
The Iraqi Republican Guard was a branch of the Iraqi military from 1969 to 2003, which existed primarily during the presidency of Saddam Hussein. It later became known as the Republican Guard Corps, and then the Republican Guard Forces Command (RGFC) with its expansion into two corps. The Republican Guard was disbanded in 2003 after the invasion of Iraq by a U.S.-led international coalition.

Fedayeen Saddam was a paramilitary militia Fedayeen organization intensely loyal to the Ba'athist Iraqi government of Saddam Hussein. The name was chosen to mean "Saddam's Men of Sacrifice". At its height, the group had 30,000–40,000 members. The Fedayeen operated completely outside the law, above and outside political and legal structures.

The Battle of Baghdad, also known as the Fall of Baghdad, was a military engagement that took place in Baghdad in early April 2003, as part of the invasion of Iraq.

The occupation of Iraq (2003–2011) began on 20 March 2003, when the United States invaded with a military coalition to overthrow Iraqi president Saddam Hussein and his Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, and continued until 18 December 2011, when the final batch of American troops left the country. While the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia were the largest contributors to the coalition, 29 other countries, such as Japan, were involved in the Iraq War in a lesser capacity. Additionally, several private military contractors took part in enforcing the occupation.

The following is a timeline of major events during the Iraq War, following the 2003 invasion of Iraq.
Events in the year 2004 in Iraq.

Fallujah is a city in Al Anbar Governorate, Iraq. Situated on the Euphrates River, it is located roughly 69 kilometres (43 mi) to the west of the capital city of Baghdad.

The First Battle of Fallujah, code-named Operation Vigilant Resolve, was an operation against militants in Fallujah as well as an attempt to apprehend or kill the perpetrators of the killing of four U.S. contractors in March 2004.

An Iraqi insurgency began shortly after the 2003 American invasion deposed longtime leader Saddam Hussein. It is considered to have lasted until the end of the Iraq War and U.S. withdrawal in 2011. It was followed by a renewed insurgency.

After the 2003 invasion of Iraq was completed and the regime of Saddam Hussein was toppled in May 2003, an Iraqi insurgency began that would last until the United States left in 2011. The 2003–2006 phase of the Iraqi insurgency lasted until early 2006, when it escalated from an insurgency to a Sunni-Shia civil war, which became the most violent phase of the Iraq War.

The Second Battle of Fallujah, initially codenamed Operation Phantom Fury, Operation al-Fajr was an American-led offensive of the Iraq War that began on 7 November 2004 and lasted about six weeks.

The Iraqi Ground Forces, also referred to as the Iraqi Army, is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was formerly known as the Royal Iraqi Army up until the coup of July 1958. The current commander is Lieutenant General Qassim Muhammad Salih.
Muhammed Latif is an Iraqi major general, and former member of the Baath Party. The city of Fallujah was handed over to Muhammed Latif, replacing the earlier U.S. choice, Jasim Mohammed Saleh, when it was discovered that the latter had been involved in atrocities against Kurds during the Iran–Iraq War.
The United States bombardment of Fallujah began in April 2003, one month after the beginning of the invasion of Iraq. In April 2003 United States forces fired on a group of demonstrators who were protesting against the US presence. US forces alleged they were fired at first, but Human Rights Watch, who visited the site of the protests, concluded that physical evidence did not corroborate US allegations and confirmed the residents' accusations that the US forces fired indiscriminately at the crowd with no provocation. 17 people were killed and 70 were wounded. In a later incident, US soldiers fired on protesters again; Fallujah's mayor, Taha Bedaiwi al-Alwani, said that two people were killed and 14 wounded. Iraqi insurgents were able to claim the city a year later, before they were ousted by a siege and two assaults by US forces. These events caused widespread destruction and a humanitarian crisis in the city and surrounding areas. As of 2004, the city was largely ruined, with 60% of buildings damaged or destroyed, and the population at 30%–50% of pre-war levels.

The 2004 Iraq spring fighting was a series of operational offensives and various major engagements during the Iraq War. It was a turning point in the war; the Spring Fighting marked the entrance into the conflict of militias and religiously based militant Iraqi groups, such as the Shi'a Mahdi Army.
Al-Karmah, also sometimes transliterated as Karma, Karmah, or Garma, is a city in central Iraq, 16 km (10 mi) northeast of Fallujah in the province of Al Anbar.

The Anbar campaign consisted of fighting between the United States military, together with Iraqi security forces, and Sunni insurgents in the western Iraqi governorate of Al Anbar. The Iraq War lasted from 2003 to 2011, but the majority of the fighting and counterinsurgency campaign in Anbar took place between April 2004 and September 2007. Although the fighting initially featured heavy urban warfare primarily between insurgents and U.S. Marines, insurgents in later years focused on ambushing the American and Iraqi security forces with improvised explosive devices (IEDs), large scale attacks on combat outposts, and car bombings. Almost 9,000 Iraqis and 1,335 Americans were killed in the campaign, many in the Euphrates River Valley and the Sunni Triangle around the cities of Fallujah and Ramadi.

Beginning in December 2012, Sunnis in Iraq protested against the Maliki government. On 28 December 2013, a Sunni MP named Ahmed al-Alwani was arrested in a raid on his home in Ramadi. Alwani was a prominent supporter of the anti-government protests. This incident led to violence in Al Anbar Governorate between the Iraqi Army and a loose alliance of tribal militias and other groups fighting alongside the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL).
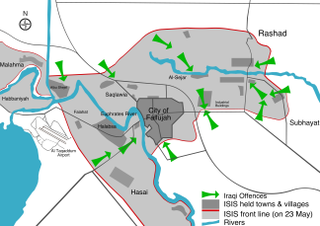
The Third Battle of Fallujah, code-named Operation Breaking Terrorism by the Iraqi government, was a military operation against ISIL launched to capture the city of Fallujah and its suburbs, located about 69 kilometres (43 mi) west of Baghdad, the capital of Iraq. The operation began on 22 May 2016, three months after the Iraqi forces had started the total siege of Fallujah. On 26 June, Iraqi forces recaptured the city of Fallujah, before recapturing the remaining pocket of ISIL resistance in Fallujah's western outskirts two days later.
The Iraqi conflict is a series of violent events that began with the 2003 American-led invasion of Iraq and deposition of Iraqi president Saddam Hussein, followed by the War in Iraq, an armed conflict between Iraq and its allies and the Islamic State. The most recent conflict is the ongoing Islamic State insurgency,















