
The International Electrotechnical Commission is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology". IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology and marine energy as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards.
Conformance testing — an element of conformity assessment, and also known as compliance testing, or type testing — is testing or other activities that determine whether a process, product, or service complies with the requirements of a specification, technical standard, contract, or regulation. Testing is often either logical testing or physical testing. The test procedures may involve other criteria from mathematical testing or chemical testing. Beyond simple conformance, other requirements for efficiency, interoperability or compliance may apply. Conformance testing may be undertaken by the producer of the product or service being assessed, by a user, or by an accredited independent organization, which can sometimes be the author of the standard being used. When testing is accompanied by certification, the products or services may then be advertised as being certified in compliance with the referred technical standard. Manufacturers and suppliers of products and services rely on such certification including listing on the certification body's website, to assure quality to the end user and that competing suppliers are on the same level.
The ISO 9000 family of quality management systems (QMS) is a set of standards that helps organizations ensure they meet customer and other stakeholder needs within statutory and regulatory requirements related to a product or service. ISO 9000 deals with the fundamentals of QMS, including the seven quality management principles that underlie the family of standards. ISO 9001 deals with the requirements that organizations wishing to meet the standard must fulfill.
ISO 14000 is a family of standards related to environmental management that exists to help organizations (a) minimize how their operations negatively affect the environment ; (b) comply with applicable laws, regulations, and other environmentally oriented requirements; and (c) continually improve in the above.

On commercial products, the letters CE mean that the manufacturer or importer affirms the good's conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is not a quality indicator or a certification mark. The CE marking is required for goods sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), but is also found on products sold elsewhere that have been manufactured to EEA standards.
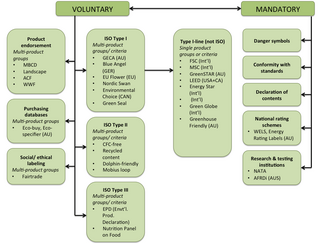
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.
SEMI is an industry association comprising companies involved in the electronics design and manufacturing supply chain. They provide equipment, materials and services for the manufacture of semiconductors, photovoltaic panels, LED and flat panel displays, micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS), printed and flexible electronics, and related micro and nano-technologies.
ISO 13485Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes is a voluntary standard, published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for the first time in 1996, and contains a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices. The latest version of this standard supersedes earlier documents such as EN 46001 and EN 46002 (1996), the previously published ISO 13485, and ISO 13488.
The Yacht Safety Bureau, Inc. (YSB) was a non-profit corporation organized under the membership corporation law of the State of New York that provided safety and testing standards for the marine industry in the United States. Located in Westwood, New Jersey, the YSB developed boat safety tests, developed test equipment for these tests, and wrote standards for such testing, completely independently of commercial interests. It later became the Marine Department of Underwriters' Laboratories.

The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies certification and standards-related services to businesses.

IPC is a trade association whose aim is to standardize the assembly and production requirements of electronic equipment and assemblies. It was founded in 1957 as the Institute of Printed Circuits. Its name was later changed to the Institute for Interconnecting and Packaging Electronic Circuits to highlight the expansion from bare boards to packaging and electronic assemblies. In 1999, the organization formally changed its name to IPC with the accompanying tagline, Association Connecting Electronics Industries.

The Archery Trade Association (ATA), is the trade group representing manufacturers, retailers, distributors, sales representatives and others working in the archery and bowhunting industry. The ATA has served its members since 1953. It is dedicated to making the industry profitable by decreasing business overhead, reducing taxes and government regulation, and increasing participation in archery and bowhunting.
Croatian Register of Shipping, also known as CRS, is an independent classification society established in 1949. It is a non-profit organisation working on the marine market, developing technical rules and supervising their implementation, managing risk and performing surveys on ships. The Society's head office is in Split.
The Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) is a private organization working as a "Coalition of Action" from The Consumer Goods Forum (CGF) bringing together retailers and brand owners (manufacturers) from across the CGF membership operating as multistakeholder governance with objective to create "an extended food safety community to oversee food safety standards for businesses and help provide access to safe food for people everywhere". GFSI's work in benchmarking and harmonization aims to foster mutual acceptance of GFSI-recognized certification programmes across the industry with the ambition to enable a “once certified, accepted everywhere” approach.
The International Marine Certification Institute was established in Brussels, Belgium as an independent certification organisation to serve the interests of the European and International recreational boating industry.
The International Association of Amusement Parks and Attractions (IAAPA) represents over 6,000 amusement-industry members in more than 100 countries worldwide and operates several global attractions-industry trade shows. Its annual IAAPA Expo in Orlando, Florida, is recognized as the world's largest attractions trade show in the number of attendees and exhibitors and providing members insight into current amusement trends, laws, operations and industry methodology. IAAPA also helps to promote guest-safety and ride-safety guidelines in conjunction with ASTM International and assists its members to uphold the highest amusement-industry safety and professional standards.
The European Materials Handling Federation, is the association representing material handling, lifting and storage equipment manufacturers in Europe.
The Recreational Craft Directive, Directive 2013/53/EU, originally Directive 94/25/EC on recreational craft amended by Directive 2003/44/EC, is a European Union directive which sets out minimum technical, safety and environmental standards for boats, personal watercraft, marine engines and components in Europe. It covers boats between 2.5 and 24m, personal watercraft, engines and a number of components built since 1998. It ensures their suitability for sale and use in Europe.
The Korea International Boat Show (KIBS) is one of the three biggest boat shows in Asia, representing the Korean marine leisure industry. The latest edition of KIBS was held jointly from 19 to 22 May 2016, at KINTEX, with the associated Asia Marine Conference. Despite the Sewol ferry disaster and the rising public concern on maritime safety, many exhibitors remained confident about the Korean market's potential. The convention brought together 240 exhibitors and buyers from 40 countries, and occupied a gross exhibition area of 57,557 m2.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to underwater diving:







