Related Research Articles
Phil Ineson is a chair in Global Change Ecology at the University of York. Ineson is particularly noted for his work with stable isotopes.
Ecological psychology ia the scientific study of the relationship between perception and action, grounded in a direct realist approach. This school of thought is heavily influenced by the writings of Roger Barker and James J. Gibson and stands in contrast to the mainstream explanations of perception offered by cognitive psychology. Ecological psychology is primarily concerned with the interconnectedness of perception, action and dynamical systems. A key principle in this field is the rejection of the traditional separation between perception and action, emphasizing instead that they are inseparable and interdependent.
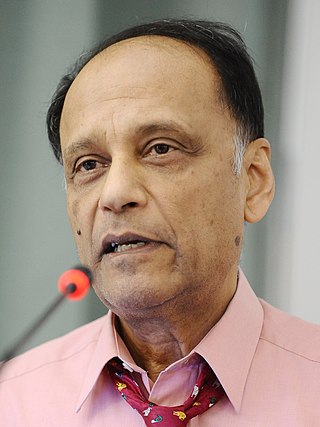
Sir Partha Sarathi Dasgupta is an Indian-British economist who is Frank Ramsey Professor Emeritus of Economics at the University of Cambridge, United Kingdom, and a fellow of St John's College, Cambridge.
The environmental humanities is an interdisciplinary area of research, drawing on the many environmental sub-disciplines that have emerged in the humanities over the past several decades, in particular environmental literature, environmental philosophy, environmental history, science and technology studies, environmental anthropology, and environmental communication. Environmental humanities employs humanistic questions about meaning, culture, values, ethics, and responsibilities to address pressing environmental problems. The environmental humanities aim to help bridge traditional divides between the sciences and the humanities, as well as between Western, Eastern, and Indigenous ways of relating to the natural world and the place of humans within it. The field also resists the traditional divide between "nature" and "culture," showing how many "environmental" issues have always been entangled in human questions of justice, labor, and politics. Environmental humanities is also a way of synthesizing methods from different fields to create new ways of thinking through environmental problems.
An isoscape is a geologic map of isotope distribution. It is a spatially explicit prediction of elemental isotope ratios (δ) that is produced by executing process-level models of elemental isotope fractionation or distribution in a geographic information system (GIS).
Simon Asher Levin is an American ecologist and the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professor in Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and the director of the Center for BioComplexity at Princeton University. He specializes in using mathematical modeling and empirical studies in the understanding of macroscopic patterns of ecosystems and biological diversities.
Howard Griffiths is a physiological ecologist. He is Professor of Plant Ecology in the Department of Plant Sciences at the University of Cambridge, and a Fellow of Clare College, Cambridge. He formerly worked for the University of Dundee in the Department of Biological Sciences. He applies molecular biology techniques and physiology to investigate the regulation of photosynthesis and plant water-use efficiency.
The Lancaster Environment Centre (LEC) in Lancaster, England, is an interdisciplinary centre for teaching, research and collaboration at Lancaster University, founded in 2007.
Richard J. Hobbs FAA, is an Emeritus Professor, ARC former Australian Laureate Fellow and ecologist at the University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia. He is a fellow of the Australian Academy of Science and a Highly-Cited author who has written extensively in the areas of vegetation dynamics and management, ecosystem fragmentation, ecosystem rehabilitation and restoration, landscape ecology, and conservation biology. His research focused on managing ecosystems in a rapidly changing world and the implications of environmental and biological change for conservation and restoration.
Joy K. Ward is an American evolutionary biologist studying the impact of the environment on plants and ecosystems. She began a new role as the dean of the College of Arts & Sciences at Case Western Reserve University on July 1, 2020 - leaving behind her professorship at the University of Kansas. Her research on plant life has gained her notoriety in many scientific research fields. Aside from her work in the lab, she is also a strong advocate for advancing underrepresented communities' scientific learning and careers. As part of her deanship at the University of Kansas, Ward was an important factor in increasing the number of underrepresented individuals who held faculty positions in STEM subjects. Notably, as a result of her research efforts, she was awarded the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers by U.S. President Barack Obama.
Thure E. Cerling is a Distinguished Professor of Geology and Geophysics and a Distinguished Professor of Biology at the University of Utah. Cerling is a leading expert in the evolution of modern landscapes including modern mammals and their associated grassland ecologies and stable isotope analyses of the atmosphere. Cerling lives in Salt Lake City, Utah.

Distinguished Professor David Lindenmayer,, is an Australian scientist and academic. His research focuses on the adoption of nature conservation practices in agricultural production areas, developing ways to improve integration of native forest harvesting and biodiversity conservation, new approaches to enhance biodiversity conservation in plantations, and improved fire management practices in Australia. He specialises in large-scale, long-term research monitoring programs in south-eastern Australia, primarily in forests, reserves, national parks, plantations, and on farm land.

The term stable isotope has a meaning similar to stable nuclide, but is preferably used when speaking of nuclides of a specific element. Hence, the plural form stable isotopes usually refers to isotopes of the same element. The relative abundance of such stable isotopes can be measured experimentally, yielding an isotope ratio that can be used as a research tool. Theoretically, such stable isotopes could include the radiogenic daughter products of radioactive decay, used in radiometric dating. However, the expression stable-isotope ratio is preferably used to refer to isotopes whose relative abundances are affected by isotope fractionation in nature. This field is termed stable isotope geochemistry.

Richard B. Norgaard is a professor emeritus of ecological economics in the Energy and Resources Group at the University of California, Berkeley, the first chair and a continuing member of the independent science board of CALFED, and a founding member and former president of the International Society for Ecological Economics. He received the Kenneth E. Boulding Memorial Award in 2006 for recognition of advancements in research combining social theory and the natural sciences. He is considered one of the founders of and a continuing leader in the field of ecological economics.

Kathleen Kay Treseder is an American ecologist who specializes in the interplay between global climate change and fungal ecology. She also serves as a member of the Irvine City Council after being elected to the position in 2022. She is currently a professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of California, Irvine. She is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the American Academy of Microbiology, and the Ecological Society of America.
Diane E. Pataki is a Foundation Professor and Director of the School of Sustainability at Arizona State University.
Nancy B. Grimm is an American ecosystem ecologist and professor at Arizona State University. Grimm's substantial contributions to the understanding of urban and arid ecosystem biogeochemistry are recognized in her numerous awards. Grimm is an elected Fellow of the American Geophysical Union, Ecological Society of America, and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.

Philosophy of ecology is a concept under the philosophy of science, which is a subfield of philosophy. Its main concerns centre on the practice and application of ecology, its moral issues, and the intersectionality between the position of humans and other entities. This topic also overlaps with metaphysics, ontology, and epistemology, for example, as it attempts to answer metaphysical, epistemic and moral issues surrounding environmental ethics and public policy.
Celina A. Suarez is an American geologist. She is known for her research on using trace element and stable isotope geochemistry of fossil vertebrates and invertebrates to understand paleoecology, paleoclimatology, and taphonomy of ancient terrestrial ecosystems. She is an associate profession in the Department of Geosciences at the University of Arkansas. The dinosaur Geminiraptor suarezarum is named after Suarez and her twin sister, Marnia Suarez, co-discovers of the site on which it was found.
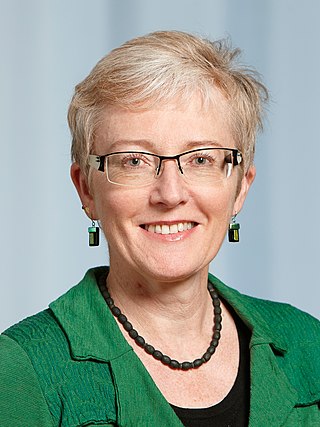
Nina Buchmann is a German ecologist known for her research on the physiology of plants and the impact of plants on biogeochemical cycling. She is a member of the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina and an elected fellow of the American Geophysical Union.
References
- ↑ Groote, Michael De (28 November 2010). "20 researchers at Utah universities are ranked among most cited". Deseret News. Archived from the original on December 2, 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- ↑ AGU (2016), Honoring Earth and space scientists, Eos, 97, https://doi.org/10.1029/2016EO056319. Published on 25 July 2016.