Related Research Articles
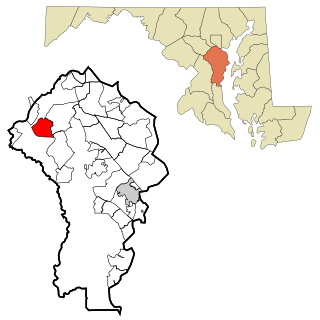
Fort Meade is a census-designated place (CDP) in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, United States. The population was 9,327 at the 2010 census. It is the home to the National Security Agency, Central Security Service, United States Cyber Command and the Defense Information Systems Agency, which are located on the U.S. Army post Fort George G. Meade.

Walla Walla University is a private Adventist university in College Place, Washington. The university has five campuses throughout the Pacific Northwest. It was founded in 1892 and is affiliated with the Seventh-day Adventist Church.
Parsons School of Design, known colloquially as Parsons, is a private art and design college located in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of New York City. Founded in 1896 after a group of progressive artists broke away from established Manhattan art academies in protest of limited creative autonomy, Parsons is one of the oldest schools of art and design in New York.

Great Basin College is a public college in Elko, Nevada, United States. Opened in 1967 as Elko College, it was later renamed to Northern Nevada College and then to its current name. It has 3,836 students and is a member of the Nevada System of Higher Education.

Webb Institute is a private college focused on engineering and located in Glen Cove, New York. Each graduate of Webb Institute earns a Bachelor of Science degree in naval architecture and marine engineering. The school is noted in the marine industry for its unique emphasis on ship design, systems engineering, practical work experience, and free tuition for domestic students.
Dana College was a private college in Blair, Nebraska. Its rural 150-acre campus is approximately 26 miles (40 km) northwest of Omaha and overlooks a portion of the Missouri River Valley. It closed in 2010.

Green River College is a public community college in Auburn, Washington, United States. It has a student body of over 13,000 and has satellite campuses in nearby cities of Kent and Enumclaw, Washington. The college primarily awards associates degrees but also offers 9 bachelor's degrees.

Parsons College was a private liberal arts college located in Fairfield, Iowa. The school was named for its wealthy benefactor, Lewis B. Parsons Sr., and was founded in 1875 with one building and 34 students. Over the years new buildings were constructed as enrollment expanded. The school lost its accreditation in 1948 but regained it two years later. In 1955 the school appointed Millard G. Roberts as its president and this began a period of rapid expansion with the student population rising as high as 5,000 by 1966. There was a turning point, however, in 1966 when Life magazine published an article criticizing the college and its president. In the spring of 1967, the school lost its accreditation and Roberts was asked to resign as president. Although they regained their accreditation in the spring of 1970, enrollment had quickly declined and the college floundered with $14 million in debt and closed under bankruptcy in 1973.

Southeast Community College (SCC) is a public community college system in the southeast portion of Nebraska.

The Joint Forces Staff College (JFSC), located in Norfolk, Virginia, was established as the Armed Forces Staff College in 1946 and incorporated into the National Defense University in August 1981. It educates and acculturates joint and multinational warfighters to plan and lead at the operational level. Military operations increasingly require the Armed Services to work jointly, and JFSC provides students the tools to operate in a joint environment. JFSC is composed of three schools, each with different student populations and purposes.
The history of school counseling in the United States of America varies greatly based on how local communities have chosen to provide academic, career, college readiness, and personal/social skills and competencies to K-12 children and their families based on economic and social capital resources and public versus private educational settings in what is now called a school counseling program.
The history of New York University begins in the early 19th century. A group of prominent New York City residents from the city's landed class of merchants, bankers, and traders established NYU on April 18, 1831. These New Yorkers believed the city needed a university designed for young men who would be admitted based on merit, not birthright or social class. Albert Gallatin, one of the founders of the university, described his motivation in a letter to a friend: "It appeared to me impossible to preserve our democratic institutions and the right of universal suffrage unless we could raise the standard of general education and the mind of the laboring classes nearer to a level with those born under more favorable circumstances." For the school's founders, the classical curriculum offered at American colonial colleges needed to be combined with a more modern and practical education. Educators in Paris, Vienna, and London were beginning to consider a new form of higher learning, where students began to focus not only on the classics and religion, but also modern languages, philosophy, history, political economy, mathematics, and physical science; so students might become merchants, bankers, lawyers, physicians, architects, and engineers. Although the new school would be non-denominational – unlike many American colonial colleges, which at the time offered classical educations centered on theology – the founding of NYU was also a reaction by evangelical Presbyterians to what they perceived as the Episcopalianism of Columbia College.

Hiram Scott College was a private liberal arts college that operated from 1965 to 1972 in Scottsbluff, Nebraska. Named after Hiram Scott (1805–1828), a fur trapper with the Rocky Mountain Fur Company who was found dead in the vicinity on his return trip from a fur expedition, the institution was one of several Midwestern colleges established by local civic leaders with the support of Parsons College in Fairfield, Iowa. These Parsons "satellite schools" were by-products of the strong growth and apparent success of Parsons during the late 1950s and early 1960s, and all followed the "Parsons Plan" academic model developed at that school. None of the schools, however, were ultimately successful.

John F. Kennedy College was founded in 1965 in Wahoo, Nebraska, United States, one of six colleges started by small-town businessmen on the model of Parsons College in Fairfield, Iowa. The college was named after President John F. Kennedy. Due to a drop in enrollment, financial difficulties and 3 fires following the end of the military conscription draft in 1973, Kennedy College closed in 1975.

The College of Artesia was a private liberal arts college that operated from 1966 to 1973 in Artesia, New Mexico. It was one of several colleges established by local civic leaders with the support and encouragement of Parsons College in Fairfield, Iowa. These Parsons "satellite schools" were by-products of the strong growth and apparent success of Parsons during the late 1950s and early 1960s, and all followed the "Parsons Plan" academic model developed at that school. None of the schools, however, was ultimately successful.
Lea College was a private liberal arts college that operated from 1966 to 1973 in Albert Lea, Minnesota, United States. Lea was one of several Midwestern colleges established by local civic leaders with the support and encouragement of Parsons College in Fairfield, Iowa. These Parsons "satellite schools" were by-products of the strong growth and apparent success of Parsons during the late 1950s and early 1960s, and all followed the "Parsons Plan" academic model developed at that school. None of the schools, however, was ultimately successful.

Midwestern College was a private liberal arts college that operated from 1965 to 1970 in Denison, Iowa. Midwestern was one of several colleges in the upper Midwest established by local civic leaders with the support and encouragement of Parsons College in Fairfield, Iowa. These Parsons "satellite schools" were by-products of the strong growth and apparent success of Parsons during the late 1950s and early 1960s, and all followed the "Parsons Plan" academic model developed at that school. None of the schools, however, were ultimately successful.
Charles City College was a private liberal arts college that operated from 1967 to 1968 in Charles City, Iowa. It was one of several Midwestern colleges established by local civic leaders with the support and encouragement of Parsons College in Fairfield, Iowa. These Parsons "satellite schools" were by-products of the strong growth and apparent success of Parsons during the late 1950s and early 1960s, and all followed the "Parsons Plan" academic model developed at that school. None of the schools, however, were ultimately successful.

Lehigh Carbon Community College (LCCC), often pronounced "L-tri-C," is an American public community college with a main campus in Schnecksville, Pennsylvania, in the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. The college also maintains satellite campuses in Allentown, also in the Lehigh Valley, and Tamaqua in Schuylkill County.

University City High School was a public secondary school in the University City section of West Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, which operated from 1972 to 2013.
References
- Koerner, James D. (1970). The Parsons College Bubble: A Tale of Higher Education in America . New York: Basic Books, Inc. pp. 217–220. ISBN 9780465054541.
40°15′39″N96°47′22″W / 40.26083°N 96.78944°W