
The Netherlands Antilles was a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The country consisted of several island territories located in the Caribbean Sea. The islands were also informally known as the Dutch Antilles. The country came into being in 1954 as the autonomous successor of the Dutch colony of Curaçao and Dependencies and was dissolved in 2010. The Dutch colony of Surinam, although it was relatively close by on the continent of South America, did not become part of the Netherlands Antilles but became a separate autonomous country in 1954. All the island territories that belonged to the Netherlands Antilles remain part of the kingdom today, although the legal status of each differs. As a group they are still commonly called the Dutch Caribbean, regardless of their legal status. People from this former territory continue to be called Antilleans (Antillianen) in the Netherlands.

Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It has a territorial extension of 916,445 km2, and the population of Venezuela was estimated at 28 million in 2019. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas.

The foreign relations of Venezuela had since the early twentieth century been particularly strong with the United States. However, with the election of Hugo Chávez as President of Venezuela in 1998, the foreign policy differed substantially from that of previous Venezuelan governments.

The Lesser Antilles are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies.

Carabobo State is one of the 23 states of Venezuela, located in the north of the country, about two hours by car from Caracas. The capital city of this state is Valencia, which is also the country's main industrial center. The state's area is 4,369 km2 (1,687 sq mi) and as of the 2011 census, had a population of 2,245,744.
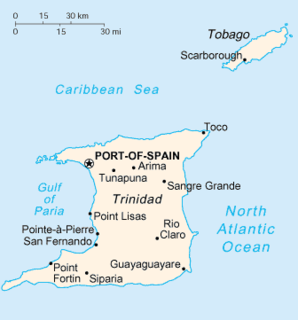
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 5,131 km2 (1,981 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.

Isla de Aves, or Aves Island, is a Federal Dependency of Venezuela. It has been the subject of numerous territorial disputes between the neighboring independent islands, such as Dominica, and European mother countries of surrounding dependent islands, such as the Netherlands. It is a part of the Aves Ridge and lies to the west of the Windward Islands chain at 15°40′18″N63°36′59″W. It is 375 metres (1,230 ft) in length and never more than 50 metres (160 ft) in width, and rises 4 metres (13 ft) above the sea on a calm day. Under a particular interpretation of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea it could be classified as a rock, which would only give Venezuela a twelve nautical mile economic zone. However, Venezuela claims it is an island, which grants it a 200-mile (320 km) exclusive economic zone. Mostly sand, a small portion has some scrubby vegetation. It is sometimes completely submerged during hurricanes. It is 185 kilometres (115 mi) southwest of the closest land, Montserrat, 225 kilometres (140 mi) west of Dominica and 547 kilometres (340 mi) north of the Venezuelan mainland.
Petróleos de Venezuela, S.A. is the Venezuelan state-owned oil and natural gas company. It has activities in exploration, production, refining and exporting oil as well as exploration and production of natural gas. Since its founding on 1 January 1976 with the nationalization of the Venezuelan oil industry, PDVSA has dominated the oil industry of Venezuela, the world's fifth largest oil exporter.
Telesur is a Latin American terrestrial and satellite television network headquartered in Caracas, Venezuela and sponsored primarily by the government of Venezuela, with additional funding from the governments of Cuba and Nicaragua. It was launched in 2005, under the government of Hugo Chávez, with the aim of being "a Latin socialist answer to CNN".
The Federal Dependencies of Venezuela encompass most of Venezuela's offshore islands in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Venezuela, excluding those islands that form the State of Nueva Esparta and some Caribbean coastal islands that are integrated with nearby states. These islands, with a total area of 342 square kilometres, are sparsely populated – according to the preliminary results of the 2011 Census only 2,155 people live there permanently, with another hundred from Margarita Island who live there seasonally to engage in fishing. Local government is officially under the authority of Central government in Caracas, although de facto power is often held in the heads of the sparse and somewhat isolated communities that decorate the territories.

Chacachacare is an island in the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, located at 10° 41' north latitude and 61° 45' west longitude. The island is 360 hectares in area.

The Bolivarian Navy of Venezuela, commonly known as the Venezuelan Navy, is the naval branch of the National Bolivarian Armed Forces of Venezuela.

The Guácharo Cave National Park is located 12 km from the town of Caripe, Monagas, Venezuela. It has as its centerpiece a large limestone cave.

Los Roques archipelago is a federal dependency of Venezuela consisting of approximately 350 islands, cays, and islets in a total area of 40.61 square kilometers. The archipelago is located 128 kilometers (80 mi) directly north of the port of La Guaira, in the Caribbean Sea.

The Los Monjes islands is a federal dependency of Venezuela are located to the northwest 80 kilometres of the Gulf of Venezuela, 34.8 kilometres off the coast of Guajira Peninsula at the border between Colombia and the Venezuelan state of Zulia.

Canada–Venezuela relations have been on good terms since the establishment of diplomatic relationship between the two countries in the 1950s. Those relations however began to sour under Prime Ministers Stephen Harper and Justin Trudeau, especially in relation to the policies of Presidents Hugo Chávez and Nicolás Maduro. Canada has imposed targeted sanctions against 70 government officials in the Venezuelan Government.
Caquetio is an extinct Arawakan language of Venezuela. The Caquetio people lived along the shores of Lake Maracaibo and on the Dutch 'ABC' islands of Aruba, Curaçao and Bonaire.
Alyz Sabimar Henrich Ocando is a Venezuelan model, environmentalist, humanitarian advocate and beauty queen. She represented Falcón state at Miss Venezuela 2012 pageant where she was crowned Miss Venezuela Earth. On December 7, Henrich was crowned Miss Earth 2013 in the Philippines. She is the second Miss Earth winner from Venezuela next to Alexandra Braun and the first Miss Earth winner from Osmel Sousa owned Miss Venezuela. Alyz is the chairwoman of the Miss Earth Venezuela Organization.















