
The Basilica of Saint-Denis is a large former medieval abbey church and present cathedral in the commune of Saint-Denis, a northern suburb of Paris. The building is of singular importance historically and architecturally as its choir, completed in 1144, is widely considered the first structure to employ all of the elements of Gothic architecture.

Louis VI, called the Fat or the Fighter, was King of the Franks from 1108 to 1137. Like his father Philip I, Louis made a lasting contribution to centralizing the institutions of royal power. He spent much of his twenty-nine-year reign fighting either the "robber barons" who plagued the Ile de France or Henry I of England for his continental possession of Normandy. Nonetheless, Louis VI managed to reinforce his power considerably, often resorting to force to bring lawless knights to justice, and was the first member of the house of Capet to issue ordonnances applying to the whole of the kingdom of France.

Philip I, called the Amorous, was King of the Franks from 1060 to 1108. His reign, like that of most of the early Capetians, was extraordinarily long for the time. The monarchy began a modest recovery from the low it had reached during the reign of his father, Henry I, and he added the Vexin region and the viscountcy of Bourges to his royal domaine.

Chartres is the prefecture of the Eure-et-Loir department in the Centre-Val de Loire region in France. It is located about 90 km (56 mi) southwest of Paris. At the 2019 census, there were 170,763 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Chartres, 38,534 of whom lived in the city (commune) of Chartres proper.
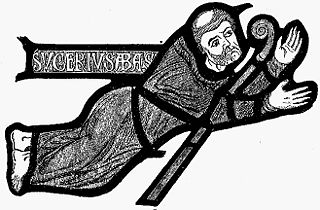
Suger was a French abbot and statesman. He was a key advisor to King Louis VI and his son Louis VII, acting as the latter's regent during the Second Crusade. His writings remain seminal texts for early twelfth-century Capetian history, and his reconstruction of the Basilica of Saint-Denis where he was abbot was instrumental in the creation of Gothic architecture.

The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.

Ivo of Chartres, Can.Reg., also Ives, Yves, or Yvo; Latin: Ivo Carnutensis; c. 1040 – 23 December 1115), was a French canon regular and abbot who then served as the Bishop of Chartres from 1090 until his death. He was an important authority in Catholic canon law during the Investiture Crisis of that era. He is honored as a saint in the Catholic Church.

MonsieurPhilippe I, Duke of Orléans was the younger son of King Louis XIII of France and Anne of Austria, and the younger brother of King Louis XIV. He was the founder of the House of Orléans, a cadet branch of the ruling House of Bourbon.

Adela of Normandy, of Blois, or of England, also known as Saint Adela in Roman Catholicism, was a daughter of William the Conqueror and Matilda of Flanders. She later became the countess of Blois, Chartres, and Meaux by marriage to Stephen II of Blois. Her husband greatly benefited from the increased social status and prestige that came with a marriage into such a wealthy and powerful family. She was regent of Blois during the absence of her spouse in 1096–1100 and 1101–02, and during the minority of her son from 1102 until 1120. Her marriage also laid the groundwork for a period of extended strife in the Anglo Norman lands, Adela was the mother of King Stephen of England whose taking of the throne in preference to her niece Empress Matilda led to the civil war known as The Anarchy.
Fulcher of Chartres was a priest who participated in the First Crusade. He served Baldwin I of Jerusalem for many years and wrote a Latin chronicle of the Crusade.

John I was a scion of the French royal family who ruled the Burgundian State from 1404 until his assassination in 1419. He played a key role in French national affairs during the early 15th century, particularly in the struggles to rule the country for the mentally ill King Charles VI, his cousin, and the Hundred Years' War with England. A rash, ruthless and unscrupulous politician, John murdered the king's brother, the Duke of Orléans, in an attempt to gain control of the government, which led to the eruption of the Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War in France and in turn culminated in his own assassination in 1419.

During the Middle Ages, the counts of Blois were among the most powerful vassals of the King of France.

The Archdiocese of Reims or Rheims is a Latin Church ecclesiastic territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in France. Erected as a diocese around 250 by Sixtus of Reims, the diocese was elevated to an archdiocese around 750. The archbishop received the title "primate of Gallia Belgica" in 1089.

The Diocese of Beauvais, Noyon, and Senlis is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in France. The diocese encompasses the department of Oise in the region of Hauts-de-France. The diocese is a suffragan of the metropolitan Archdiocese of Reims. The current bishop is Jacques Benoit-Gonnin, appointed in 2010.

Robert I of Dreux, nicknamed the Great, was the fifth son of Louis VI of France and Adélaide de Maurienne.

Constance of France was Countess of Troyes from her first marriage and Princess of Antioch from her second marriage. She was regent during the minority of her son. Constance was the eldest of five children and was the only daughter from her father's first marriage. Her brother was Louis VI of France.

The siege of Chartres was a key event of the second French Wars of Religion. The siege saw the Huguenot forces fail to take the heavily defended town, ultimately concluding the second civil war in a negotiated settlement a week later. One of the very few engagements in the second civil war, the siege was led by Louis, Prince of Condé, fresh off regrouping after his defeat at the Battle of Saint-Denis. The defensive efforts were run by the military governor of Chartres, Nicolas des Essars, Sieur de Linières.
The County of Châteaudun was held in the 9th century by counts who also held the County of Blois. Theobald I created the first viscount of Châteaudun with the appointment of Geoffrey I, founder of the House of Châteaudun. The viscounts were entrusted with the government of the county of Châteaudun, records of whom are continuous from the mid-10th century. The actual rule of Châteaudun between the late 9th and the mid-10th centuries, and the relationships between the count and viscounts, is uncertain. The county was revived in 1439 when the region was recreated as the County of Dunois and granted to Jean Levieux Valois des Orléans, the illegitimate son of Louis I, Duke of Orléans, son of Charles V of France.
Hugh I of Le Puiset, son of Everard I of Breteuil and his wife Humberge.
Hugh III, Seigneur of Le Puiset, son of Éverard III, Seigneur of Puiset and Viscount of Chartres, and Adelaide, Countess of Corbeil. Count of Corbel.
















