Related Research Articles

Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
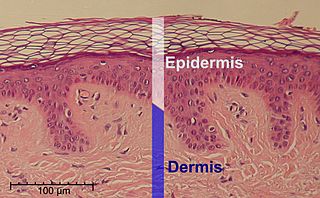
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss.

Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma (cSCC), also known as squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin or squamous-cell skin cancer, is one of the three principal types of skin cancer, alongside basal-cell carcinoma and melanoma. cSCC typically presents as a hard lump with a scaly surface, though it may also present as an ulcer. Onset and development often occurs over several months.

Panniculitis is a group of diseases whose hallmark is inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Symptoms include tender skin nodules, and systemic signs such as weight loss and fatigue.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red and/or flesh-colored, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs.

Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.

Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin. Actinic keratosis is a disorder of epidermal keratinocytes that is induced by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure.

A radiation burn is a damage to the skin or other biological tissue and organs as an effect of radiation. The radiation types of greatest concern are thermal radiation, radio frequency energy, ultraviolet light and ionizing radiation.

Erythema ab igneEAI, also known as hot water bottle rash, is a skin condition caused by long-term exposure to heat. Prolonged thermal radiation exposure to the skin can lead to the development of reticulated erythema, hyperpigmentation, scaling, and telangiectasias in the affected area. Some people may complain of mild itchiness and a burning sensation, but often, unless a change in pigmentation is seen, it can go unnoticed.

Granuloma annulare (GA) is a rare, sometimes chronic skin condition which presents as reddish bumps on the skin arranged in a circle or ring. It can initially occur at any age, though two-thirds of patients are under 30 years old, and it is seen most often in children and young adults. Females are two times as likely to have it as males.

Skin care or skincare is a range of practices that support skin integrity, enhance its appearance, and relieve skin conditions. They can include nutrition, avoidance of excessive sun exposure, and appropriate use of emollients. Practices that enhance appearance include the use of cosmetics, botulinum, exfoliation, fillers, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, peels, retinol therapy, and ultrasonic skin treatment. Skin care is a routine daily procedure in many settings, such as skin that is either too dry or too moist, and prevention of dermatitis and prevention of skin injuries.

Cheilitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the lips. The inflammation may include the perioral skin, the vermilion border, or the labial mucosa. The skin and the vermilion border are more commonly involved, as the mucosa is less affected by inflammatory and allergic reactions.

The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin".

Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch or painful, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. Other symptoms include blistering, peeling skin, swelling, itching, and nausea. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of (primarily) non-malignant skin tumors, which in extreme cases can be life-threatening. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells' DNA is overly damaged by UV radiation, type I cell-death is triggered and the tissue is replaced.
Smoker's face describes the characteristic changes that happen to the faces of many people who smoke tobacco products. Smoking causes damage to the skin by depleting the skin of oxygen and nutrients. The general appearance is of accelerated ageing of the face, with a characteristic pattern of facial wrinkling and sallow coloration.
Melanonychia is a black or brown pigmentation of a nail, and may be present as a normal finding on many digits in Afro-Caribbeans, as a result of trauma, systemic disease, or medications, or as a postinflammatory event from such localized events as lichen planus or fixed drug eruption.

Photoaging or photoageing is a term used for the characteristic changes to skin induced by chronic UVA and UVB exposure. Tretinoin is the best studied retinoid in the treatment of photoaging.
Senile pruritus is one of the most common conditions in the elderly or people over 65 years of age with an emerging itch that may be accompanied with changes in temperature and textural characteristics. In the elderly, xerosis, is the most common cause for an itch due to the degradation of the skin barrier over time. However, the cause of senile pruritus is not clearly known. Diagnosis is based on an elimination criteria during a full body examination that can be done by either a dermatologist or non-dermatologist physician.
References
- ↑ YU RJ, Van Scott EJ: Alpha-hydroxy Acids: Science and Therapeutic Use. A Sup to Cosmetic Dermatology, Oct 1994. 1(1):1-5.
- ↑ Gilchrest BA: Overview of skin aging. J Cut Aging & Cos Derm 1(1):1-2, 1998
- ↑ Klingman AM, Klingman LH: Photoaging. In: Fitzpatick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Freedberg IM, Austen KF (eds.): Dermatology in General Medicine, Vol. II. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, Inc.; 1993:2972-2970
- ↑ Uitto J, Fazio MJ, Olsen DR: Cutaneous aging: Molecular alterations in elastic fibers. J Cuta Aging & Cos Derm 1(1):13-26, 1998.