A graphic novel is a long-form work of sequential art. The term graphic novel is often applied broadly, including fiction, non-fiction, and anthologized work, though this practice is highly contested by comics scholars and industry professionals. It is, at least in the United States, typically distinct from the term comic book, which is generally used for comics periodicals and trade paperbacks.

Ronald Joseph Goulart (; was an American popular culture historian and mystery, fantasy and science fiction author.

Dwight Graydon "Gray" Morrow was an American illustrator of comics, magazine covers and paperback books. He is co-creator of the Marvel Comics muck-monster the Man-Thing and of DC Comics Old West vigilante El Diablo.

Joseph Orlando was an Italian-American illustrator, writer, editor and cartoonist during a lengthy career spanning six decades. He was the associate publisher of Mad and the vice president of DC Comics, where he edited numerous titles and ran DC's Special Projects department.
Frank Bellamy was a British comics artist, best known for his work on the Eagle comic, for which he illustrated Heros the Spartan and Fraser of Africa. He reworked its flagship Dan Dare strip.
Lew Stringer is a freelance comic artist and scriptwriter.

Mir Fantastiki, officially abbreviated as MirF, is a Russian monthly science fiction and fantasy magazine. The name also refers to the website run by the magazine, Mirf.ru.
TV Century 21, later renamed TV21, TV21 and Tornado, TV21 and Joe 90, and TV21 again, was a weekly British children's comic published by City Magazines during the latter half of the 1960s. Originally produced in partnership with Gerry and Sylvia Anderson's Century 21 Productions, it promoted the company's many science-fiction television series. The comic was published in the style of a newspaper of the future, with the front page usually dedicated to fictional news stories set in the worlds of Fireball XL5, Stingray, Thunderbirds, Captain Scarlet and the Mysterons and other stories. The front covers were also in colour, with photographs from one or more of the Anderson series or occasionally of the stars of the back-page feature.
Francis X. McLaughlin was an American comics artist who co-created the comic book character Judomaster, drew the comic strip Gil Thorp, and assisted on such strips as Brenda Starr, Reporter and The Heart of Juliet Jones. He also wrote and illustrated books about cartooning and comic art.

Blue Ribbon Comics is the name of two American comic book anthology series, the first published by the Archie Comics predecessor MLJ Magazines Inc., commonly known as MLJ Comics, from 1939 to 1942, during the Golden Age of Comic Books. The revival was the second comic published in the 1980s by Archie Comics under the Red Circle and Archie Adventure Series banners.
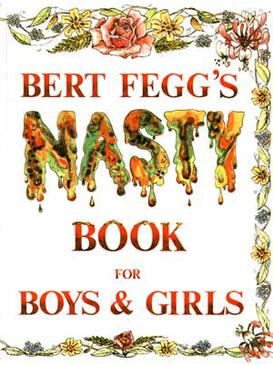
Bert Fegg's Nasty Book for Boys And Girls is a humorous book first published by Methuen in 1974 which purports to have been written by a psychopathic character, Dr. Fegg. In fact, the book is the work of Terry Jones and Michael Palin, who adapted a range of material from scripts written for the television comedy series, Monty Python's Flying Circus. Some material was later used in the duo's later TV series, Ripping Yarns (1975–78). The first edition was sold bearing a sticker on the front cover which read "A Monty Python Educational Product".
Black people have been portrayed in comics since the medium's beginning, with their portrayals often the subject of controversy. Mainstream comic publishing companies have had a historical trend of being predominantly white and male, reflecting the lack of representation and inaccurate depictions of Black people in comics. The integration of black characters in mainstream and superhero comics has endured various obstacles and challenges. Critics have noted that black men and women have historically often been portrayed as jungle or ghetto stereotypes, and as sidekicks as opposed to primary characters. Occiasionally, comic book creators would lampshade stereotypes, lack of representation and emphasize social injustices. In recent years, with the integration of more Black people in mainstream comic writing rooms as well as the creation of comics on digital platforms has changed the representation and portrayals of Black people in comics and has started to reflect the complexities of Black people across the diaspora.
This is a list of Dalek comic strips, illustrated annuals and graphic novels. Cameo appearances and reprints are only covered if notable.

Hilary Boniface Ng'weno (1938-2021) was a Kenyan historian and journalist. The Harvard-educated scientist was born in Nairobi in 1938, to the late Morris Onyango. After graduating from Harvard with a degree in nuclear physics, Ng'weno worked as a reporter for the Daily Nation for nine months before his appointment as the newspaper’s first Kenyan editor-in-chief. He resigned in 1965 and established a successful career as a journalist for more than forty years. In 1973, together with journalist Terry Hirst, he founded Joe, a political satire comic magazine that circulated in many parts of Africa until the late seventies when its publication ceased. He is best known as the editor-in-chief of the Weekly Review, a weekly newsmagazine than ran from 1975 to 1999. He is also the founder of The Nairobi Times and the first independent TV news station in Kenya, STV. He was the producer of documentary videos on Kenyan history, including the Making of a Nation and Kenya's Darkest Hour.

The Phoenix is a British weekly story comic for children aged 7– 14, published by David Fickling Comics Ltd. The comic was launched on 7 January 2012 with a preview issue which was released in late 2011. The comic is often considered a successor to The DFC: both are published by the same people and many of The Phoenix's creators had worked on The DFC.

Frank Odoi, one of Africa's foremost cartoonists, was born in the mining town of Tarkwa in western Ghana in 1948. He was the only boy amongst seven sisters. He lost his father at an early age and was primarily raised by his mother. He was married to Monicah Asami, who later changed her name to Caroline Odoi. They had three daughters Maureen Atulo, Francesca Ajua Odoi and Francine Ashardey Odoi.

Rocket's Blast Comicollector (RBCC) was a comics advertising fanzine published from 1964 to 1983. The result of a merger with a similar publication, RBCC's purpose was to bring fans together for the purpose of adding to their comic book collections. It also proved to be a launching pad for aspiring comic book creators, many of whom corresponded and exchanged their work through RBCC, and published work in the fanzine as amateurs.
Terry Hirst (1932–2015), was a British-Kenyan cartoonist and one of the leading figures in Africa's post-independence "golden age" of art and scholarship from the mid-1960s to the early 1980s which saw a flowering of work in the arts, cinema and the academic world. Terry Hirst was born in 1932 in Brighton in England. In 1965, Hirst moved to Kenya where he was to spend the rest of his life.

BEM, originally known as Bemusing Magazine, was a British fanzine focused on comic books which was published from 1973 to 1982. The brainchild of Martin Lock and billed as "The Comics News Fanzine," BEM featured American and British comics industry news and gossip, interviews, comic reviews, essays, columns, and comic strips.

June was a British weekly girls' comic anthology published by Fleetway Publications and IPC Magazines from 18 March 1961 to 15 June 1974. Designed as a response to DC Thomson's hit Bunty, June never quite eclipsed its Scottish rival but was nevertheless a success on its own terms, reaching 631 issues before being merged into Tammy in 1974.