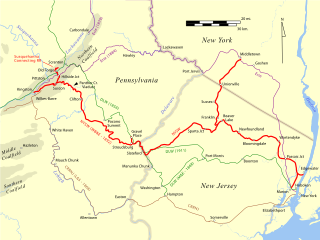
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad built in the Northeastern United States to haul anthracite coal from the Pennsylvania Coal Region. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846 for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, wares, merchandise and minerals in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the railroad was incorporated and established on September 20, 1847 as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad Company. On January 7, 1853, the railroad's name was changed to Lehigh Valley Railroad. It was sometimes known as the Route of the Black Diamond, named after the anthracite it transported. At the time, anthracite was transported by boat down the Lehigh River. The railroad ended operations in 1976 and merged into Conrail along with several northeastern railroads that same year.

The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines, was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of the Northeastern United States.
Conrail Shared Assets Operations (CSAO) is the commonly used name for modern-day Conrail, an American railroad company. It operates three networks—the North Jersey, South Jersey/Philadelphia, and Detroit Shared Assets Areas, where it serves as a contract local carrier and switching company for its owners, CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway. When most of the former Conrail's track was split between these two railroads, the three shared assets areas were kept separate to avoid giving one railroad an advantage in those areas. The company operates using its own employees and infrastructure, but owns no equipment outside MOW equipment.

For the purposes of this article, the Jersey City area extends North to Edgewater, South to Bayonne and includes Kearny Junction and Harrison but not Newark. Many routes east of Newark are listed here.

Conrail's Passaic and Harsimus Line serves freight in northeastern New Jersey, as an alternate to the mainly passenger Northeast Corridor. It takes trains from the Northeast Corridor and Lehigh Line near Newark Liberty International Airport northeast and east into Jersey City, New Jersey, serving as part of CSX's main corridor from upstate New York to the rest of the east coast.
The New Jersey Midland Railway was a 19th-century predecessor to the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway (NYS&W) that operated in Northern New Jersey and Orange County, New York.
The Morris and Essex Railroad was a railroad across northern New Jersey, later part of the main line of the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad.

Roselle Park is a New Jersey Transit railroad station in Roselle Park, New Jersey. Located on the Conrail Lehigh Line which is owned by Conrail Shared Assets Operations on West Lincoln Avenue between Chestnut Street and Locust Street, it is served by Raritan Valley Line trains that travel between Newark Penn Station and Raritan. There is also limited service between High Bridge and New York Penn Station and one weekday morning train to Hoboken Terminal.

Easton and Amboy Railroad was a railroad built across central New Jersey by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR) in the 1870s. The line was built to connect the Lehigh Valley Railroad coal hauling operations in Pennsylvania with the Port of New York and New Jersey to serve consumer markets in New York metropolitan area. Until it was built, the terminus of the LVRR had been at Phillipsburg, New Jersey on the Delaware River opposite Easton, Pennsylvania. It is now part of Norfolk Southern Railway operations, partially the Lehigh Line

The Newark and Roselle Railway was incorporated on Aug 28, 1889 by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR) to advance tracks from the terminus of the Roselle and South Plainfield Railway at Roselle, New Jersey to Pennsylvania Avenue in Newark. It formed part of the route connecting the LVRR's Easton and Amboy Railroad at South Plainfield to the Jersey City terminal.

The Newark and Passaic Railway was incorporated on Nov 22, 1889 by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR). It was chartered as a short line in Newark, New Jersey from the Passaic River to a connection with the LVRR's Newark and Roselle Railway near Pennsylvania Avenue in Newark. The lower mile of its length closed a gap in the route of the LVRR from South Plainfield to Jersey City.

The Newark Railway was incorporated on December 10, 1890, and was a short, 1-mile connection between the Lehigh Valley Railroad's Newark and Roselle Railway and the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR). Upon completion on Feb 16, 1891, all passenger traffic, which had previously been routed to the PRR at Metuchen, instead took the route from South Plainfield to Newark, where it connected with the PRR and continued to the PRR station in Jersey City. The Newark Railway also served a LVRR freight and coal depot at Pennsylvania Avenue, adjacent to the PRR junction.

The Roselle and South Plainfield Railway was a railroad built by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR) in 1888 to connect the LVRR's Easton and Amboy Railroad with the Central Railroad of New Jersey (CNJ), and provided access over the CNJ to the Hudson River waterfront in Jersey City. The LVRR had built coal docks in Perth Amboy when it built the Easton and Amboy in the 1870s, but it desired a terminal on the Hudson River close to New York City.
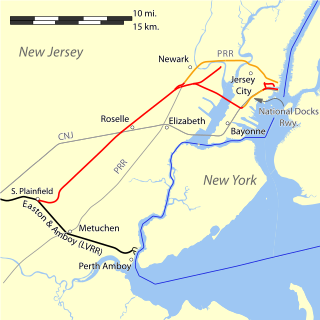
The Lehigh Valley Terminal Railway was a Lehigh Valley Railroad company organized in 1891 through the consolidation of the companies that formed the Lehigh Valley's route from South Plainfield through Newark to Jersey City via its bridge across Newark Bay. Until 1895, when the Greenville and Hudson Railway was constructed, the Lehigh Valley depended on the National Docks Railway to reach the Hudson River terminal.

The Upper Bay Bridge, or the Lehigh Valley Railroad Bridge, is a vertical lift bridge spanning the Newark Bay in northeastern New Jersey. It is used by CSX Transportation travelling through the North Jersey Shared Assets Area of the United States rail network along the National Docks Secondary line. The bridge is just north and parallel to the New Jersey Turnpike's Newark Bay Bridge. A notable train using the bridge is the Juice Train, which originates in Florida.

Oak Island Yard is a freight rail yard located north of Port Newark-Elizabeth Marine Terminal and Newark International Airport in an industrial area of Ironbound, Newark, New Jersey at 91 Bay Ave., United States. The sprawling complex includes engine house, classification yard, auto unloading terminal, and maintenance facilities. It has ten reception tracks, an automated hump, 30 relatively short classification tracks, and nine departure tracks. In 1999, it classified 800 to 1000 cars per day.
National Docks Secondary is a freight rail line within Conrail's North Jersey Shared Assets Area in Hudson County, New Jersey, used by CSX Transportation. It provides access for the national rail network to maritime, industrial, and distribution facilities at Port Jersey, the Military Ocean Terminal at Bayonne (MOTBY), and Constable Hook as well as carfloat operations at Greenville Yard. The line is an important component in the planned expansion of facilities in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The single track right of way comprises rail beds, viaducts, bridges, and tunnels originally developed at the end of the 19th century by competing railroads.

WR Draw is an out-of-service railroad bridge crossing the Passaic River between Newark and the Arlington section of Kearny, New Jersey. The plate girder rim-bearing swing bridge, originally built in 1897 and modified in 1911 and 1950, is the 14th bridge from the river's mouth at Newark Bay and is 8.1 miles (13.0 km) upstream from it. Last used for regular passenger service in 2002, it is welded in closed position as its height is not considered a hazard to navigation.
The Newark Branch was a branch of the Erie Railroad in New Jersey, United States, running between Jersey City and Paterson with stops in the Broadway Section in North Newark. Inaugurated in the 1870s, the line was last used for passenger service on September 30, 1966. However freight service still remains on a section of the branch.

The Lehigh Line is a railroad line in central New Jersey and northeastern Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The line runs west from the vicinity of the Port of New York and New Jersey to the Susquehanna River valley at the south end of the Wyoming Valley Coal Region. Administratively it is part of Norfolk Southern's Keystone Division (Harrisburg) and is also part of the Crescent Corridor. As of 2021 the line is freight-only, although there are perennial proposals to restore passenger service over all or part of the line.

 The Jersey City, Newark and Western Railway was incorporated on July 6, 1889, and acquired by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR). Construction was completed in 1893. It started in Jersey City, New Jersey at a connection with the National Docks Railway in Communipaw east of the Central Railroad of New Jersey line, and extended westward on the bridge across Newark Bay to connect with the LVRR's Newark and Passaic Railway.
The Jersey City, Newark and Western Railway was incorporated on July 6, 1889, and acquired by the Lehigh Valley Railroad (LVRR). Construction was completed in 1893. It started in Jersey City, New Jersey at a connection with the National Docks Railway in Communipaw east of the Central Railroad of New Jersey line, and extended westward on the bridge across Newark Bay to connect with the LVRR's Newark and Passaic Railway.














