modes can be excited. After decades of research and development, EMAT has found its applications in many industries such as primary metal manufacturing and processing, automotive, railroad, pipeline, boiler and pressure vessel industries, in which they are typically used for nondestructive testing (NDT) of metallic structures.
Acoustic microscopy is microscopy that employs very high or ultra high frequency ultrasound. Acoustic microscopes operate non-destructively and penetrate most solid materials to make visible images of internal features, including defects such as cracks, delaminations and voids.

Guided wave testing (GWT) is a non-destructive evaluation method. The method employs acoustic waves that propagate along an elongated structure while guided by its boundaries. This allows the waves to travel a long distance with little loss in energy. Nowadays, GWT is widely used to inspect and screen many engineering structures, particularly for the inspection of metallic pipelines around the world. In some cases, hundreds of meters can be inspected from a single location. There are also some applications for inspecting rail tracks, rods and metal plate structures.
A density meter, also known as a densimeter, is a device that measures the density. Density is usually abbreviated as either or . Typically, density either has the units of or . The most basic principle of how density is calculated is by the formula:
Robotic non-destructive testing (NDT) is a method of inspection used to assess the structural integrity of petroleum, natural gas, and water installations. Crawler-based robotic tools are commonly used for in-line inspection (ILI) applications in pipelines that cannot be inspected using traditional intelligent pigging tools.

Anisotropic terahertz microspectroscopy (ATM) is a spectroscopic technique in which molecular vibrations in an anisotropic material are probed with short pulses of terahertz radiation whose electric field is linearly polarized parallel to the surface of the material. The technique has been demonstrated in studies involving single crystal sucrose, fructose, oxalic acid, and molecular protein crystals in which the spatial orientation of molecular vibrations are of interest.










