
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization headquartered in New York City that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policymakers, companies, and individual human rights abusers to denounce abuse and respect human rights, and often works on behalf of refugees, children, migrants, and political prisoners.

Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital punishment, but the term may also be applied in a broader sense to include euthanasia and other forms of suicide. The drugs cause the person to become unconscious, stops their breathing, and causes a heart arrhythmia, in that order.
Prison sexuality consists of sexual relationships between prisoners or between a prisoner and a prison employee or other persons to whom prisoners have access. Since prisons are usually separated by sex, most sexual activity is with a same-sex partner. Exceptions to this include sex with spouses/partners during conjugal visits and sex with a prison employee of the opposite sex.
Some victims of rape or other sexual violence incidents are male. It is estimated that approximately one in six men experienced sexual abuse during childhood. Historically, rape was thought to be, and defined as, a crime committed solely against females. This belief is still held in some parts of the world, but rape of males is now commonly criminalized and has been subject to more discussion than in the past.
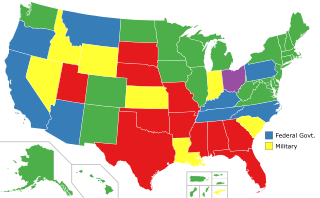
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty throughout the country at the federal level, in 27 states, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 19 states currently have the ability to execute death sentences, with the other 8, as well as the federal government and military, being subject to different types of moratoriums.
Prison rape commonly refers to the rape of inmates in prison by other inmates or prison staff. In 2001, Human Rights Watch estimated that at least 4.3 million inmates had been raped while incarcerated in the United States. A United States Department of Justice report, Sexual Victimization in Prisons and Jails Reported by Inmates, states that "In 2011–12, an estimated 4.0% of state and federal prison inmates and 3.2% of jail inmates reported experiencing one or more incidents of sexual victimization by another inmate or facility staff in the past 12 months or since admission to the facility, if less than 12 months." However, advocates dispute the accuracy of the numbers, saying they seem to under-report the real numbers of sexual assaults in prison, especially among juveniles.

Prisoner abuse is the mistreatment of persons while they are under arrest or incarcerated. Prisoner abuse can include physical abuse, psychological abuse, sexual abuse, torture, or other acts such as refusal of essential medication, and it can be perpetuated by either fellow inmates or prison faculty.

Rehabilitation is the process of re-educating those who have committed a crime and preparing them to re-enter society. The goal is to address all of the underlying root causes of crime in order to decrease the rate of recidivism once inmates are released from prison. It generally involves psychological approaches which target the cognitive distortions associated with specific kinds of crime committed by individual offenders, but it may also entail more general education like reading skills and career training. The goal is to re-integrate offenders back into society.
A death in custody is a death of a person in the custody of the police, other authorities, or while in prison. In the 21st century, death in custody remains a controversial subject, with the authorities often being accused of abuse, neglect and cover-ups of the causes of these deaths.

Human rights in Georgia are guaranteed by the country's constitution. There is an independent human rights Public Defender of Georgia elected by the parliament to ensure such rights are enforced. However, it has been alleged by Amnesty International, Human Rights Watch, the United States Department of State and the Georgian opposition that these rights are often breached.
Rape can be categorized in different ways: for example, by reference to the situation in which it occurs, by the identity or characteristics of the victim, and by the identity or characteristics of the perpetrator. These categories are referred to as types of rape. The types described below are not mutually exclusive: a given rape can fit into multiple categories, by for example being both a prison rape and a gang rape, or both a custodial rape and the rape of a child.

A talibé is a boy, usually from Senegal, the Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Chad, Mali or Mauritania, who studies the Quran at a daara. This education is guided by a teacher known as a marabout. In most cases talibés leave their parents to stay in the daara.

The National Prison Rape Elimination Commission (NPREC) was a U.S. bipartisan panel established by the 2003 Prison Rape Elimination Act. The commission was charged with studying sexual assaults in U.S. jails and prisons and presenting a report based on its findings.
No Escape: Male Rape in U.S. Prisons is the title of an influential, book-length 2001 report by Human Rights Watch on prison rape in the United States. The report is credited with playing a major role in the 2003 passage of the Prison Rape Elimination Act.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people face difficulties in prison such as increased vulnerability to sexual assault, other kinds of violence, and trouble accessing necessary medical care. While much of the available data on LGBTQ inmates comes from the United States, Amnesty International maintains records of known incidents internationally in which LGBTQ prisoners and those perceived to be lesbian, gay, bisexual or transgender have suffered torture, ill-treatment and violence at the hands of fellow inmates as well as prison officials.
Prison rape or jail rape is sexual assault of people while they are incarcerated. The phrase is commonly used to describe rape of inmates by other inmates, or to describe rape of inmates by staff. It is a significant, if controversial, part of what is studied under the wider concept of prison sexuality.

There have been persistent concerns over human rights in El Salvador. Some of these date from the civil war of 1980–92. More recent concerns have been raised by Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch. They include women's rights, child labor, and unlawful killings and harassment of labor union members and other social activists.

The incarceration of women in the United States refers to the imprisonment of women in both prisons and jails in the United States. There are approximately 219,000 incarcerated women in the US according to a November 2018 report by the Prison Policy Initiative, and the rate of incarceration of women in the United States is at a historic and global high, with 133 women in correctional facilities per every 100,000 female citizens. The United States is home to just 4% of the world's female population, yet the US is responsible for 33% of the entire world's incarcerated female population. The steep rise in the population of incarcerated women in the US is linked to the complex history of the war on drugs and the US's prison–industrial complex, which lead to mass incarceration among many demographics, but had particularly dramatic impacts on women and especially women of color. However, women made up only 10.4% of the US prison and jail population, as of 2015.

The death of Clayton Derrell Lockett occurred on April 29, 2014, when he suffered a heart attack during an execution by lethal injection in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Lockett, aged 38, was convicted in 2000 of murder, rape, and kidnapping.

The execution of John Grant took place in the U.S. state of Oklahoma by means of lethal injection. Grant was sentenced to death for the 1998 murder of prison cafeteria worker Gay Carter.











