
The geography of Croatia is defined by its location—it is described as located at the crossroads of Central Europe and Southeast Europe, or within the wider region of Southern Europe. Croatia's territory covers 56,594 km2 (21,851 sq mi), making it the 127th largest country in the world. Bordered by Slovenia in the northwest, Hungary in the northeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia in the east, Montenegro in the southeast and the Adriatic Sea in the south, it lies mostly between latitudes 42° and 47° N and longitudes 13° and 20° E. Croatia's territorial waters encompass 18,981 square kilometres (7,329 sq mi) in a 12 nautical miles wide zone, and its internal waters located within the baseline cover an additional 12,498 square kilometres (4,826 sq mi).
The foreign relations of Croatia is primarily formulated and executed via its government which guides the state's interactions with other nations, their citizens, and foreign organizations. Active in global affairs since the 9th century, modern Croatian diplomacy is considered to have formed following their independence from Yugoslavia in 1991. As an independent state, Croatia established diplomatic relations with most world nations – 187 states in total – during the 1990s, starting with Germany (1991) and ending most recently with Togo (2023). Croatia has friendly relations with most of its neighboring countries, namely Slovenia, Hungary, Montenegro, Albania, and Italy. They maintain colder, more tense relations with Serbia as well as Bosnia and Herzegovina due to historic nation-building conflict and differing political ideologies.
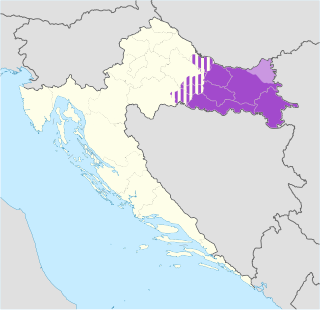
Slavonia is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Located in the Pannonian Plain and taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja, Požega-Slavonia, Virovitica-Podravina, and Vukovar-Syrmia, although the territory of the counties includes Baranya, and the definition of the western extent of Slavonia as a region varies. The counties cover 12,556 square kilometres or 22.2% of Croatia, inhabited by 806,192—18.8% of Croatia's population. The largest city in the region is Osijek, followed by Slavonski Brod and Vinkovci.

Republika Srpska is one of the two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located in the north and the east of the country and has a population of 1,228,423 people as of the 2013 census. Its largest city and administrative centre is Banja Luka, lying on the Vrbas river, and with a population of about 138,963 people.

Vukovar-Srijem County, Vukovar-Sirmium County or Vukovar-Syrmia County, named after the eponymous town of Vukovar and the region of Syrmia, is the easternmost Croatian county. It includes the eastern parts of the region of Slavonia and the western parts of the region of Syrmia, as well as the lower Sava river basin, Posavina and Danube river basin Podunavlje. Due to the overlapping definitions of geographic regions, division on Slavonia and Syrmia approximately divides the county vertically into north-west and south-east half, while division on Posavina and Podunavlje divides it horizontally on north-east and south-west half.

The Sava is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally through Serbia, feeding into the Danube in its capital, Belgrade. The Sava forms the main northern limit of the Balkan Peninsula, and the southern edge of the Pannonian Plain.

The Vrbas is a major river with a length of 250 kilometres (160 mi), in western Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is a right tributary of the Sava river. The city of Banja Luka is located on the river banks.

The Southeast European Cooperative Initiative (SECI) is a multilateral regional initiative that has been initiated by the European Union, the United States of America and the countries of Southeast Europe within the framework of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) as a support to the implementation of the Dayton Accords in December 1996 at the inaugural session at Geneva on the basis of Final Points of Common EU-USA Understanding.

The Banovina of Croatia or Banate of Croatia was an administrative subdivision (banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1939 and 1941. It was formed by a merger of Sava and Littoral banovinas into a single autonomous entity, with small parts of the Drina, Zeta, Vrbas and Danube banovinas also included. Its capital was Zagreb and it included most of present-day Croatia along with portions of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. Its sole Ban during this period was Ivan Šubašić.

The International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River (ICPDR) is an international organisation with its permanent secretariat in Vienna. It was established by the Danube River Protection Convention, signed by the Danube countries in Sofia, Bulgaria, in 1994.

The University of Banja Luka is the second-oldest university in Bosnia and Herzegovina. A public university, it is the flagship institution of higher education in Republika Srpska, one of two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2018–19 school year, there are 11,186 enrolled students.

The Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia was an unrecognized geopolitical entity and quasi-state in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was proclaimed on 18 November 1991 under the name Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia as a "political, cultural, economic and territorial whole" in the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and abolished on 14 August 1996.
On 25 March 1991, the presidents of the Yugoslav federal states SR Croatia and SR Serbia, Franjo Tuđman and Slobodan Milošević, met at the Karađorđevo hunting ground in northwest Serbia. The publicized topic of their discussion was the ongoing Yugoslav crisis. Three days later all the presidents of the six Yugoslav republics met in Split. Although news of the meeting taking place was widely publicized in the Yugoslav media at the time, the meeting was overshadowed by the crisis in progress, that would lead to the breakup of Yugoslavia.

The foreign relations between Bosnia and Herzegovina (BiH) and Croatia are bound together by shared history, language, neighboring geography and cultural commonalties. They established diplomatic relations in 1992, following the dissolution of Yugoslavia and independence of Croatia. The two countries share a 932-kilometer (579 mi) border – the second longest external land border in the European Union (EU). Modern relations between the two states are functional but remain tense after ineffective 21st-century attempts at détente.
United Nations Security Council resolution 820, adopted on 17 April 1993, after reaffirming all previous resolutions on the topic for a lasting peace settlement in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the region, the council discussed the peace plan for Bosnia and Herzegovina and comprehensive steps to ensure its implementation.

United Nations Security Council resolution 981, adopted unanimously on 31 March 1995, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in the former Yugoslavia, the council established the United Nations Confidence Restoration Operation in Croatia (UNCRO) for a period terminating 30 November 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1031, adopted unanimously on 15 December 1995, after recalling all previous resolutions on the conflicts in the former Yugoslavia, the council, acting under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, discussed the transfer of authority from the United Nations Protection Force (UNPROFOR) to the multinational Implementation Force (IFOR).

Posavina is a geographical region that stretches along the Sava river, encompassing only the inner areas of the Sava river basin, that are adjacent or near to the Sava river itself, namely catch region spanning from the Julian Alps in the northwest to the confluence with the Danube in the southeast. It passes through several countries of former Yugoslavia, namely Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. In Slovene, the term Posavina is not used to describe the parts of Slovenia that lie by the Sava river. Instead, the terms Posavje, Zasavje and Zgornjesavska dolina are used.
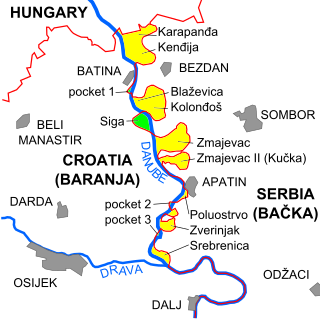
The border between Croatia and Serbia in the area of the Danube is disputed, an important part of their broader diplomatic relations. While Serbia claims that the thalweg of the Danube valley and the centerline of the river represents the international border between the two countries, Croatia disagrees, claiming that the international border lies along the boundaries of the cadastral municipalities located along the river—departing from the course at several points along a 140-kilometre (87 mi) section. The cadastre-based boundary reflects the course of the Danube which existed in the 19th century, before anti-meandering and hydrotechnical engineering works altered its course. The area size of the territory in dispute is reported variously, up to 140 km2.


















