Lt.Col.-Dr. John A. English (born 12 October 1940) is a Canadian Army veteran and a writer on historical and military topics.
Lt.Col.-Dr. John A. English (born 12 October 1940) is a Canadian Army veteran and a writer on historical and military topics.
English was educated at Royal Roads (1958–60) and the Royal Military College (1960–62), he went on leave without pay to attain an MA in history from Duke University in 1963-64. He passed final promotion exams in 1966 and graduated from Canadian Forces Staff College in 1972. He first joined the King's Own Calgary Regiment and from 1962 served in the Queen's Own Rifles of Canada until 1970, when he moved to Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry.
In 1980 he attained an MA in war studies from RMC, and a Ph.D. from Queen's University in 1989 while still in service. During his career he saw service with Canadian and British regiments in England, Germany, Denmark, Cyprus, Canada, and Alaska. English also served as a NATO war plans officer, Chief of Tactics of the Combat Training Centre, instructor at the Canadian Land Forces Command and Staff College, and curriculum director of the National Defence College. English retired from the Canadian army after 37 years of service in 1993. [1]
In 1992 English accepted a $60,000 Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada (SSHRCC) fellowship and a professorship at Queen's University. Two years later he was awarded a $31,000 SSHRCC research grant. For five years between 1997 and 2002 English served as a Professor of Strategy with the US Naval War College. On return to Canada he was employed until November 2003 as director of the Defence Minister's Monitoring Committee on Change. On 19 October 2004 the Minister appointed him Honorary Lieutenant-Colonel of the Brockville Rifles and from 2010 to 2013 he served as Honorary Colonel.
English is the author of:
He was also the co-author of On Infantry: Revised Edition (Praeger, 1994) [translated into Chinese] and principal editor of The Mechanized Battlefield: A Tactical Analysis (Pergamon, 1984). He has additionally produced numerous chapters for books and his articles have appeared in Military Affairs, Jane's Military Review, the Naval War College Review, Infantry magazine, the Marine Corps Gazette, the Canadian Defence Quarterly, the Canadian Military Journal and the proceedings of the Canadian Institute of Strategic Studies. He has been a member of the Royal Canadian Military Institute since 1971 and continues to write on military subjects.
Surrender Invites Death: Fighting the Waffen SS in Normandy (Stackpole, 2011).

Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and the Second World War.

The Queen's Own Rifles of Canada is a Primary Reserve regiment of the Canadian Armed Forces, based in Toronto. The regiment is part of 4th Canadian Division's 32 Canadian Brigade Group. It is the only reserve regiment in Canada to currently have a parachute role. The regiment consists of the reserve battalion, the Regimental Association, and the Regimental Band and Bugles. The official abbreviation is The QOR of C, but the name is often abbreviated to QOR.
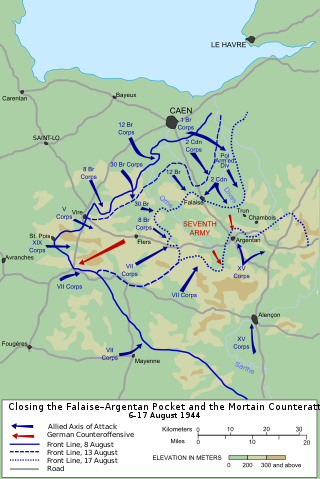
The Falaise pocket or battle of the Falaise pocket was the decisive engagement of the Battle of Normandy in the Second World War. Allied forces formed a pocket around Falaise, Calvados, in which German Army Group B, consisting of the 7th Army and the Fifth Panzer Army, were encircled by the Western Allies. The battle resulted in the destruction of most of Army Group B west of the Seine, which opened the way to Paris and the Franco-German border.

Paul Hausser also known as Paul Falk after taking his birth name post war was a German general and then a high-ranking commander in the Waffen-SS who played a key role in the post-war efforts by former members of the Waffen-SS to achieve historical and legal rehabilitation.

The 55th Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army's Territorial Army (TA) that was formed in 1920 and existed through the Second World War, although it did not see combat. The division had originally been raised in 1908 as the West Lancashire Division, part of the British Army's Territorial Force (TF). It fought in the First World War, as the 55th Division, and demobilised following the fighting. In 1920, the 55th Division started to reform. It was stationed in the county of Lancashire throughout the 1920s and 1930s, and was under-funded and under-staffed. In the late 1930s, the division was reduced from three to two infantry brigades and gave up some artillery and other support units to become a motorised formation, the 55th Motor Division. This was part of a British Army doctrine change that was intended to increase battlefield mobility.

The SS Division Hitlerjugend or 12th SS Panzer Division "Hitlerjugend" was a German armoured division of the Waffen-SS during World War II. The majority of its junior enlisted men were drawn from members of the Hitler Youth, while the senior NCOs and officers were from other Waffen-SS divisions. Most of the enlisted men were teenagers, starting from the ages of 16 or even 15.

General Henry Duncan Graham Crerar was a senior officer of the Canadian Army who became the country's senior field commander in the Second World War as commander of the First Canadian Army in the campaign in North West Europe in 1944–1945, having rapidly risen in rank from brigadier in 1939 to that of a full general in 1944.

Lieutenant-General Guy Granville Simonds, was a senior Canadian Army officer who served with distinction during World War II. Acknowledged by many military historians and senior commanders, among them Sir Max Hastings and Field Marshal Sir Bernard Montgomery, as one of the best Canadian generals of the war, Simonds, after serving the first few years of the Second World War mainly as a staff officer, commanded the 1st Canadian Infantry Division with distinction in Sicily and Italy from July 1943 until January 1944, and later II Canadian Corps during the Battle of Normandy from June−August 1944 and throughout the subsequent campaign in Western Europe from 1944, towards the end of which he temporarily commanded the First Canadian Army during the Battle of the Scheldt, until victory in Europe Day in May 1945. The historian J. L. Granatstein states about Simonds: "No Canadian commander rose higher and faster in the Second World War, and none did as well in action. Simonds owed his success wholly to his own abilities and efforts—and those of the men who served under him."

Alexander McCarrell Patch was a senior United States Army officer who fought in both world wars, rising to rank of general. During World War II, he commanded U.S. Army and Marine Corps forces during the Guadalcanal Campaign in the Pacific, and the Seventh Army on the Western Front in Europe.

Operation Charnwood was an Anglo-Canadian offensive that took place from 8 to 9 July 1944, during the Battle for Caen, part of the larger Operation Overlord in the Second World War. The operation was intended to capture the German-occupied city of Caen, which was an important objective for the Allies during the opening stages of Overlord. It was also hoped that the attack would forestall the transfer of German armoured units from the Anglo-Canadian sector to the American sector to the west, where an offensive was being prepared. The British and Canadians advanced on a broad front and by the evening of the second day had taken Caen up to the Orne and Odon rivers.

The Battle for Caen was a military engagement between the British Second Army and the German Panzergruppe West in the Second World War for control of the city of Caen and its vicinity during the Battle of Normandy.

Operation Tractable was the final attack conducted by Canadian and Polish troops, supported by a British tank brigade, during the Battle of Normandy during World War II. The operation was to capture the tactically important French town of Falaise and then the smaller towns of Trun and Chambois. This operation was undertaken by the First Canadian Army with the 1st Polish Armoured Division and a British armoured brigade against Army Group B of the Westheer in what became the largest encirclement on the Western Front during the Second World War. Despite a slow start and limited gains north of Falaise, novel tactics by the 1st Polish Armoured Division during the drive for Chambois enabled the Falaise Gap to be partially closed by 19 August 1944, trapping about 150,000 German soldiers in the Falaise Pocket.

Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful liberation of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Normandy landings. A 1,200-plane airborne assault preceded an amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August.

Operation Windsor(4–5 July 1944), was a Canadian attack of the Battle of Normandy during the Second World War. The attack was undertaken by the 3rd Canadian Infantry Division to take Carpiquet and the adjacent airfield from troops of the 12th SS-Panzer Division Hitler Jugend of Panzergruppe West. The attack was originally intended to take place during the later stages of Operation Epsom, to protect the eastern flank of the main assault but was postponed for a week.

The Battle of Le Mesnil-Patry during the Second World War, was the last attack by an armoured battle group conducted by Canadian troops in Normandy in June 1944. The Queen's Own Rifles of Canada of the 8th Canadian Infantry Brigade of the 3rd Canadian Division, supported by the 6th Armoured Regiment of the 2nd Canadian Armoured Brigade attacked the village of Le Mesnil-Patry in Normandy, to advance southwards towards the higher ground of Hill 107 to the west of Cheux. The attack was intended to support a larger operation by the 50th (Northumbrian) Infantry Division and the 7th Armoured Division to capture the city of Caen and to advance in the centre of the bridgehead next to the First US Army. The battle was a German defensive success but the greater German objective of defeating the invasion by a counter-offensive also failed.

The First Canadian Army was a field army and a formation of the Canadian Army in World War II in which most Canadian elements serving in North-West Europe were assigned. It served on the Western Front from July 1944 until May 1945. It was Canada's first and, so far, only field army.
The 85th Infantry Division was a Wehrmacht division used in the Second World War. It participated in the German defence in the Battle of Normandy, and took part in the German counter-offensive in the Ardennes.
The 70th Infantry Division was a unit of the German Army during World War II. It was formed in 1944 from personnel previously exempted from military service due to stomach disorders or injuries.
The following units and commanders participated in the Lorraine campaign from September 1 to December 18, 1944.
J.J. Fedorowicz Publishing is a Canadian publishing house that specialises in literature on the German armed forces of the World War II era. Its authors are both popular history writers such as Paul Carell and Franz Kurowski, along with the war-time veterans, including Kurt Meyer of the SS Division Hitlerjugend and Otto Weidinger of the SS Division Das Reich.