
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.

Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to even a greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well-engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use to this day.

A dome is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them.

The ancient Romans were the first civilization to build large, permanent bridges. Early Roman bridges used techniques introduced by Etruscan immigrants, but the Romans improved those skills, developing and enhancing methods such as arches and keystones. There were three major types of Roman bridge: wooden, pontoon, and stone. Early Roman bridges were wooden, but by the 2nd century stone was being used. Stone bridges used the arch as their basic structure, and most used concrete, the first use of this material in bridge-building.

An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today.

Rustication is a range of masonry techniques used in classical architecture giving visible surfaces a finish texture that contrasts with smooth, squared-block masonry called ashlar. The visible face of each individual block is cut back around the edges to make its size and placing very clear. In addition the central part of the face of each block may be given a deliberately rough or patterned surface.
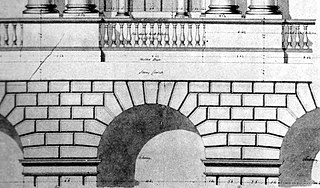
A voussoir is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault.

A multifoil arch, also known as a cusped arch, polylobed arch, or scalloped arch, is an arch characterized by multiple circular arcs or leaf shapes that are cut into its interior profile or intrados. The term foil comes from the old French word for "leaf." A specific number of foils is indicated by a prefix: trefoil (three), quatrefoil (four), cinquefoil (five), sexfoil (six), octofoil (eight). The term multifoil or scalloped is specifically used for arches with more than five foils. The multifoil arch is characteristic of Islamic art and architecture; particularly in the Moorish architecture of al-Andalus and North Africa and in Mughal architecture of the Indian subcontinent. Variants of the multifoil arch, such as the trefoil arch, are also common in other architectural traditions such as Gothic architecture.

Ancient Egyptian architecture is best known for its monumental temples and tombs built in stone, including its famous pyramids, such as the pyramids of Giza. These were built with a distinctive repertoire of elements including pylon gateways, hypostyle halls, obelisks, and hieroglyphic decoration. The advent of Greek Ptolemaic rule, followed by Roman rule, introduced elements of Greco-Roman architecture into Egypt, especially in the capital city of Alexandria. After this came Coptic architecture, including early Christian architecture, which continued to feel ancient classical and Byzantine influences.

A four-centered arch is a low, wide type of arch with a pointed apex. Its structure is achieved by drafting two arcs which rise steeply from each springing point on a small radius, and then turning into two arches with a wide radius and much lower springing point. It is a pointed sub-type of the general flattened depressed arch. This type of arch uses space efficiently and decoratively when used for doorways. It is also employed as a wall decoration in which arcade and window openings form part of the whole decorative surface. Two of the most notable types are known as the Persian arch, which is moderately "depressed" and found in Islamic architecture, and the Tudor arch, which is much flatter and found in English architecture. Another variant, the keel arch, has partially straight rather than curved sides and developed in Fatimid architecture.

Bab al-Futuh is one of three remaining gates in the city wall of the old city of Cairo, Egypt. It is located at the northern end of al-Mu'izz Street. The other two remaining gates are Bab al-Nasr in the north and Bab Zuwayla in the south. The gate was built during the Fatimid period, originally in the 10th century, then rebuilt in its current form in the late 11th century.

A Gibbs surround or Gibbs Surround is a type of architectural frame surrounding a door, window or niche in the tradition of classical architecture otherwise known as a rusticated doorway or window. The formula is not fixed, but several of the following elements will be found. The door is surrounded by an architrave, or perhaps consists of, or is flanked by, pilasters or columns. These are with "blocking", where rectangular blocks stick out at intervals, usually alternating to represent half the surround. Above the opening there are large rusticated voussoirs and a keystone and a pediment above that. The most essential element is the alternation of blocking with non-blocking elements. Some definitions extend to including arches or square openings merely with alternate blocked elements that continue round the top in the same manner as the sides, as in the rectangular windows of the White House's north front basement level.

The Qalawun complex is a massive pious complex in Cairo, Egypt, built by Sultan al-Mansur Qalawun from 1284 to 1285. It is located at Bayn al-Qasrayn on al-Mu'izz street and like many other pious complexes includes a hospital (bimaristan), a madrasa and mausoleum. Despite controversy surrounding its construction, this building is widely regarded as one of the major monuments of Islamic Cairo and of Mamluk architecture, notable for the size and scope of its contributions to legal scholarship and charitable operations as well as for the richness of its architecture.

The horseshoe arch, also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is an emblematic arch of Christian architecture, especially Visigothic architecture, subsequently adapted into Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or lobed form.
Chesters Bridge was a Roman bridge over the River North Tyne at Chollerford, Northumberland, England, and adjacent to the Roman fort of Cilurnum on Hadrian's Wall. The fort, mentioned in the Notitia Dignitatum, and now identified with the fort found at Chesters, was known as Cilurnum or Cilurvum.
The architecture of Palestine and ancient Israel covers a vast historical time frame and a number of different styles and influences over the ages. The urban architecture of the region of Palestine prior to 1850 was relatively sophisticated. The Palestinian townhouse shared in the same basic conceptions regarding the arrangement of living space and apartment types commonly seen throughout the Eastern Mediterranean. The rich diversity and underlying unity of the architectural culture of this wider region stretching from the Balkans to North Africa was a function of the exchange fostered by the caravans of the trade routes, and the extension of Ottoman rule over most of this area, beginning in the early 16th century through until the end of World War I.

Ablaq is an architectural technique involving alternating or fluctuating rows of light and dark stone. Records trace the beginnings of this type of masonry technique to the southern parts of Syria. It is associated as an Arabic term, especially as related to Arabic Islamic architectural decoration. The first recorded use of the term ablaq pertained to repairs of the Great Mosque of Damascus in 1109, but the technique itself was used much earlier.

The Fatimid architecture that developed in the Fatimid Caliphate (909–1167 CE) of North Africa combined elements of eastern and western architecture, drawing on Abbasid architecture, Byzantine, Ancient Egyptian, Coptic architecture and North African traditions; it bridged early Islamic styles and the medieval architecture of the Mamluks of Egypt, introducing many innovations.

Islamic rule in South Asia brought with it the use of domes constructed with stone, brick and mortar, and iron dowels and cramps. Centering was made from timber and bamboo. The use of iron cramps to join together adjacent stones was known in pre-Islamic India, and was used at the base of domes for hoop reinforcement. The synthesis of styles created by this introduction of new forms to the Hindu tradition of trabeate construction created a distinctive architecture.

The Mosque of Qaytbay, also known as the Madrasa of Qaytbay, is a historic religious structure in the Qal'at al-Kabsh neighbourhood of Cairo, Egypt. Completed in 1475, it is one of multiple monuments sponsored by the Mamluk sultan al-Ashraf Qaytbay. It is not to be confused with the more famous Funerary complex of Qaytbay in the Northern Cemetery. It is described as both a madrasa and a mosque by scholars, but functions as a mosque today.


















