Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure, is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as 101,325 Pa (1,013.25 hPa), which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inches Hg, or 14.696 psi. The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm.

Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of atmospheric changes that define average climates and their change over time climate variability. Aeronomy is the study of the upper layers of the atmosphere, where dissociation and ionization are important. Atmospheric science has been extended to the field of planetary science and the study of the atmospheres of the planets and natural satellites of the Solar System.

Atmospheric chemistry is a branch of atmospheric science that studies the chemistry of the Earth's atmosphere and that of other planets. This multidisciplinary approach of research draws on environmental chemistry, physics, meteorology, computer modeling, oceanography, geology and volcanology, climatology and other disciplines to understand both natural and human-induced changes in atmospheric composition. Key areas of research include the behavior of trace gasses, the formation of pollutants, and the role of aerosols and greenhouse gasses. Through a combination of observations, laboratory experiments, and computer modeling, atmospheric chemists investigate the causes and consequences of atmospheric changes.

Paul Jozef Crutzen was a Dutch meteorologist and atmospheric chemist. In 1995, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry alongside Mario Molina and Frank Sherwood Rowland for their work on atmospheric chemistry and specifically for his efforts in studying the formation and decomposition of atmospheric ozone. In addition to studying the ozone layer and climate change, he popularized the term Anthropocene to describe a proposed new epoch in the Quaternary period when human actions have a drastic effect on the Earth. He was also amongst the first few scientists to introduce the idea of a nuclear winter to describe the potential climatic effects stemming from large-scale atmospheric pollution including smoke from forest fires, industrial exhausts, and other sources like oil fires.
The Surface Ocean Lower Atmosphere Study (SOLAS) is a global and multidisciplinary research project dedicated to understanding the key biogeochemical-physical interactions and feedbacks between the ocean and the atmosphere. Further, SOLAS seeks to link ocean-atmosphere interactions with climate and people. Achievements of these goals are essential in order to understand and quantify the role that ocean-atmosphere interactions play in the regulation of climate and global change.
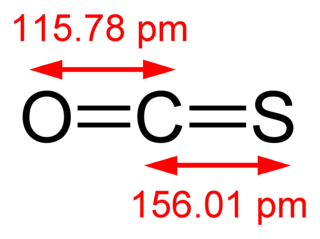
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the linear formula O=C=S. It is a colorless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl double bonded to a sulfur atom. Carbonyl sulfide can be considered to be intermediate between carbon dioxide and carbon disulfide, both of which are valence isoelectronic with it.
Fluoroform, or trifluoromethane, is the chemical compound with the formula CHF3. It is a hydrofluorocarbon as well as being a part of the haloforms, a class of compounds with the formula CHX3 with C3v symmetry. Fluoroform is used in diverse applications in organic synthesis. It is not an ozone depleter but is a greenhouse gas.

The Max Planck Institute for Chemistry is a non-university research institute under the auspices of the Max Planck Society in Mainz, Germany. It was created as the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Chemistry in 1911 in Berlin.
Chlorotrifluoromethane, R-13, CFC-13, or Freon 13, is a non-flammable, non-corrosive, nontoxic chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) and also a mixed halomethane. It is a man-made substance used primarily as a refrigerant. When released into the environment, CFC-13 has a high ozone depletion potential, and long atmospheric lifetime. Only a few other greenhouse gases surpass CFC-13 in global warming potential (GWP). The IPCC AR5 reported that CFC-13's atmospheric lifetime was 640 years.

The National Environmental Research Institute of Denmark, abbreviated NERI, was an independent research institute under the Ministry of the Environment. It was created in 1989 by merging the existing laboratories of the Environmental Protection Agency, which covered marine, freshwater and air pollution, soil ecology and analytical chemistry, with the Danish Wildlife Research, under the Ministry of Agriculture. The laboratories were physically located on Risø, in Silkeborg and on Kalø, north of Aarhus. In 1995, Greenland Biological Research laboratory was added.
The high-resolution dynamics limb sounder (HIRDLS) is an instrument on board the NASA Aura. It follows in the heritage of LRIR (Nimbus-6), LIMS and SAMS (Nimbus-7), ISAMS and CLAES (UARS). It was designed to observe global distribution of temperature and concentrations of O3, H2O, CH4, N2O, NO2, HNO3, N2O5, CFC-11, CFC-12, ClONO2, and aerosols in the upper troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere.

Global Emissions InitiAtive (GEIA) is a community effort dedicated to atmospheric emissions information exchange and competence building. GEIA was created in 1990 under the (IGBP) and is a joint IGAC / iLEAPS / AIMES activity. GEIA is governed by an international steering committee and hosts biennial conferences.

Tellus Series B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology is an open access scientific journal that is published by Stockholm University Press for the International Meteorological Institute in Stockholm, Sweden since 2022. Between 2012 and 2022, the issues were published online by Co-action Publishing. The journal publishes original articles, short contributions, and correspondence on atmospheric chemistry, surface exchange processes, long-range and global transport, aerosol science, and cloud physics including related radiation transfer. Biogeochemical cycles including related aspects of marine chemistry and geochemistry also represent a central theme.
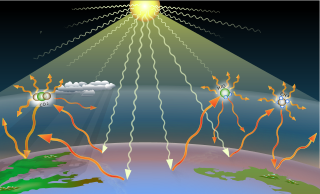
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. What distinguishes them from other gases is that they absorb the wavelengths of radiation that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F).
Lucy Jane Carpenter is a British chemist who is a professor of physical chemistry at the University of York and director of the Cape Verde Atmospheric Observatory (CVAO).
Arlene M. Fiore is an atmospheric chemist whose research focuses on issues surrounding air quality and climate change.

Johannes "Jos" Lelieveld is a Dutch atmospheric chemist. Since 2000, he has been a Scientific Member of the Max Planck Society and director of the Atmospheric Chemistry Department at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Mainz. He is also professor at the University of Mainz and at the Cyprus Institute in Nicosia.
Jennifer G. Murphy is a Canadian environmental chemist and an associate professor at the University of Toronto. She is known for her research how air pollutants such as increased reactive nitrogen affect the global climate.
Kerri Pratt is an American chemist and Associate Professor of Chemistry at the University of Michigan. Her research considers atmospheric chemistry and how it impacts human health. She studies the interactions of atmospheric gases using mass spectrometry based techniques.








