
Count Joachim von Pfeil (1857-1924) was a German explorer and colonist in Africa and New Guinea.

Count Joachim von Pfeil (1857-1924) was a German explorer and colonist in Africa and New Guinea.
He was born at Neurode, in Silesia, studied at the gymnasium of Göttingen. In 1873, he went to the Colony of Natal. There he learned the vernacular and stayed in the country four years. In 1879, after a visit to Europe, he settled in Orange Free State and with Wilson mapped the course of the Limpopo river. After falling ill, he returned to Germany. In 1884, having entered the employ of the Society for German Colonization, Pfeil went to East Africa with Carl Peters and Karl Ludwig Jühlke, and in 1886 succeeded the latter as general manager of the company in Somaliland. This post he resigned in 1887, and entered the service of the New Guinea Company. He died on March 12, 1924 in Friedersdorf.
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(July 2014) |

German New Guinea consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, became a German protectorate in 1884. Other island groups were added subsequently. The Bismarck Archipelago, and the North Solomon Islands were declared a German protectorate in 1885. The Caroline Islands, Palau, and the Mariana Islands were bought from Spain in 1899. German New Guinea annexed the formerly separate German Protectorate of Marshall Islands, which also included Nauru, in 1906. German Samoa, though part of the German colonial empire, was not part of German New Guinea.

Carl Peters was a German explorer and colonial administrator. He was a major promoter of the establishment of the German colony of East Africa and one of the founders of the German East Africa Company. He was a controversial figure in Germany for his views and his brutal treatment of native Africans, which ultimately led to his dismissal from government service in 1897.

The German colonial empire constituted the overseas colonies, dependencies, and territories of the German Empire. Unified in 1871, the chancellor of this time period was Otto von Bismarck. Short-lived attempts at colonization by individual German states had occurred in preceding centuries, but Bismarck resisted pressure to construct a colonial empire until the Scramble for Africa in 1884. Claiming much of the remaining uncolonized areas of Africa, Germany built the third-largest colonial empire at the time, after the British and French. The German colonial empire encompassed parts of several African countries, including parts of present-day Burundi, Rwanda, Tanzania, Namibia, Cameroon, Gabon, Congo, Central African Republic, Chad, Nigeria, Togo, Ghana, as well as northeastern New Guinea, Samoa and numerous Micronesian islands.

The Hermannsburg Mission was founded as the Hermannsburg Mission Centre in 1849 in Hermannsburg, near Celle, North Germany, by Louis Harms. In 1977, the independent mission society was merged into the work of the Evangelical-Lutheran Mission in Lower Saxony. As a result, it became an institution recognised by the state church.
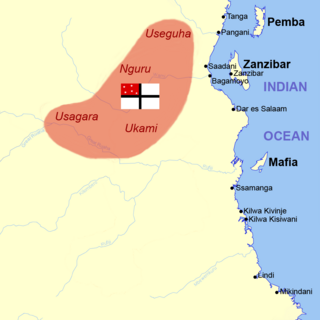
The Society for German Colonization was founded on 28 March 1884 in Berlin by Carl Peters. Its goal was to accumulate capital for the acquisition of German colonial territories in overseas countries.

Felix Ritter von Luschan was a medical doctor, anthropologist, explorer, archaeologist and ethnographer born in the Austrian Empire.

Maggi is an international brand of seasonings, instant soups, and noodles that originated in Switzerland in the late 19th century. The Maggi company was acquired by Nestlé in 1947.
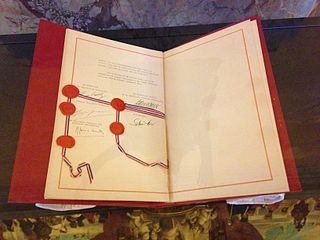
The Élysée Treaty was a treaty of friendship between France and West Germany, signed by President Charles de Gaulle and Chancellor Konrad Adenauer on 22 January 1963 at the Élysée Palace in Paris. With the signing of this treaty, Germany and France established a new foundation for relations, bringing an end to centuries of French–German enmity and wars.

Ernst Kals was a Kapitän zur See with the Kriegsmarine during World War II. He commanded the Type IXC U-boat U-130 on five patrols. He was awarded the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross.
Joachim, Count of Schönburg-Glauchau was the nominal successor head of the former mediatised German Counts of Schönburg-Glauchau until 1945. Dispossessed and expelled from his homeland in 1945, he and his family migrated to the Rhineland, where he was an author and journalist. After the fall of the Berlin Wall, he returned to his homeland, represented the district in the Bundestag, and served in local government.

Johann Flierl was a pioneer Lutheran missionary in New Guinea. He established mission schools and organised the construction of roads and communication between otherwise remote interior locations. Under his leadership, Lutheran evangelicalism flourished in New Guinea. He founded the Evangelical Lutheran Mission in the Sattelberg, and a string of filial stations on the northeastern coast of New Guinea including the Malahang Mission Station.
Pfeil may refer to:

SMS Leipzig was a German flush-deck steam corvette, the lead ship of the Leipzig class, named after the 1813 Battle of Leipzig. She was built for the Kaiserliche Marine in the 1870s, being laid down in early 1875, launched in September that year, and commissioned into the fleet in May 1877. She had one sister ship, SMS Prinz Adalbert. Intended for long cruises abroad, the ship was fitted with a full ship rig to supplement her steam engine if coal was unavailable. She carried a battery of twelve 17 cm (6.7 in) guns.

SMS Pfeil was an aviso of the Imperial German Navy, the second and final member of the Blitz class. Her primary offensive armament consisted of a bow-mounted torpedo tube, and she was armed with a battery of light guns to defend herself against torpedo boats, a sign of the growing importance of torpedoes as effective weapons in the period. The Blitz class featured a number of innovations in German warship design: they were the first steel hulled warships and the first cruiser-type ships to discard traditional sailing rigs.

The Blitz class was a pair of avisos built for the German Kaiserliche Marine in the early 1880s. The ships, Blitz and Pfeil, were the first steel-hulled ships of any kind built by the German Navy, were among the first torpedo cruiser type warships in the world, and were the progenitors of the later light cruisers of the Gazelle class. They were armed with a 12.5 cm (4.9 in) gun and one 35 cm (13.8 in) torpedo tube as their principal armament, and were capable of a top speed in excess of 15 knots. They were very successful warships, remaining in active service for more than three decades.

SMS Sperber was an unprotected cruiser built for the German Kaiserliche Marine, the second member of the Schwalbe class. She had one sister ship, Schwalbe. Sperber was built at the Kaiserliche Werft in Danzig; her keel was laid down in September 1887 and her completed hull was launched in August 1888. She was commissioned for service in April 1889. Designed for colonial service, Sperber was armed with a main battery of eight 10.5-centimeter (4.1 in) guns and had a cruising radius of over 3,000 nautical miles ; she also had an auxiliary sailing rig to supplement her steam engines.
Carl Georg Eduard Friederici was a German ethnologist. He wrote extensively on the customs and language of peoples affected by European colonization in America and Oceania.
Ferdinand Broili was a German paleontologist.

Friedrich Wilhelm Leopold Pfeil was a German forester.

Ulrich Pfeil is a German historian based in France.