The Hepialoidea are the superfamily of "ghost moths" and "swift moths".
Jibeinia is a genus of enantiornithean bird. Only one species has been named, Jibeinia luanhera. It is known from one holotype fossil found in the Hebei province, People's Republic of China. This fossil is now lost. The holotype was, however, described and figured in detail by Hou (1997).
Corixa is a genus of aquatic bugs in the family Corixidae. The fossil species C. elegans is from the Rott Formation in Nordrhein-Westfalen.
Alloiomma is an extinct genus of ants that once belonged to the subfamily Dolichoderinae. A. changweiensis was the first extinct species to be discovered by Zhang in 1989, and another fossil species was discovered in 1994, known as A.differentialis. The ants were endemic to China.
Elaphrodites is an extinct genus of ants of the subfamily Dolichoderinae. Two fossils were discovered and described by Zhang in 1989.
Eldermyrmex is an extinct genus of ant in the Formicidae subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus contains a single described species Eldermyrmex oblongiceps. Eldermyrmex is known to be from the Baltic Amber.
Eurymyrmex is an extinct genus of ant in the Formicidae subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus contains a single described species Eurymyrmex geologicus. It was described in 1994, where the first fossils of the ant were found in China.
Myopopone sinensis is an extinct species of ant in the genus Myopopone. Fossils were discovered in 1989 in China, and was later described by Zhang in that year.
Dolichoderus evolans is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Dolichoderus. Described by Zhang in 1989, the fossilised species was discovered in China, where a possible queen has been described.
Dolichoderus jiaoyanshanensis is an extinct species of ant in the genus Dolichoderus. Fossils containing the species were found in China, and it was described by Hong in 1985. The ant is from Shanwang and is presumed to be a Miocene insect.
Dolichoderus lacinius is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Dolichoderus. Described by Zhang in 1989, fossils of a queen specimen were found in China.
Dolichoderus luridivenosus is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Dolichoderus. Described by Zhang, Sun and Zhang in 1994, the species was discovered after a fossil of a queen was found in China.
Dolichoderus transversipetiolaris is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Dolichoderus. Described by Zhang, Sun and Zhang in 1994, the species was discovered after a fossil of a queen was found in China.
Liometopum eremicum is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Liometopum. Described by Zhang in 1989, the fossils were found in China.
Liometopum lubricum is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Liometopum. Described by Zhang, Sun and Zhang 1994, the fossils were found in China.
Liometopum potamophilum is an extinct species of Miocene ant in the genus Liometopum. Described by Zhang in 1989, the fossils were found in China.
Tapinoma baculum is an extinct species of ant in the genus Tapinoma. Described by Zhang in 1989, fossils of the species were found in China.
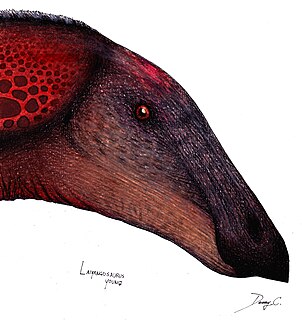
Laiyangosaurus is a genus of saurolophine hadrosaurid from the Late Cretaceous of China. It is known from one species, L.youngi, found in the Laiyang Basin within the province of Shandong.
Chiappeavis is a genus of enantiornithean bird from Early Cretaceous of northeastern China. The only species is Chiappeavis magnapremaxillo. Chiappeavis is classified within the family Pengornithidae. It is known from a single, almost complete skeleton including feather impressions discovered in the Jiufotang Formation of the Jehol Group. Long feathers formed a fan-shaped tail that was probably employed in flight.


