Related Research Articles

The 31st Infantry Regiment of the United States Army was formed on 13 August 1916, and was part of USAFFE's Philippine Division during World War II. The unit is rare in that it was formed and has spent most of its life on non-American soil.

Cheorwon County, also spelled Chorwon, is a county in Gangwon Province, South Korea. It is located right next to the North Korean border.

Pork Chop Hill is a 1959 American Korean War film starring Gregory Peck, Woody Strode, Rip Torn, and George Peppard. The film, which was the final war film directed by Lewis Milestone, is based upon the 1956 book by U.S. military historian Brigadier General S. L. A. Marshall. It depicts the first fierce Battle of Pork Chop Hill between the U.S. Army's 7th Infantry Division and Chinese and North Korean forces in April 1953.

The Battle of Pork Chop Hill, known as Battle of Seokhyeon-dong Northern Hill in China, is a pair of related Korean War infantry battles that took place on April 16 and July 11, 1953 while the United Nations Command (UN) and the Chinese and North Koreans were negotiating the Korean Armistice Agreement.

Richard Thomas Shea, Jr. was a soldier in the United States Army in the Korean War. He was listed as missing in action on July 8, 1953, during the Second Battle of Pork Chop Hill, and was later declared killed in action. Lt. Shea received the Medal of Honor posthumously. In 1987, Shea was inducted into the Virginia Sports Hall of Fame.

The Battle of Hill Eerie refers to several Korean War engagements between the United Nations Command (UN) forces and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) in 1952 at Hill Eerie, a military outpost about 10 miles (16 km) west of Ch'orwon. It was taken several times by both sides; each sabotaging the others' position.

Shangganling is a 1956 Chinese war film, also translated as Battle of Shangganling and Battle on Shangganling Mountain. It depicts the Battle of Triangle Hill during the Korean War, an especially bloody battle that resulted in eventual Chinese victory.

Charles Heyward Barker was a United States Army soldier in the Korean War who received the U.S. military's highest decoration, the Medal of Honor.

The 82nd Group Army, Unit 31677, formerly the 38th Group Army, is a military formation of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Ground Forces (PLAGF). The 82nd Group Army is one of thirteen total group armies of the PLAGF, the largest echelon of ground forces in the People's Republic of China, and one of three assigned to the nation's Central Theater Command.

The Battle of Old Baldy was a series of five engagements for Hill 266 in west-central Korea. They occurred over a period of 10 months in 1952–1953, though there was also vicious fighting both before and after these engagements.

The Battle of White Horse Hill took place during the Korean War. White Horse Hill in the Iron Triangle, formed by Pyonggang at its peak and Gimhwa-eup and Cheorwon-eup at its base, a strategic transportation route in the central region of the Korean peninsula.

The 9th Infantry Division, also known as White Horse Division after the victory of Battle of White Horse Hill, is an infantry division of the Republic of Korea Army. The unit is composed of the 28th, 29th, 30th infantry brigades, and an artillery brigade.

The Kagnew Battalions were a number of military units from the Imperial Ethiopian Army which fought as part of United Nations Command in the Korean War (1950–53). The battalions rotated yearly, with the First Kagnew Battalion arriving at the front in 1951. The Third Kagnew Battalion which arrived in 1953, stayed through the signing of the armistice into 1954. Over the next two years more Ethiopians guarded the stalemate in Korea as part of the Fourth Kagnew Battalion and the Fifth Kagnew Company. Even though some publications indicate Ethiopians remained in Korea until 1965, in fact they remained a part of the United Nations Command until 1975. Members of Kagnew Battalion were, with few exceptions, drawn from the Ethiopian Imperial Bodyguard Division.
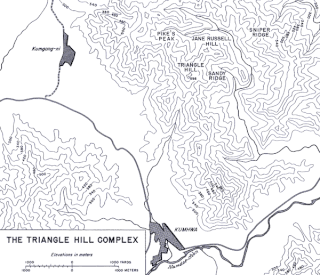
The Battle of Triangle Hill, also known as Operation Showdown or the Shangganling Campaign, was a protracted military engagement during the Korean War. The main combatants were two United Nations (UN) infantry divisions, with additional support from the United States Air Force, against elements of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 15th and 12th Corps. The battle was part of UN attempts to gain control of the "Iron Triangle" and took place from 14 October to 25 November 1952.

The Battle of the Samichon River was fought during the final days of the Korean War between United Nations (UN) forces—primarily Australian and American—and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA). The fighting took place on a key position on the Jamestown Line known as "the Hook", and resulted in the defending UN troops, including the 2nd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment from the 28th British Commonwealth Brigade and the US 7th Marine Regiment, repulsing numerous assaults by the PVA 137th Division during two concerted night attacks, inflicting numerous casualties on the PVA with heavy artillery and small-arms fire. The action was part of a larger, division-sized PVA attack against the US 1st Marine Division, with diversionary assaults mounted against the Australians. With the peace talks in Panmunjom reaching a conclusion, the Chinese had been eager to gain a last-minute victory over the UN forces, and the battle was the last of the war before the official signing of the Korean armistice.

Many films, books, and other media have depicted the 1950—53 Korean War. The TV series M*A*S*H is one well known example. The 1959 novel The Manchurian Candidate has twice been made into films. The 1982 film Inchon about the historic battle that occurred there in September 1950 was a financial and critical failure. By 2000 Hollywood alone had produced 91 feature films on the Korean War. Many films have also been produced in South Korea and other countries as well.

Colonel Joseph Gordon Clemons, Jr. was a decorated soldier in the United States Army in the Korean War and in the Vietnam War. His actions in the 1953 Battle of Pork Chop Hill were the subject of a 1959 movie, Pork Chop Hill.
The Battle of Chatkol was the name given to the series of skirmishes in early 1953 between United Nations Command (UN) and Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) forces near the village of Chatkol at the centre of the Iron Triangle during the Korean War. The position was held by the Belgian UN contingent for 55 consecutive nights, during which time they came under heavy attack.

The Kingdom of Thailand was one of the 21 countries who responded to the United Nations request to send troops to aid South Korea during the Korean War 1950–1953.
The Battle of Arrowhead Hill or the Battle of Arrowhead Ridge, was a battle in which UN Forces fought against the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (CPVA) during the Korean War.
References
- O’Neill, Robert (1985). Australia in the Korean War 1950–53. Volume II: Combat Operations. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. ISBN 0-642-04330-2.
- Tucker, Spencer C.; Kim, Jinwung; Nichols, Michael R.; Pierpaoli, Paul G.; Zehr, Norman R. (2000). Encyclopedia of the Korean War: A Political, Social, and Military History. Volume II. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-029-1.