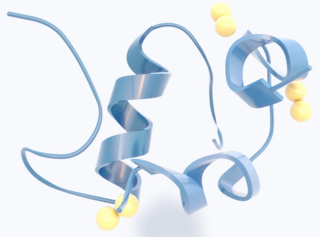
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (INS) gene. It is the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules in the cells. Low insulin in the blood has the opposite effect, promoting widespread catabolism, especially of reserve body fat.

John James Rickard Macleod, was a Scottish biochemist and physiologist. He devoted his career to diverse topics in physiology and biochemistry, but was chiefly interested in carbohydrate metabolism. He is noted for his role in the discovery and isolation of insulin during his tenure as a lecturer at the University of Toronto, for which he and Frederick Banting received the 1923 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.

The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum levels can be used to distinguish between different conditions with similar clinical features.

Eli Lilly and Company, doing business as Lilly, is an American multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana, with offices in 18 countries. Its products are sold in approximately 125 countries. The company was founded in 1876 by Eli Lilly, a pharmaceutical chemist and Union Army veteran of the American Civil War for whom the company was later named.

The Indiana University School of Medicine (IUSM) is a major, multi-campus medical school located throughout the U.S. state of Indiana and is the graduate medical school of Indiana University. There are nine campuses throughout the state; the principal research, educational, and medical center is located on the campus of Indiana University Indianapolis. With 1,461 MD students, 195 PhD students, and 1,442 residents and fellows in the 2023–24 academic year, IUSM is the largest medical school in the United States. The school offers many joint degree programs including an MD/PhD Medical Scientist Training Program. It has partnerships with Purdue University's Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, other Indiana University system schools, and various in-state external institutions. It is the medical school with the largest number of graduates licensed in the United States per a 2018 Federation of State Medical Boards survey with 11,828 licensed physicians.

Tolbutamide is a first-generation potassium channel blocker, sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic medication. This drug may be used in the management of type 2 diabetes if diet alone is not effective. Tolbutamide stimulates the secretion of insulin by the pancreas.

Eli Lilly was a Union Army officer, pharmacist, chemist, and businessman who founded Eli Lilly and Company.

The Sidney & Lois Eskenazi Hospital is a public hospital located in Indianapolis, Indiana. The hospital is the flagship medical center for Eskenazi Health, founded in 1859 as Indiana's oldest public healthcare system. The hospital is operated by Health and Hospital Corporation of Marion County. The current hospital opened December 7, 2013, less than 1,300 feet (400 m) to the west of the original campus, replacing Wishard Memorial Hospital.

Donald Frederick Steiner was an American biochemist and a professor at the University of Chicago.
Robert William Schrier was founding editor-in-chief of the magazine Nature Clinical Practice Nephrology. Schrier was formerly Chairman of the Department of Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine for 26 years, and Head of the Division of Renal Diseases and Hypertension for 20 years. At the time of his death, he was Professor Emeritus at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. He died in Potomac, Maryland.

Robert J. Desnick is an American human geneticist whose basic and translational research accomplishments include significant discoveries in genomics, pharmacogenetics, gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the treatment of genetic diseases. His translational research has led to the development of the enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and the chaperone therapy for Fabry disease, ERT for Niemann–Pick disease type B, and the RNA Interference Therapy for the Acute Hepatic Porphyrias.

James M. Galloway is an American public health physician. Galloway served as the Regional Health Administrator for the United States Department of Health and Human Services for the six eastern states that comprise Region V under Presidents George W. Bush and Barack Obama. He also served as the Senior Federal Official for Health for Pandemic Influenza and Bioterrorism for the Department of Homeland Security's Region C, which includes an additional six states. Galloway was the lead for one of CDC's lead efforts as the Director of the Office of Health System Collaboration, integrating clinical care and public health at a national level.

Moussa B. H. Youdim is an Israeli neuroscientist specializing in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology. He is the discoverer of both monoamine oxidase (MAO) B inhibitors l-deprenyl (Selegiline) and rasagiline (Azilect) as anti-Parkinson drugs which possess neuroprotective activities. He is currently professor emeritus at Technion - Faculty of Medicine and President of Youdim Pharmaceuticals.

Carl Ronald Kahn is an American physician and scientist, best known for his work with insulin receptors and insulin resistance in diabetes and obesity. He is the Chief Academic Officer at Joslin Diabetes Center, the Mary K. Iacocca Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and a member of the National Academy of Sciences since 1999.

José F. Caro is an American physician, scientist, and educator most notable for his research in obesity and diabetes. The Institute for Scientific Information listed him the third most cited investigator in the world in the field of obesity research during the 1991-2000 period for his work on Leptin. Caro is an artist and a signature member of the Pastel Society of America.
Harvey N. Middleton was an American physician and cardiologist in Indianapolis, Indiana, who is best known for his efforts to open opportunities for black physicians to serve on the staffs of Indianapolis hospitals and for his community service. Middleton was born in Denmark, South Carolina, and received a Bachelor of Arts degree from Benedict College (1919) in Columbia, South Carolina. He attended two years of medical school at Boston University before transferring to Meharry Medical College, in Nashville, Tennessee, where he received a medical degree (M.D.) in 1926. Middleton took short courses for additional training at Harvard University; the University of London, England; the University of Michigan; Indiana University; and Michael Reese Hospital in Chicago. In 1928 Middleton moved to Anderson, Indiana, where he joined the staff of Saint Johns Hospital. Around 1935 he relocated to Indianapolis, established a private medical practice, and volunteered at Indianapolis General (City) Hospital's outpatient heart clinic. Middleton was accepted as a member of City Hospital staff in 1942 and joined the staffs at other Indianapolis hospitals. Middleton wrote several articles relating to cardiology that appear in state and national medical journals. He was a member of the American Medical Association, the National Medical Association, the American Heart Association, the Indiana State Medical Association, the Hoosier State Medical Society, and others.
Shashank R. Joshi is an Indian endocrinologist, diabetologist and medical researcher, considered by many as one of the prominent practitioners of the trade in India. He was honoured by the Government of India, in 2014, by bestowing on him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, for his services to the field of medicine. He is a part of the COVID-19 Task Force for the state of Maharashtra, India.
Pharmaceutical innovations are currently guided by a patent system, the patent system protects the innovator of medicines for a period of time. The patent system does not currently stimulate innovation or pricing that provides access to medicine for those who need it the most, It provides for profitable innovation. As of 2014 about $140 Billion is spent on research and development of pharmaceuticals which produces 25–35 new drugs annually. Technology, which is transforming science, medicine, and research tools has increased the speed at which we can analyze data but we currently still must test the products which is a lengthy process. Differences in the performance of medical care may be due to variation in the introduction and circulation of pharmaceutical innovations.
Undurti Narasimha Das shortly Undurti N. Das and U. N. Das is an Indian clinical immunologist, endocrinologist and the founder president and chief executive officer of UND Life Sciences. Additionally, he serves as the Chief Medical Officer and the Chairman of the Scientific Advisory Board of Asha Nutrition Sciences, Inc. An elected fellow of the National Academy of Medical Sciences, Das is known for his researches in the fields of Immunology, Endocrinology and Rheumatology. He holds a number of patents for his work The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Medical Sciences in 1992.
Richard B. Gaynor is an American physician specializing in hematology-oncology, educator, drug developer, and business executive. He served as an Associate Professor of Medicine at UCLA School of Medicine for nearly a decade, and subsequently as an endowed Professor of Medicine and Microbiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical School prior to joining the pharmaceutical industry in 2002. His research on NF-κB, IκB kinase, and other mechanisms regulating viral and cellular gene expression has been covered in leading subject reviews. He has been a top executive at several pharmaceutical companies, with respect to the development and clinical testing of novel anticancer drugs and cell therapies. For over a decade and a half, he worked at Eli Lilly and Company, where he became the Senior Vice President of Oncology Clinical Development and Medical Affairs in 2013. Gaynor was President of R&D at Neon Therapeutics from 2016 to 2020, when he became the President of BioNTech US, both pharmaceutical companies headquartered in Cambridge, MA. His honors include being elected a member of the American Society for Clinical Investigation, and the Association of American Physicians.













