Related Research Articles

National Tsing Hua University (NTHU) is a public research university in Hsinchu, Taiwan.

An amorphous metal is a solid metallic material, usually an alloy, with disordered atomic-scale structure. Most metals are crystalline in their solid state, which means they have a highly ordered arrangement of atoms. Amorphous metals are non-crystalline, and have a glass-like structure. But unlike common glasses, such as window glass, which are typically electrical insulators, amorphous metals have good electrical conductivity and can show metallic luster.
Hsiang-Tsung Kung is a Taiwanese-born American computer scientist. He is the William H. Gates professor of computer science at Harvard University. His early research in parallel computing produced the systolic array in 1979, which has since become a core computational component of hardware accelerators for artificial intelligence, including Google's Tensor Processing Unit (TPU). Similarly, he proposed optimistic concurrency control in 1981, now a key principle in memory and database transaction systems, including MySQL, Apache CouchDB, Google's App Engine, and Ruby on Rails. He remains an active researcher, with ongoing contributions to computational complexity theory, hardware design, parallel computing, routing, wireless communication, signal processing, and artificial intelligence.

Brian Cantor has been a long-serving university leader, is a visiting professor in the Department of Materials at the University of Oxford, and a consultant at the Brunel Centre for Advanced Solidification Technology (BCAST) at Brunel University. He was the vice-chancellor of the University of Bradford from 2013 to 2019. Prior to this appointment he was the vice-chancellor at the University of York from 2002 to 2013, and previously he was the head of the Mathematical and Physical Sciences Division at the University of Oxford.
Wei ShyyJP is an aerospace engineer who served as the 4th President of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) from 2018 to 2022 with his acting presidency starting from 1 February 2018. He also holds a concurrent appointment as Chair Professor of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering. He first joined HKUST in August 2010 as Provost.
Chen Wen-tsuen is an ethnic Taiwanese computer scientist, a distinguished research fellow at the Academia Sinica and a lifelong national chair of the Ministry of Education, Taiwan. From 2006 to 2010, he was the president of the National Tsing Hua University, a premier research university in Taiwan.

Ming-Fa Lin was a Taiwanese theoretical physicist. He was a distinguished professor in the Department of Physics in the National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan. His main scientific interests focus on the essential properties of carbon-related materials and low-dimensional systems. He presided over more than 10 Ministry of Science and Technology research projects. He published more than 300 peer-reviewed articles and over 10 academic books. His research principles include innovation, uniqueness, diversity, completeness, and generalization. In 2023, Prof. Ming-Fa Lin was awarded the top 2% of the world's top scientists for honoring his career-long research works.
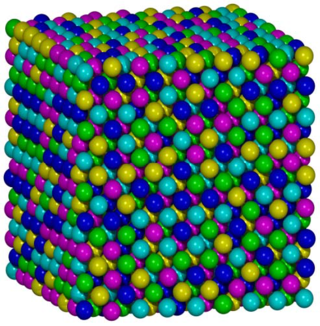
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are alloys that are formed by mixing equal or relatively large proportions of (usually) five or more elements. Prior to the synthesis of these substances, typical metal alloys comprised one or two major components with smaller amounts of other elements. For example, additional elements can be added to iron to improve its properties, thereby creating an iron-based alloy, but typically in fairly low proportions, such as the proportions of carbon, manganese, and others in various steels. Hence, high-entropy alloys are a novel class of materials. The term "high-entropy alloys" was coined by Taiwanese scientist Jien-Wei Yeh because the entropy increase of mixing is substantially higher when there is a larger number of elements in the mix, and their proportions are more nearly equal. Some alternative names, such as multi-component alloys, compositionally complex alloys and multi-principal-element alloys are also suggested by other researchers.

Robert Oliver Ritchie is the H.T. and Jessie Chua Distinguished Professor of Engineering at the University of California, Berkeley and senior faculty scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Dipankar Banerjee is an Indian physical metallurgist, materials engineer and a former chief controller of R&D at the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO). Known for his studies on titanium alloys, Banerjee is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies namely Indian Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy and National Academy of Sciences, India as well as the Indian National Academy of Engineering. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Engineering Sciences in 1993. He received the fourth highest Indian civilian honour of Padma Shri from the Government of India in 2005.
Events from the year 2018 in Taiwan, Republic of China. This year is numbered Minguo 107 according to the official Republic of China calendar.

Yi Cui is a Chinese-American scientist specializing in the fields of nanotechnology, materials science, sustainable energy, and chemistry. Cui is Fortinet Founders Professor at Stanford University, where he also serves as a professor of materials science and engineering and of energy science and engineering. He is a Highly Cited Researcher in the fields of materials science, environment and ecology, engineering, and chemistry as of 2023. From 2020 to 2023, Cui was the director of the Precourt Institute for Energy, and since 2023 he has served as the inaugural faculty director of the Sustainability Accelerator in the Doerr School of Sustainability.
Galit Shmueli is a data scientist who works in Taiwan as Tsing Hua Distinguished Professor at the Institute of Service Science, National Tsing Hua University. She is the author of many textbooks in business statistics and is known for her work on information quality, and on clarifying the difference between explanations and predictions in statistical analyses.

High-entropy oxides (HEOs) are complex oxides that contain five or more principal metal cations and have a single-phase crystal structure. The first HEO, (MgNiCuCoZn)0.2O in a rock salt structure, was reported in 2015 by Rost et al. HEOs have been successfully synthesized in many structures, including fluorites, perovskites, and spinels. HEOs are currently being investigated for applications as functional materials.
Thermal shock synthesis (TSS) is a method in which materials are synthesized via rapid, high-temperature heating. In the TSS process, temperatures as high as 3000 K are applied for a duration of just seconds or milliseconds, followed by rapid cooling (a TSS image shown in Fig. 1). In this regard, TSS is distinct from conventional high-temperature syntheses that feature slow and near-equilibrium heating at limited temperature ranges (e.g., 1500 K for furnace heating) for extended periods of time (typically hours) and generally slow heating and cooling (~10 K/min).
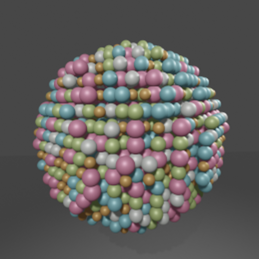
High-entropy-alloy nanoparticles (HEA-NPs) are nanoparticles having five or more elements alloyed in a single-phase solid solution structure. HEA-NPs possess a wide range of compositional library, distinct alloy mixing structure, and nanoscale size effect, giving them huge potential in catalysis, energy, environmental, and biomedical applications.
Hans-Jörg Fecht is Chaired Professor at the University of Ulm, Germany in the departments of Engineering and Computer Science. He is also an Office Director of the EUREKA Cluster Metallurgy Europe in the Same university, and a member of the European Academy of Sciences and Arts. He has published over 450 scientific publications, directed numerous national, European, and international research initiatives.

Zhong Lin Wang is a Chinese-American physicist, materials scientist and engineer specialized in nanotechnology, energy science and electronics. He received his PhD from Arizona State University in 1987. He is the Hightower Chair in Materials Science and Engineering and Regents' Professor Chair Emeritus at the Georgia Institute of Technology, US.

Dierk Raabe is a German materials scientist and researcher, who has contributed significantly to the field of materials science. He is a professor at RWTH Aachen University and director of the Max Planck Institute for Iron Research in Düsseldorf. He is the recipient of the 2004 Leibniz Prize, and the 2022 Acta Materialia's Gold Medal. He also received the honorary doctorate of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology.
References
- ↑ "Jien-Wei Yeh". National Tsing Hua University Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Retrieved 2023-10-25.
- ↑ "Jien-Wei Yeh". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ↑ "Jien-Wei Yeh profile" . Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ↑ Balasubramanian, N (November 2016). "High-entropy alloys: An interview with Jien-Wei Yeh: www.mrs.org/fall2016". MRS Bulletin. 41 (11): 905–06. doi: 10.1557/mrs.2016.257 . ISSN 0883-7694. S2CID 137802916.
- ↑ Yeh, JW; Chen, SK; Lin, SJ; Gan, JY; Chin, TS; Shun, TT; Tsau, CH; Chang, SY (May 2004). "Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes". Advanced Engineering Materials. 6 (5): 299–303. doi:10.1002/adem.200300567. ISSN 1438-1656. S2CID 137380231.
- 1 2 Biswas, K; Yeh, JW; Bhattacharjee, PP; DeHosson, JM (November 2020). "High entropy alloys: Key issues under passionate debate". Scripta Materialia. 188: 54–58. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.010. ISSN 1359-6462. S2CID 224864551.
- ↑ Kim, KB; Zhang, Y; Warren, PJ; Cantor, B (July 2003). "Crystallization behaviour in a new multicomponent Ti 16.6 Zr 16.6 Hf 16.6 Ni 20 Cu 20 Al 10 metallic glass developed by the equiatomic substitution technique". Philosophical Magazine. 83 (20): 2371–81. Bibcode:2003PMag...83.2371K. doi:10.1080/0141861031000113343. ISSN 1478-6435. S2CID 136579175.