
The Organisation internationale de la Francophonie is an international organization representing countries and regions where French is a lingua franca or customary language, where a significant proportion of the population are francophones, or where there is a notable affiliation with French culture. It is also called the French Commonwealth.
The Commonwealth Secretariat is the main intergovernmental agency and central institution of the Commonwealth of Nations. It is responsible for facilitating co-operation between members; organising meetings, including the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meetings (CHOGM); assisting and advising on policy development; and providing assistance to countries in implementing the decisions and policies of the Commonwealth.

The Inter-Parliamentary Union is an international organization of national parliaments. Its primary purpose is to promote democratic governance, accountability, and cooperation among its members; other initiatives include advancing gender parity among legislatures, empowering youth participation in politics, and sustainable development.
The Commonwealth Parliamentary Association (CPA), previously known as the Empire Parliamentary Association, is an organisation which works to support good governance, democracy and human rights.
A national human rights institution (NHRI) is an independent state-based institution with the responsibility to broadly protect and promote human rights in a given country. The growth of such bodies has been encouraged by the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), which has provided advisory and support services, and facilitated access for NHRIs to the United Nations (UN) treaty bodies and other committees. There are over one hundred such institutions, about two-thirds assessed by peer review as compliant with the United Nations standards set out in the Paris Principles. Compliance with the Principles is the basis for accreditation at the UN, which, uniquely for NHRIs, is not conducted directly by a UN body but by a sub-committee of the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) called the Sub-Committee on Accreditation. The secretariat to the review process is provided by the National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Section of the OHCHR.
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
The Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action (VDPA) is a human rights declaration adopted by consensus at the World Conference on Human Rights on 25 June 1993 in Vienna, Austria. The position of United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights was recommended by this Declaration and subsequently created by General Assembly Resolution 48/141.
Human rights education (HRE) is the learning process that seeks to build knowledge, values, and proficiency in the rights that each person is entitled to. This education teaches students to examine their own experiences from a point of view that enables them to integrate these concepts into their values. Decision-making, and daily situations. According to Amnesty International, HRE is a A way to empower people is by training them so that their skills and behaviors promote dignity and equality within their communities, societies, and throughout the world.

The United Nations Integrated Mission in East Timor (UNMIT) was established on 25 August 2006 by UN Security Council Resolution 1704. Its objectives are "to support the Government in consolidating stability, enhancing a culture of democratic governance, and facilitating political dialogue among Timorese stakeholders, in their efforts to bring about a process of national reconciliation and to foster social cohesion". In its most recent resolution on UNMIT, the Council extended its mandate until 26 February 2012. UNMIT and ISF troops left the country at the end of 2012.

Luis Alfonso de Alba Góngora is a Mexican diplomat.
The Paris Principles were defined at the first International Workshop on National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights held in Paris on 7–9 October 1991. They were adopted by the United Nations Human Rights Commission by Resolution 1992/54 of 1992, and by the UN General Assembly in its Resolution 48/134 of 1993. In addition to exchanging views on existing arrangements, the workshop participants drew up a comprehensive series of recommendations on the role, composition, status and also functions of national human rights institutions (NHRIs). These built on standards previously adopted by the 1978 Geneva Seminar on National and Local Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights’, which produced the ‘Guidelines on the Structure and Functioning of National and Local Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights’. The 1993 Paris Principles regulate to the status and functioning of national institutions for the protection and promotion of human rights known as National Human Rights Institutions.

At Italy's instigation, a resolution for a moratorium on the death penalty was presented by the European Union in partnership with eight co-author member States to the General Assembly of the United Nations, calling for general suspension of capital punishment throughout the world. It was approved on 15 November 2007 by the Third Committee, and then subsequently adopted on 18 December by the United Nations General Assembly resolution 62/149. New Zealand played a central role facilitating agreement between the co-author group and other supporters.

An ombudsman is a government employee who investigates and tries to resolve complaints, usually through recommendations or mediation. They are usually appointed by the government or by parliament.
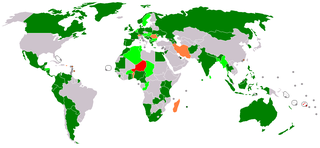
The Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions is a global network of national human rights institutions (NHRIs) which coordinates the relationship between NHRIs and the United Nations human rights system, and is unique as the only non-UN body whose internal accreditation system, based on compliance with the 1993 Paris Principles, grants access to UN committees. Institutions accredited by the Subcommittee for Accreditation (SCA) of GANHRI with "A status", meaning full compliance with the Paris Principles, are usually accorded speaking rights and seating at human rights treaty bodies and other UN organs, mainly to the Human Rights Council. GANHRI representatives often present statements on behalf of individual NHRIs or the regional groups.
The Network of African National Human Rights Institutions (NANHRI) is one of four regional groupings within the global network, the Global Alliance for National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI). NANHRI promotes the establishment of national human rights institutions throughout Africa, and supports co-operation and training to strengthen and develop the monitoring, promotion, protection and advocacy work of African NHRIs.
A children's ombudsman, children's commissioner, youth commissioner, child advocate, children's commission, youth ombudsman or equivalent body is a public authority in various countries charged with the protection and promotion of the rights of children and young people, either in society at large, or in specific categories such as children in contact with the care system. The agencies usually have a substantial degree of independence from the executive, the term is often used differently from the original meaning of ombudsman, it is often an umbrella term, often used as a translation convention or national human rights institutions, dealing with individual complaints, intervening with other public authorities, conducting research, and – where their mandate permits them to engage in advocacy – generally promoting children's rights in public policy, law and practice. The first children's commissioner was established in Norway in 1981. The creation of such institutions has been promoted by the United Nations Committee on the Rights of the Child, and, from 1990 onwards, by the Council of Europe.
The Office of the Provedor for Human Rights and Justice, or Provedoria dos Direitos Humanos e Justiça (PDHJ), is the National Human Rights Institution of the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste. It was established under Section 27 of the Constitution of Timor-Leste in May 2002 and first opened its doors in 2006. The PDHJ has a dual mandate covering human rights and good governance.
The Defensoría del Pueblo de la República Bolivariana de Venezuela is a state-funded human rights agency in Venezuela responsible for investigating complaints against any public authority. Along with the Public Ministry and the Comptroller-General of the Republic, the office forms the 'citizens’ power' branch of the Government of Venezuela. The three bodies collectively form the Republican Moral Council, a body established to promote moral and ethical behaviour by public officials.

Human rights in Namibia are currently recognised and protected by the Namibian constitution formed in 1990 by a 72-seat assembly. The assembly consisted of differing political parties. After a draft, the constitution was agreed upon by all members of the seven political parties involved. 21 March 1990 marks the first day Namibia operated under the Constitution and also marks the recognition of Namibia as an independent nation. Chapter 3 of the constitution entitled Fundamental Human Rights and Freedoms, also referred to as the Bill of Rights, outlines the human rights of all Namibian citizens.
An ombudsman is a government employee who represents a country's citizens. Most countries offer ombudsman services.







