Related Research Articles

The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing lifelong healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers and outpatient clinics located throughout the country. Non-healthcare benefits include disability compensation, vocational rehabilitation, education assistance, home loans, and life insurance. The VA also provides burial and memorial benefits to eligible veterans and family members at 135 national cemeteries.

A veteran is a person who has significant experience and expertise in an occupation or field.

A military funeral is a memorial or burial rite given by a country's military for a soldier, sailor, marine or airman who died in battle, a veteran, or other prominent military figures or heads of state. A military funeral may feature guards of honor, the firing of volley shots as a salute, drumming and other military elements, with a flag draping over the coffin.

An old soldiers' home is a military veterans' retirement home, nursing home, or hospital, or sometimes an institution for the care of the widows and orphans of a nation's soldiers, sailors, and marines, etc.
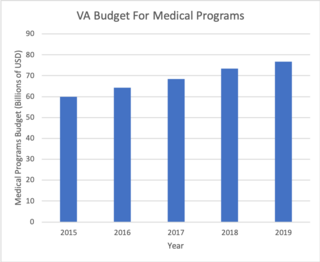
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationalized healthcare service in the United States, providing healthcare and healthcare-adjacent services to veterans through the administration and operation of 146 VA Medical Centers (VAMC) with integrated outpatient clinics, 772 Community Based Outpatient Clinics (CBOC), and 134 VA Community Living Centers Programs. It is the largest division in the department, and second largest in the entire federal government, employing over 350,000 employees. All VA hospitals, clinics and medical centers are owned by and operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs, and all of the staff employed in VA hospitals are federal employees. Because of this, veterans that qualify for VHA healthcare do not pay premiums or deductibles for their healthcare but may have to make copayments depending on the medical procedure. VHA is not a part of the US Department of Defense Military Health System.

Veterans for Peace is an organization founded in 1985. Initially made up of US military veterans of World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War - later including veterans of the Gulf War, the War in Afghanistan and the Iraq War - as well as peacetime veterans and non-veterans, it has since spread overseas and has an active offshoot in the United Kingdom. The group works to promote alternatives to war.
Military deployment is the movement of armed forces and their logistical support infrastructure around the world.

The Disabled American Veterans (DAV) is an organization created in 1920 by World War I veterans for disabled military veterans of the United States Armed Forces that helps them and their families through various means. It was issued a federal charter by Congress in 1932. It currently has over 1 million members. As a 501(c)(4) social welfare organization, it is outside the purview of – and therefore not rated by – Charity Navigator. DAV's Employer Identification Number (EIN) is 31–0263158.

Iraq and Afghanistan Veterans of America (IAVA), is a nonprofit 501(c)(3) veterans organization founded by Paul Rieckhoff, an American writer, social entrepreneur, advocate, activist and veteran of the United States Army and the Iraq War. He served as an Army First Lieutenant and infantry rifle platoon leader in Iraq from 2003 through 2004. Rieckhoff was released from the Army National Guard in 2007.

The Madigan Army Medical Center, located on Joint Base Lewis-McChord just outside Lakewood, Washington, is a key component of the Madigan Healthcare System and one of the largest military hospitals on the West Coast of the United States.
Operation Iron Hammer, also called Operation Matraqa Hadidia, was a military undertaking by the United States Armed Forces, and the New Iraqi Army, which was conducted east of Hīt, Iraq, from 30 November, to 3 January 2006, during the Iraq War, against the Iraqi insurgency. It was reported that both the New Iraqi Army, and the United States Armed Forces, sustained no losses during the operation. No civilian casualties were reported either. The operation is believed to have benefited villages on the eastern side of the Euphrates River with an increase in security and stability.

Wounded Warrior Project (WWP) is an American charity and veterans service organization that operates as a nonprofit 501(c)(3). WWP offers a variety of programs, services and events for wounded veterans who incurred a physical or mental injury, illnesses, or co-incident to their military service on or after September 11, 2001. Military family members and caregivers are also eligible for WWP programs.

The Illinois Department of Veterans' Affairs (IDVA) is the department of the Illinois state government that assists veterans and their families in navigating the system of federal state and local resources and benefits, provides long-term health care for eligible veterans, and helps veterans address education, mental health, housing, employment, and other challenges.
American Armed Forces Mutual Aid Association (AAFMAA) is a Virginia-based not-for-profit, tax-exempt, member-owned association that provides diversified financial services, including life insurance, investing and trust services, mortgage services, and survivor services to the U.S. Armed Forces communities. At the end of 2019, membership exceeded 85,000

The United States has compensated military veterans for service-related injuries since the Revolutionary War, with the current indemnity model established near the end of World War I. The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) began to provide disability benefits for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in the 1980s after the diagnosis became part of official psychiatric nosology.

A military funeral in the United States is a memorial or burial rite conducted by the United States Armed Forces for a Soldier, Marine, Sailor, Airman, Guardian or Coast Guardsman who died in battle, a veteran, or other prominent military figures or a president. A military funeral may feature guards of honor, the firing of volley shots as a salute, drumming and other military elements, with a flag draping over the coffin.
Daniel Somers was an American soldier who committed suicide in 2013. He had been suffering from various health problems, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and left a suicide note that was later published on Gawker, after which it went viral.

United States military veteran suicide is an ongoing phenomenon regarding the high rate of suicide among U.S. military veterans in comparison to the general civilian public. A focus on preventing veteran suicide began in 1958 with the opening of the first suicide prevention center in the United States. During the mid-1990s, a paradigm shift in addressing veteran suicide occurred with the development of a national strategy which included several Congressional Resolutions. More advancements were made in 2007, when the Joshua Omvig Veterans Suicide Prevention Act created a comprehensive program including outreach at each Veterans Affairs Office (VA) and the implementation of a 24-hour crisis hotline. PTSD, depression, and combat-related guilt in veterans are often related to suicide as it can be difficult for veterans to transition to civilian life.
Operational stress injury or OSI is a non-clinical, non-medical term referring to a persistent psychological difficulty caused by traumatic experiences or prolonged high stress or fatigue during service as a military member or first responder. The term does not replace any individual diagnoses or disorders, but rather describes a category of mental health concerns linked to the particular challenges that these military members or first responders encounter in their service. There is not yet a single fixed definition. The term was first conceptualized within the Canadian Armed Forces to help foster understanding of the broader mental health challenges faced by military members who have been impacted by traumatic experiences and who face difficulty as a result. OSI encompasses a number of the diagnoses found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) classification system, with the common thread being a linkage to the operational experiences of the afflicted. The term has gained traction outside of the military community as an appropriate way to describe similar challenges suffered by those whose work regularly exposes them to trauma, particularly front line emergency first responders such as but not limited to police, firefighters, paramedics, correctional officers, and emergency dispatchers. The term, at present mostly used within Canada, is increasingly significant in the development of legislation, policy, treatments and benefits in the military and first responder communities.
The Minnesota Department of Veterans Affairs (MDVA) is a state agency that provides services to current and former members of the United States military. The department provides care and housing through five veterans homes located in Fergus Falls, Hastings, Luverne, Minneapolis and Silver Bay. The department also assists veterans in obtaining healthcare, education, special veterans benefits and burials. The agency works with the United States Federal Veterans Administration Hospitals and Clinics including the Minneapolis VA Health Care System as well as coordination with the Minnesota National Guard and the American Legion.
References
- 1 2 "Iraq War Veterans Organization". December 30, 2005. Archived from the original on December 30, 2005.
- ↑ IWVO mailing list "Message from the commander" Archived December 30, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 Challenge Aspen: CAMO
- 1 2 Kors, Joshua (April 9, 2007). "How Specialist Town Lost His Benefits". The Nation . Retrieved November 5, 2018.