John FitzJohn | |
|---|---|
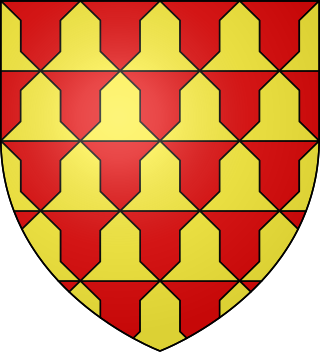
 Arms of John FitzJohn. Quarterly, or and gules, a border vair. [1] | |
| Died | 1275 |
| Father | John Fitzgeoffrey |
| Mother | Isabel Bigod |
John FitzJohn (died 1275) was an English nobleman who was a leading baron during the Second Barons' War.
John FitzJohn | |
|---|---|
 Arms of John FitzJohn. Quarterly, or and gules, a border vair. [1] | |
| Died | 1275 |
| Father | John Fitzgeoffrey |
| Mother | Isabel Bigod |
John FitzJohn (died 1275) was an English nobleman who was a leading baron during the Second Barons' War.
Fitz-John was the eldest son of John Fitzgeoffrey and Isabel Bigod.
John married Margery, daughter of Philip Basset and his wife Hawise de Lovaine. During 1263, FitzJohn joined the baronial revolt led by Simon de Montfort, Earl of Leicester. He was a leader of a division of the baronial army at the Battle of Lewes. [2] After the battle he marched with Montfort towards Wales, reducing Richard's Castle and Ludlow Castle. He was subsequently appointed by the rebel barons, Sheriff of Westmorland, keeper of the castles in Westmorland and governor of Windsor Castle. [2] FitzJohn was later captured at the Battle of Evesham and was imprisoned. FitzJohn was forfeited of his lands, with King Henry III of England granting them to Gilbert de Clare, Earl of Gloucester. [2] FitzJohn was able to recover his lands afterwards under the "dictum of Kenilworth".
FitzJohn died in 1275, without issue, and was succeeded by his brother Richard. [2]

The Dictum of Kenilworth, issued on 31 October 1266, was a pronouncement designed to reconcile the rebels of the Second Barons' War with the royal government of England. After the baronial victory at the Battle of Lewes in 1264, Simon de Montfort took control of royal government, but at the Battle of Evesham the next year Montfort was killed, and King Henry III restored to power. A group of rebels held out in the stronghold of Kenilworth Castle, however, and their resistance proved difficult to crush.

Year 1264 (MCCLXIV) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.

Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, later sometimes referred to as Simon V de Montfort to distinguish him from his namesake relatives, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the baronial opposition to the rule of King Henry III of England, culminating in the Second Barons' War. Following his initial victories over royal forces, he became de facto ruler of the country, and played a major role in the constitutional development of England.

The Battle of Lewes was one of two main battles of the conflict known as the Second Barons' War. It took place at Lewes in Sussex, on 14 May 1264. It marked the high point of the career of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, and made him the "uncrowned King of England". Henry III left the safety of Lewes Castle and St. Pancras Priory to engage the barons in battle and was initially successful, his son Prince Edward routing part of the baronial army with a cavalry charge. However, Edward pursued his quarry off the battlefield and left Henry's men exposed. Henry was forced to launch an infantry attack up Offham Hill where he was defeated by the barons' men defending the hilltop. The royalists fled back to the castle and priory and the King was forced to sign the Mise of Lewes, ceding many of his powers to de Montfort.
The Battle of Evesham was one of the two main battles of 13th century England's Second Barons' War. It marked the defeat of Simon de Montfort, Earl of Leicester, and the rebellious barons by the future King Edward I, who led the forces of his father, King Henry III. It took place on 4 August 1265, near the town of Evesham, Worcestershire.
Peter II, called the Little Charlemagne, was Count of Savoy from 1263 until his death in 1268. He was also holder of the Honour of Richmond, Yorkshire, England, the Honour of the Eagle also known as the Honour of Pevensey and the Honour of Eu also known as the Honour of Hastings. His significant land holdings in Sussex were also marked by his holding of the wardship of John de Warenne, 6th Earl of Surrey which brought with it lands centred upon Lewes castle. Briefly, from 1241 until 1242, castellan of Dover Castle and Keeper of the Coast. In 1243 he was granted land by the Thames in London where he later built the Savoy Palace.

Ralph Neville, 1st Earl of WestmorlandEarl Marshal, was an English nobleman of the House of Neville.

The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in England between the forces of a number of barons led by Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of King Henry III, led initially by the king himself and later by his son, the future King Edward I. The barons sought to force the king to rule with a council of barons, rather than through his favourites. The war also involved a series of massacres of Jews by de Montfort's supporters, including his sons Henry and Simon, in attacks aimed at seizing and destroying evidence of baronial debts. To bolster the initial success of his baronial regime, de Montfort sought to broaden the social foundations of parliament by extending the franchise to the commons for the first time. However, after a rule of just over a year, de Montfort was killed by forces loyal to the king at the Battle of Evesham.
Richard FitzRoy was the illegitimate son of King John of England and was feudal baron of Chilham, in Kent. His mother was Adela, his father's first cousin and a daughter of Hamelin de Warenne by his wife Isabel de Warenne, 4th Countess of Surrey.

Henry of Almain, also called Henry of Cornwall, was the eldest son of Richard, Earl of Cornwall, afterwards King of the Romans, by his first wife Isabel Marshal. His surname is derived from a vowel shift in pronunciation of d'Allemagne ; he was so called by the elites of England because of his father's status as the elected German King of Almayne.
Peter de Montfort of Beaudesert Castle was an English magnate, soldier and diplomat. He is the first person recorded as having presided over Parliament as a parlour or prolocutor, an office now known as Speaker of the House of Commons. He was one of those elected by the barons to represent them during the constitutional crisis with Henry III in 1258. He was later a leading supporter of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester against the King. Both he and Simon de Montfort were slain at the Battle of Evesham on 4 August 1265.
Robert de Ferrers, 6th Earl of Derby (1239–1279) was an English nobleman.
Events from the 1260s in England.

The Neville or Nevill family is a noble house of early medieval origin, which was a leading force in English politics in the Late Middle Ages. The family became one of the two major powers in northern England and played a central role in the Wars of the Roses along with their rival, the House of Percy.

The Mise of Amiens was a settlement given by King Louis IX of France on 23 January 1264 in the conflict between King Henry III of England and his rebellious barons, led by Simon de Montfort. Louis' one-sided decision for King Henry led directly to the hostilities of the Second Barons' War.
Alice Neville, Baroness FitzHugh or Lady Alice FitzHugh, was the wife of Henry FitzHugh, 5th Baron FitzHugh. She is best known for being the great-grandmother of queen consort Catherine Parr and her siblings, Anne and William, as well as one of the sisters of Warwick the 'Kingmaker'. Her family was one of the oldest and most powerful families of the North. They had a long-standing tradition of military service and a reputation for seeking power at the cost of the loyalty to the crown as was demonstrated by her brother, the Earl of Warwick.
Robert de Vieuxpont, also called Vipont, Veteripont, or de Vetere Ponte, Baron of Westmorland, was an Anglo-Norman noble landowner and administrator.
William Devereux, was an important Marcher Lord, and held Lyonshall Castle controlling a strategically vital approach to the border of Wales. The castle's significance was heightened by the rebellion of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, Prince of Wales. With strong family ties to the politically powerful families of Cantilupe and Giffard, his support was strongly sought after by Henry III and Simon de Montfort throughout the Second Barons' War.

There have been four different baronies held by the Marmion family, two feudal baronies, one purported barony created by Simon de Montfort and one barony by writ.

Robert de Neville, 2nd Baron Neville of Raby, was a medieval English nobleman.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)