James Russell | |
|---|---|
 Russell tagging a grey-faced petrel in 2016 | |
| Born | James Charles Russell |
| Nationality | New Zealand |
James Charles Russell is a New Zealand conservation biologist and professor at the University of Auckland.
James Russell | |
|---|---|
 Russell tagging a grey-faced petrel in 2016 | |
| Born | James Charles Russell |
| Nationality | New Zealand |
James Charles Russell is a New Zealand conservation biologist and professor at the University of Auckland.
Russell gained a PhD on the genetics and invasion ecology of rats from the University of Auckland. [1]
Russell is most widely known for his research on Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) in New Zealand. One of the rats he studied swam over 400 metres between two Hauraki Gulf islands, breaking the swimming distance record for rats. The intentions of the rat are believed to have been amorous. The rat, known as Razza, was featured in Nature in 2005, [2] and later in a children's book by Witi Ihimaera in 2006. [3]
He writes a blog for National Geographic on island conservation as of 2018. [4]
In 2015, he and a team wrote a paper estimating how much government funding would be required to develop new eradication technologies to eliminate predators in New Zealand, resulting in government funding for a research project. [5]
In 2023, the BBC described him as a champion of New Zealand's initiative to eradicate predators in New Zealand to save native birds by 2050, called Predator Free 2050 Ltd, a public body. BBC reported that he "did much" to give scientific backing to the project. [6] Also aiming to eradicate all invasive mammals, the plan was unveiled by Prime Minister John Key in 2016. [7]
In 2022, he co-authored a paper that concluded that New Zealand was the top country in the world for eradicating invasive species, responsible for around a quarter of the world's island pest eradications, followed by Australia. [8]
In 2012, Russell was awarded the New Zealand Prime Minister's MacDiarmid Emerging Scientist Prize, worth NZ$200,000, for his work using DNA fingerprinting of rats and statistical modelling to address conservation problems. [9]
In 2014, Russell was awarded a Rutherford Discovery Fellowship, worth NZ$800,000, for research on conservation complexity: scaling vertebrate pest control. [10] [11]

The black rat, also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus Rattus, in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide.

Witi Tame Ihimaera-Smiler is a New Zealand author. Raised in the small town of Waituhi, he decided to become a writer as a teenager after being convinced that Māori people were ignored or mischaracterised in literature. He was the first Māori writer to publish a collection of short stories, with Pounamu, Pounamu (1972), and the first to publish a novel, with Tangi (1973). After his early works, he took a ten-year break from writing, during which he focused on editing an anthology of Māori writing in English.

Auckland Island is the main island of the eponymous uninhabited archipelago in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the New Zealand subantarctic area. It is inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage list together with the other New Zealand Subantarctic Islands in the region.

The Polynesian rat, Pacific rat or little rat, or kiore, is the third most widespread species of rat in the world behind the brown rat and black rat. Contrary to its vernacular name, the Polynesian rat originated in Southeast Asia, and like its relatives has become widespread, migrating to most of Polynesia, including New Zealand, Easter Island, and Hawaii. It shares high adaptability with other rat species extending to many environments, from grasslands to forests. It is also closely associated with humans, who provide easy access to food. It has become a major pest in most areas of its distribution.

A number of introduced species, some of which have become invasive species, have been added to New Zealand's native flora and fauna. Both deliberate and accidental introductions have been made from the time of the first human settlement, with several waves of Polynesian people at some time before the year 1300, followed by Europeans after 1769.

Little Barrier Island, or Hauturu in Māori, lies off the northeastern coast of New Zealand's North Island. Located 80 kilometres (50 mi) to the north of Auckland, the island is separated from the mainland to the west by the Jellicoe Channel, and from the larger Great Barrier Island to the east by the Cradock Channel. The two aptly named islands shelter the Hauraki Gulf from many of the storms of the Pacific Ocean.

The ecological restoration of islands, or island restoration, is the application of the principles of ecological restoration to islands and island groups. Islands, due to their isolation, are home to many of the world's endemic species, as well as important breeding grounds for seabirds and some marine mammals. Their ecosystems are also very vulnerable to human disturbance and particularly to introduced species, due to their small size. Island groups, such as New Zealand and Hawaii, have undergone substantial extinctions and losses of habitat. Since the 1950s several organisations and government agencies around the world have worked to restore islands to their original states; New Zealand has used them to hold natural populations of species that would otherwise be unable to survive in the wild. The principal components of island restoration are the removal of introduced species and the reintroduction of native species.
An ecological island is a term used in New Zealand, and increasingly in Australia, to refer to an area of land isolated by natural or artificial means from the surrounding land, where a natural micro-habitat exists amidst a larger differing ecosystem. In New Zealand the term is used to refer to one of several types of nationally protected areas.

The Campbell snipe, also known as the Campbell Island snipe, is a rare subspecies of the Subantarctic snipe, endemic to Campbell Island, a subantarctic island south of New Zealand in the Southern Ocean. It was not formally described until January 2010. The subspecific name alludes to the name of the sealing brig Perseverance, captained by Frederick Hasselborough, that discovered Campbell Island in 1810, and which probably inadvertently introduced rats to the island when it was wrecked there in 1828.
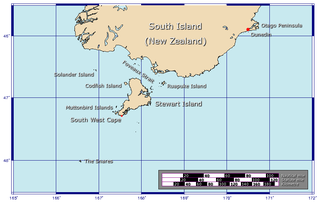
Taukihepa / Big South Cape Island is an offshore island of New Zealand to the west of the southern tip of Stewart Island / Rakiura. The island is the largest of the Tītī / Muttonbird Islands, and as such has no permanent inhabitants but is visited by muttonbirders in search of sooty shearwaters, known in New Zealand as "muttonbirds".

The stoat was introduced into New Zealand to control introduced rabbits and hares, but is now a major threat to the native bird population. The natural range of the stoat is limited to parts of the Northern Hemisphere. Immediately before human settlement, New Zealand did not have any land-based mammals apart from bats, but Polynesian and European settlers introduced a wide variety of animals. Rarely, in Southland, the fur of stoats has been reported to turn white, being the fur known as ermine, which adorns royal robes.

The Noises are a collection of islands lying northeast of Rakino Island in Auckland's Hauraki Gulf, off the coast of the North Island of New Zealand. The largest and most forested islands are Ōtata and Motuhoropapa; Orarapa and Maria/Ruapuke are also significant. After a rat eradication campaign in the 1960s, Maria was the first New Zealand island to become predator-free. The lack of invasive predators, intact native forest, and large numbers of breeding seabirds give the Noises significant conservation value. There has however been a marked decline in marine biodiversity surrounding the islands from over-fishing.

Seabirds include some of the most threatened taxa anywhere in the world. For example, of extant albatross species, 82% are listed as threatened, endangered, or critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. The two leading threats to seabirds are accidental bycatch by commercial fishing operations and introduced mammals on their breeding islands. Mammals are typically brought to remote islands by humans either accidentally as stowaways on ships, or deliberately for hunting, ranching, or biological control of previously introduced species. Introduced mammals have a multitude of negative effects on seabirds including direct and indirect effects. Direct effects include predation and disruption of breeding activities, and indirect effects include habitat transformation due to overgrazing and major shifts in nutrient cycling due to a halting of nutrient subsidies from seabird excrement. There are other invasive species on islands that wreak havoc on native bird populations, but mammals are by far the most commonly introduced species to islands and the most detrimental to breeding seabirds. Despite efforts to remove introduced mammals from these remote islands, invasive mammals are still present on roughly 80% of islands worldwide.

Island Conservation is a non-profit organization with the mission to "restore islands for nature and people worldwide" and has therefore focused its efforts on islands with species categorized as Critically Endangered and Endangered on the IUCN's Red List. Working in partnership with local communities, government management agencies, and conservation organizations, Island Conservation develops plans and implements the removal of invasive alien species, and conducts field research to document the benefits of the work and to inform future projects.
Predator Free 2050 is a plan put forth by the New Zealand government with the goal of eradicating all of its mammalian introduced predators by 2050.

Goodnature is a New Zealand company founded in 2005 by two men, Robbie van Dam and Craig Bond. Goodnature specializes in the production of traps designed for the control of animal pests..
Corinne Hannah Watts is a New Zealand entomologist and ecologist. Specimens collected by Watts are held at Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa.
Rachel M. Fewster is a British and New Zealand environmental statistician and statistical ecologist known for her work on wildlife population size, population genetics, and Benford's law, and for the development of the CatchIT citizen science project for monitoring invasive species. She is a professor of statistics in New Zealand at the University of Auckland.

Island reserves or island sanctuaries are offshore islands of New Zealand set aside by the New Zealand Government as reserves for endemic and native species.