John Churin is Chief Technology Officer for Tolven. He is well known in the industry as the original developer and architect for the ALL-IN-1 office-automation product suite in 1977 while working for Digital Equipment Corporation [1] . [2]
John Churin is Chief Technology Officer for Tolven. He is well known in the industry as the original developer and architect for the ALL-IN-1 office-automation product suite in 1977 while working for Digital Equipment Corporation [1] . [2]

Digital Equipment Corporation, using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline.

Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis. It is the study of numerical methods that attempt at finding approximate solutions of problems rather than the exact ones. Numerical analysis finds application in all fields of engineering and the physical sciences, and in the 21st century also the life and social sciences, medicine, business and even the arts. Current growth in computing power has enabled the use of more complex numerical analysis, providing detailed and realistic mathematical models in science and engineering. Examples of numerical analysis include: ordinary differential equations as found in celestial mechanics, numerical linear algebra in data analysis, and stochastic differential equations and Markov chains for simulating living cells in medicine and biology.
In computing, the Post Office Protocol (POP) is an application-layer Internet standard protocol used by e-mail clients to retrieve e-mail from a mail server. POP version 3 (POP3) is the version in common use, and along with IMAP the most common protocols for email retrieval.

OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using OpenVMS include banks and financial services, hospitals and healthcare, telecommunications operators, network information services, and industrial manufacturers. During the 1990s and 2000s, there were approximately half a million VMS systems in operation worldwide.
The Perseus Digital Library, formerly known as the Perseus Project, is a free-access digital library founded by Gregory Crane in 1987 and hosted by the Department of Classical Studies of Tufts University. One of the pioneers of digital libraries, its self-proclaimed mission is to make the full record of humanity available to everyone. While originally focused on the ancient Greco-Roman world, it has since diversified and offers materials in Arabic, Germanic, English Renaissance literature, 19th century American documents and Italian poetry in Latin, and has sprouted several child projects and international cooperation. The current version, Perseus 4.0, is also known as the Perseus Hopper, and is mirrored by the University of Chicago.

Guy Lewis Steele Jr. is an American computer scientist who has played an important role in designing and documenting several computer programming languages and technical standards.

The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and modern computing technology and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper or for chalk and slate, with or without the aid of tables.

Digital Anvil, Inc. was an American video game developer based in Austin, Texas owned by Microsoft Game Studios (MGS). It was founded in 1996 by brothers Chris and Erin Roberts along with Tony Zurovec, Marten Davies, Craig Cox, John Miles, Eric Peterson and Robert Rodriguez, creators of the Wing Commander franchise from Origin Systems.

Mobile computing is human–computer interaction in which a computer is expected to be transported during normal usage and allow for transmission of data, which can include voice and video transmissions. Mobile computing involves mobile communication, mobile hardware, and mobile software. Communication issues include ad hoc networks and infrastructure networks as well as communication properties, protocols, data formats, and concrete technologies. Hardware includes mobile devices or device components. Mobile software deals with the characteristics and requirements of mobile applications.
In parallel computing, an embarrassingly parallel workload or problem is one where little or no effort is needed to separate the problem into a number of parallel tasks. This is often the case where there is little or no dependency or need for communication between those parallel tasks, or for results between them.
AdvFS, also known as Tru64 UNIX Advanced File System, is a file system developed in the late 1980s to mid-1990s by Digital Equipment Corporation for their OSF/1 version of the Unix operating system. In June 2008, it was released as free software under the GPL-2.0-only license. AdvFS has been used in high-availability systems where fast recovery from downtime is essential.
Randi J. Rost is a computer graphics professional and frequent contributor to graphics standards. He was an early participant in the personal computer industry, creating a game called King Cribbage for the Apple II computer in 1981 and publishing numerous instructional and review articles in trade publications.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to information technology:

A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster.

A transistor computer, now often called a second-generation computer, is a computer which uses discrete transistors instead of vacuum tubes. The first generation of electronic computers used vacuum tubes, which generated large amounts of heat, were bulky and unreliable. A second-generation computer, through the late 1950s and 1960s featured circuit boards filled with individual transistors and magnetic-core memory. These machines remained the mainstream design into the late 1960s, when integrated circuits started appearing and led to the third-generation computer.
In telecommunications, echo is the local display of data, either initially as it is locally sourced and sent, or finally as a copy of it is received back from a remote destination. Local echo is where the local sending equipment displays the outgoing sent data. Remote echo is where the display is a return copy of data as received remotely. Both are used together in a computed form of error detection to ensure that data received at the remote destination of a telecommunication are the same as data sent from the local source. When (two) modems communicate in echoplex mode the remote modem echoes whatever it receives from the local modem.
In computer architecture, 16-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 16 bits wide. Also, 16-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. 16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.

Ayttm is a multi-protocol instant messaging client. It is the heir of the EveryBuddy project.
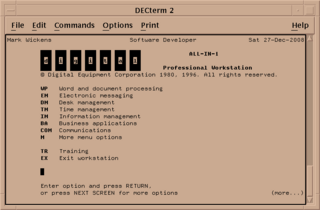
ALL-IN-1 was an office automation product developed and sold by Digital Equipment Corporation in the 1980s. It was one of the first purchasable off the shelf electronic mail products. It was later known as Office Server V3.2 for OpenVMS Alpha and OpenVMS VAX systems before being discontinued.

Michael James Halvorson is an American technology writer and historian. He was employed at Microsoft Corporation from 1985 to 1993 and contributed to the growth of the Microsoft Office and Microsoft Visual Basic software platforms. He is the author of 40 books related to computer programming, using PC software, and the histories of Europe and the United States.