Filtration is a physical process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture.
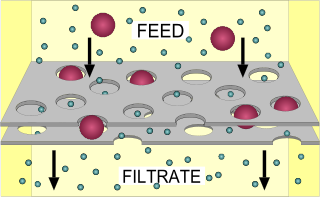
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday usage the verb "strain" is more often used; for example, using a colander to drain cooking water from cooked pasta.

Filter paper is a semi-permeable paper barrier placed perpendicular to a liquid or air flow. It is used to separate fine solid particles from liquids or gases.
Microfiltration is a type of physical filtration process where a contaminated fluid is passed through a special pore-sized membrane filter to separate microorganisms and suspended particles from process liquid. It is commonly used in conjunction with various other separation processes such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis to provide a product stream which is free of undesired contaminants.

A diving air compressor is a breathing air compressor that can provide breathing air directly to a surface-supplied diver, or fill diving cylinders with high-pressure air pure enough to be used as a hyperbaric breathing gas. A low pressure diving air compressor usually has a delivery pressure of up to 30 bar, which is regulated to suit the depth of the dive. A high pressure diving compressor has a delivery pressure which is usually over 150 bar, and is commonly between 200 and 300 bar. The pressure is limited by an overpressure valve which may be adjustable.
In the oil industry, waterflooding or water injection is where water is injected into the oil reservoir, to maintain the pressure, or to drive oil towards the wells, and thereby increase production. Water injection wells may be located on- and offshore, to increase oil recovery from an existing reservoir.
Total suspended solids (TSS) is the dry-weight of suspended particles, that are not dissolved, in a sample of water that can be trapped by a filter that is analyzed using a filtration apparatus known as sintered glass crucible. TSS is a water quality parameter used to assess the quality of a specimen of any type of water or water body, ocean water for example, or wastewater after treatment in a wastewater treatment plant. It is listed as a conventional pollutant in the U.S. Clean Water Act. Total dissolved solids is another parameter acquired through a separate analysis which is also used to determine water quality based on the total substances that are fully dissolved within the water, rather than undissolved suspended particles.

Sand filters are used as a step in the water treatment process of water purification.

A particulate air filter is a device composed of fibrous, or porous materials which removes particulates such as smoke, dust, pollen, mold, viruses and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbon) may also remove odors and gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds or ozone. Air filters are used in applications where air quality is important, notably in building ventilation systems and in engines.

A diesel particulate filter (DPF) is a device designed to remove diesel particulate matter or soot from the exhaust gas of a diesel engine.

A dust collector is a system used to enhance the quality of air released from industrial and commercial processes by collecting dust and other impurities from air or gas. Designed to handle high-volume dust loads, a dust collector system consists of a blower, dust filter, a filter-cleaning system, and a dust receptacle or dust removal system. It is distinguished from air purifiers, which use disposable filters to remove dust.

In chemical engineering, biochemical engineering and protein purification, cross-flow filtration is a type of filtration. Cross-flow filtration is different from dead-end filtration in which the feed is passed through a membrane or bed, the solids being trapped in the filter and the filtrate being released at the other end. Cross-flow filtration gets its name because the majority of the feed flow travels tangentially across the surface of the filter, rather than into the filter. The principal advantage of this is that the filter cake is substantially washed away during the filtration process, increasing the length of time that a filter unit can be operational. It can be a continuous process, unlike batch-wise dead-end filtration.

Aquarium filters are critical components of both freshwater and marine aquaria. Aquarium filters remove physical and soluble chemical waste products from aquaria, simplifying maintenance. Furthermore, aquarium filters are necessary to support life as aquaria are relatively small, closed volumes of water compared to the natural environment of most fish.
Black powder is an industry name for the abrasive, reactive particulate contamination present in all gas and hydrocarbon fluid transmission lines. Black powder ranges from light brown to black, and the mineral makeup varies per production field around the world.
Depth filters are filters that use a porous filtration medium to retain particles throughout the medium, rather than just on the surface of the medium. Depth filtration, typified by multiple porous layers with depth, is used to capture the solid contaminants from the liquid phase. These filters are commonly used when the fluid to be filtered contains a high load of particles because, relative to other types of filters, they can retain a large mass of particles before becoming clogged.

A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.
A separation process is a method that converts a mixture or a solution of chemical substances into two or more distinct product mixtures, a scientific process of separating two or more substances in order to obtain purity. At least one product mixture from the separation is enriched in one or more of the source mixture's constituents. In some cases, a separation may fully divide the mixture into pure constituents. Separations exploit differences in chemical properties or physical properties between the constituents of a mixture.

Gravity filtration is a method of filtering impurities from solutions by using gravity to pull liquid through a filter. The two main kinds of filtration used in laboratories are gravity and vacuum/suction. Gravity filtration is often used in chemical laboratories to filter precipitates from precipitation reactions as well as drying agents, inadmissible side items, or remaining reactants. While it can also be used to separate out strong products, vacuum filtration is more commonly used for this purpose.
Diatomaceous earth filtration is a special filtration process that removes particles from liquids as it passes through a layer of fossilized remains of microscopic water organism called diatoms. These diatoms are mined from diatomite deposits which are located along the Earth's surface as they have accumulated in sediment of open and moving bodies of water. Obtained diatomaceous earth is then purified using acid leaching or liquid-liquid extraction in order for it to be used in any form of application. The process of D.E. filtration is composed of three main stages: pre-coating, body feed, and cleaning.











