Idea
Stumpf's 'Uniflow' system aroused interest among engine designers in the years before the First World War, at first in his native Germany and later elsewhere. The Uniflow principle was known previously, and Stumpf's work was really its practical application. In Stumpf's system steam was admitted at one end of the cylinder, and the used steam left through a ring of ports at the other end of the cylinder. This allowed the admission end to stay hot, as it was not cooled by the exhaust on its way out, and so improved efficiency. In a double-acting engine the exhaust ports were in the middle of the cylinder.
Almost all uniflow engines were large stationary types, but the system was tried by, among others, the North Eastern Railway in England, as described by Tuplin (see sources). Briefly, the system worked well and obtained a small increase in economy by decreasing fuel consumption, but at the price structure prevailing at that time the extra constructional and maintenance costs were greater than the coal economy. H.W. Dickinson's A Short History of The Steam Engine makes it clear that the concept of the uniflow engine reached back to Montgolfier and Jacob Perkins (who patented the idea) and Leonard Jennett Todd (Patent No. 7801): Dickinson then gives Stumpf of Technische Hochschule Charlottenburg his due citing a paper by T.B. Perry Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. , 1920 (1922?).

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.

A two-strokeengine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle in two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust functions occurring at the same time.

Henri Marie Coandă was a Romanian inventor, aerodynamics pioneer, and builder of an experimental aircraft, the Coandă-1910, which never flew. He invented a great number of devices, designed a "flying saucer" and discovered the Coandă effect of fluid dynamics.

An opposed-piston engine is a piston engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head. Petrol and diesel opposed-piston engines have been used mostly in large-scale applications such as ships, military tanks, and factories. Current manufacturers of opposed-piston engines include Cummins, Achates Power and Fairbanks-Morse Defense (FMDefense).

The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion".

Variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a valve lift event in an internal combustion engine, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with variable valve lift systems. There are many ways in which this can be achieved, ranging from mechanical devices to electro-hydraulic and camless systems. Increasingly strict emissions regulations are causing many automotive manufacturers to use VVT systems.
William Hall Barnett is described as a 'founder' in his 1836 patent, and an 'ironfounder' in his 1838 patent, and later as an engineer and gas engineer, working in Brighton, UK. He worked for many years for the Brighton and Hove General Gas Company. He was born in Bradford and died in Brighton.

The Walschaerts valve gear is a type of valve gear used to regulate the flow of steam to the pistons in steam locomotives, invented by Belgian railway engineer Egide Walschaerts in 1844. The gear is sometimes named without the final "s", since it was incorrectly patented under that name. It was extensively used in steam locomotives from the late 19th century until the end of the steam era.

Jacob Perkins was an American inventor, mechanical engineer and physicist based in the United Kingdom. Born in Newburyport, Massachusetts, Perkins was apprenticed to a goldsmith. He soon made himself known with a variety of useful mechanical inventions and eventually had twenty-one American and nineteen English patents.Sometimes known as the father of the refrigerator. He was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1813 and a member of the American Philosophical Society in 1819.

A Corliss steam engine is a steam engine, fitted with rotary valves and with variable valve timing patented in 1849, invented by and named after the US engineer George Henry Corliss of Providence, Rhode Island.Corliss assumed the original invention from Frederick Ellsworth Sickels, who held the patent (1829) in the US patent office.
Engine efficiency of thermal engines is the relationship between the total energy contained in the fuel, and the amount of energy used to perform useful work. There are two classifications of thermal engines-
- Internal combustion and
- External combustion engines.

The Doble steam car was an American steam car maker from 1909 to 1931. Its latter models of steam car, with fast-firing boiler and electric start, were considered the pinnacle of steam car development. The term "Doble steam car" comprises any of several makes of steam-powered automobile in the early 20th century, including Doble Detroit, Doble Steam Car, and Doble Automobile, severally called a "Doble" because of their founding by Abner Doble.
The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced mechanical complexity, and/or reduced emissions. These engines can be divided into two groups based on the number of pistons that contribute to the six strokes.
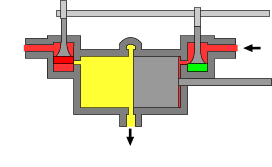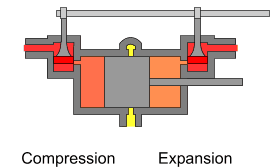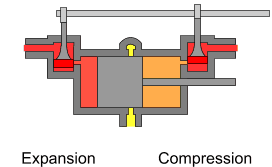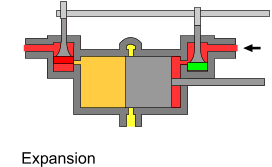
The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder and exhausts through ports at the cooler centre. By this means, the relative heating and cooling of the cylinder walls is reduced.

Advanced steam technology reflects an approach to the technical development of the steam engine intended for a wider variety of applications than has recently been the case. Particular attention has been given to endemic problems that led to the demise of steam power in small- to medium-scale commercial applications: excessive pollution, maintenance costs, labour-intensive operation, low power/weight ratio, and low overall thermal efficiency; where steam power has generally now been superseded by the internal combustion engine or by electrical power drawn from an electrical grid. The only steam installations that are in widespread use are the highly efficient thermal power plants used for generating electricity on a large scale. In contrast, the proposed steam engines may be for stationary, road, rail or marine use.

A two-stroke diesel engine is a diesel engine that uses compression ignition in a two-stroke combustion cycle. It was invented by Hugo Güldner in 1899.

The first recorded rudimentary steam engine was the aeolipile mentioned by Vitruvius between 30 and 15 BC and, described by Heron of Alexandria in 1st-century Roman Egypt. Several steam-powered devices were later experimented with or proposed, such as Taqi al-Din's steam jack, a steam turbine in 16th-century Ottoman Egypt, Denis Papin's working model of the steam digester in 1679 and Thomas Savery's steam pump in 17th-century England. In 1712, Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine became the first commercially successful engine using the principle of the piston and cylinder, which was the fundamental type of steam engine used until the early 20th century. The steam engine was used to pump water out of coal mines.

A compound engine is an engine that has more than one stage for recovering energy from the same working fluid, with the exhaust from the first stage passing through the second stage, and in some cases then on to another subsequent stage or even stages. Originally invented as a means of making steam engines more efficient, the compounding of engines by use of several stages has also been used on internal combustion engines and continues to have niche markets there.
A bash valve is a valve within a piston engine, used to control the admission of the working fluid. They are directly actuated valves, operated by contact between the piston and the valve tip.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.
















