Before the Acts of Union 1707, the barons of the shire of Inverness elected commissioners to represent them in the unicameral Parliament of Scotland and in the Convention of the Estates.

The Acts of Union were two Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act passed in 1707 by the Parliament of Scotland. They put into effect the terms of the Treaty of Union that had been agreed on 22 July 1706, following negotiation between commissioners representing the parliaments of the two countries. By the two Acts, the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland—which at the time were separate states with separate legislatures, but with the same monarch—were, in the words of the Treaty, "United into One Kingdom by the Name of Great Britain".
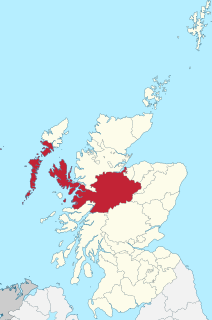
The Shire of Inverness is a historic county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. Covering much of the Highlands and Outer Hebrides, it is Scotland's largest county, though one of the smallest in population, with 67,733 people or 1.34% of the national population.

The Parliament of Scotland was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland. The parliament, like other such institutions, evolved during the Middle Ages from the king's council of bishops and earls. It is first identifiable as a parliament in 1235, during the reign of Alexander II, when it was described as a "colloquium" and already possessed a political and judicial role. By the early fourteenth century, the attendance of knights and freeholders had become important, and from 1326 commissioners from the burghs attended. Consisting of the "three estates" of clergy, nobility and the burghs sitting in a single chamber, the parliament gave consent for the raising of taxation and played an important role in the administration of justice, foreign policy, war, and all manner of other legislation. Parliamentary business was also carried out by "sister" institutions, such as General Councils or Convention of Estates. These could carry out much business also dealt with by parliament – taxation, legislation and policy-making – but lacked the ultimate authority of a full parliament.
Contents
From 1708 Inverness-shire was represented by one Member of Parliament in the House of Commons of Great Britain.

The 1708 British general election was the first general election to be held after the Acts of Union had united the Parliaments of England and Scotland.
Inverness-shire was a county constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1708 to 1801 and of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 until 1918.

The House of Commons of Great Britain was the lower house of the Parliament of Great Britain between 1707 and 1801. In 1707, as a result of the Acts of Union of that year, it replaced the House of Commons of England and the third estate of the Parliament of Scotland, as one of the most significant changes brought about by the Union of the kingdoms of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain.
