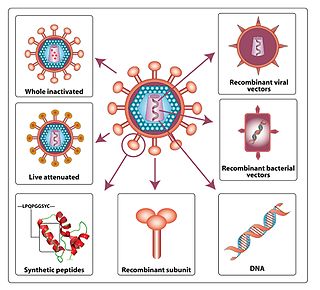
An HIV vaccine is a potential vaccine that could be either a preventive vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine, which means it would either protect individuals from being infected with HIV or treat HIV-infected individuals.

HIV/AIDS originated in Africa in the early 20th century and is a major public health concern and cause of death in many African countries. AIDS rates vary dramatically although the majority of cases are concentrated in Southern Africa. Although the continent is home to about 15.2 percent of the world's population, more than two-thirds of the total infected worldwide – some 35 million people – were Africans, of whom 15 million have already died. Sub-Saharan Africa alone accounted for an estimated 69 percent of all people living with HIV and 70 percent of all AIDS deaths in 2011. In the countries of sub-Saharan Africa most affected, AIDS has raised death rates and lowered life expectancy among adults between the ages of 20 and 49 by about twenty years. Furthermore, the life expectancy in many parts of Africa is declining, largely as a result of the HIV/AIDS epidemic with life-expectancy in some countries reaching as low as thirty-nine years.

Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases are pharmacologic agents and chemical substances that are capable of killing or destroying certain microorganisms that commonly cause human infection.
The International AIDS Society (IAS) is the world's largest association of HIV/AIDS professionals, with 11,600 members from over 170 countries as of July 2020, including clinicians, people living with HIV, service providers, policy makers and others. It aims to reduce the global impact of AIDS through collective advocacy. Founded in 1988, IAS headquarters are located in Geneva, and its president since July 2020 is Adeeba Kamarulzaman.

The International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI) is a global not-for-profit, public-private partnership working to accelerate the development of vaccines to prevent HIV infection and AIDS. IAVI researches and develops vaccine candidates, conducts policy analyses, serves as an advocate for the HIV prevention field and engages communities in the trial process and AIDS vaccine education. The organization takes a comprehensive approach to HIV and AIDS that supports existing HIV prevention and treatment programs while emphasizing the need for new AIDS prevention tools. It also works to ensure that future vaccines will be accessible to all who need them.
The European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP) is a partnership between the European Union (EU), Norway, Switzerland and developing countries and other donors, as well as the pharmaceutical industry, to enable clinical trials and the development of new medicines and vaccines against HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria. The need for global action against these diseases in order to promote poverty reduction has been recognised by the United Nations, the G8, and the African Union, and the program envisioned the provision of €600 million for the period 2003–2007 in order to translate medical research results into clinical applications relevant to the needs of developing countries.

The AIDS Clinical Trials Group network (ACTG) is one of the largest HIV clinical trials organizations in the world, playing a major role in setting standards of care for HIV infection and opportunistic diseases related to HIV and AIDS in the United States and the developing world. The ACTG is composed of, and directed by, leading clinical scientists in HIV/AIDS therapeutic research. The ACTG is funded by the Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health through the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
The Division of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (DAIDS) is a division of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, which is part of the National Institutes of Health. It was formed in 1986 as a part of the initiative to address the national research needs created by the advent and spread of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. Specifically, the Division's mission is to increase basic knowledge of the pathogenesis, natural history, and transmission of HIV disease and to support research that promotes progress in its detection, treatment, and prevention. DAIDS accomplishes this through planning, implementing, managing, and evaluating programs in (1) fundamental basic research, (2) discovery and development of therapies for HIV infection and its complications, and (3) discovery and development of vaccines and other prevention strategies.

The HIV Vaccine Trials Network (HVTN) is a non-profit organization which connects physicians and scientists with activists and community educators for the purpose of conducting clinical trials seeking a safe and effective HIV vaccine. Collaboratively, researchers and laypeople review potential vaccines for safety, immune response, and efficacy. The HVTN is a network for testing vaccines, and while its members may also work in vaccine development for other entities, the mission of the HVTN does not include vaccine design.
The Community Programs for Clinical Research on AIDS (CPCRA) was a program sponsored by National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States. Started in 1989, CPCRA was instrumental in some research databases being established. Research from the programs assisted the evaluation of therapies for treating HIV in diverse populations.
With 1.28 percent of the adult population estimated by UNAIDS to be HIV-positive in 2006, Papua New Guinea has one of the most serious HIV/AIDS epidemics in the Asia-Pacific subregion. Although this new prevalence rate is significantly lower than the 2005 UNAIDS estimate of 1.8 percent, it is considered to reflect improvements in surveillance rather than a shrinking epidemic. Papua New Guinea accounts for 70 percent of the subregion's HIV cases and is the fourth country to be classified as having a generalized HIV epidemic.
The HIV/AIDS epidemic in Ukraine is one of the fastest-growing epidemics in the world. Ukraine has one of the highest rates of increase of HIV/AIDS cases in Eastern Europe and highest HIV prevalence outside Africa. Experts estimated in August 2010 that 1.3 percent of the adult population of Ukraine was infected with HIV, the highest in all of Europe. Late 2011 Ukraine numbered 360,000 HIV-positive persons. Between 1987 and late 2012 27,800 Ukrainians died of AIDS. In 2012 tests revealed 57 new cases of HIV positive Ukrainians each day and 11 daily AIDS-related deaths.
People living with HIV/AIDS face increased challenges in maintaining proper nutrition. Despite developments in medical treatment, nutrition remains a key component in managing this condition. The challenges that those living with HIV/AIDS face can be the result of the viral infection itself or from the effects of anti-HIV therapy (HAART).
Asociación Civil Impacta Salud y Educación is a non-profit organization which promotes public health in the Andean region of Peru.

The Office of HIV/AIDS Network Coordination, known as HANC, works with the National Institutes of Health HIV/AIDS clinical trials networks with the intent of creating a more integrated, collaborative and flexible research structure. The networks are an affiliated group of national and international medical research institutions and investigators that conduct clinical HIV/AIDS research to develop safe and effective drugs, prevention strategies, and vaccines.
The Microbicide Trials Network (MTN) is the leading United States government-funded research organization working in the field of microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases. The MTN particularly focuses on research into microbicides which would prevent HIV infection. The MTN is a member of HANC.

The International Maternal Pediatric Adolescent AIDS Clinical Trials Group, known as IMPAACT, is a United States-based research network which studies HIV and AIDS in infant, pediatric, adolescent and pregnant women populations. It is a member of the Office of HIV/AIDS Network Coordination research group.
Martin T. Schechter is a Canadian epidemiologist recognized for contributions to HIV research, prevention and treatments, addiction research, and Indigenous health research. He is a professor and the former founding director of the School of Population and Public Health in the Faculty of Medicine at the University of British Columbia (UBC). Schechter received his Order of British Columbia in 1994 alongside BC's first Nobel Prize laureate Michael Smith and noted Indigenous artist Bill Reid.

Quarraisha Abdool Karim, is an infectious diseases epidemiologist and co-founder and Associate Scientific Director of CAPRISA. She is Professor in Clinical Epidemiology, Columbia University, New York and Pro-Vice Chancellor for African Health, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.
Gita Ramjee was a Ugandan-South African scientist and researcher in HIV prevention. In 2018, she was awarded the ‘Outstanding Female Scientist’ award from the European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership. She died in Umhlanga, Durban, South Africa, from COVID-19 related complications.









