The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar.

Pope Gregory I, commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the 64th Bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instituting the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregorian mission, to convert the then largely pagan Anglo-Saxons to Christianity. Gregory is also well known for his writings, which were more prolific than those of any of his predecessors as pope. The epithet Saint Gregory the Dialogist has been attached to him in Eastern Christianity because of his Dialogues. English translations of Eastern texts sometimes list him as Gregory "Dialogos" from the Greek διάλογος, or the Anglo-Latinate equivalent "Dialogus".

Theodelinda also spelled Theudelinde, was a queen of the Lombards by marriage to two consecutive Lombard rulers, Autari and then Agilulf, and regent of Lombardia during the minority of her son Adaloald, and co-regent when he reached majority, from 616 to 626. For well over thirty years, she exercised influence across the Lombard realm, which comprised most of Italy between the Apennines and the Alps. Born a Frankish Catholic, she convinced her first spouse Autari to convert from pagan beliefs to Christianity.

The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest was a conflict between the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture) and abbots of monasteries and the pope himself. A series of popes in the 11th and 12th centuries undercut the power of the Holy Roman Emperor and other European monarchies, and the controversy led to nearly 50 years of conflict.
Pope Donus was the bishop of Rome from 676 to his death. Few details survive about him or his achievements beyond what is recorded in the Liber Pontificalis.

The early Middle Ages, sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and preceding the High Middle Ages. The alternative term late antiquity, for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while early Middle Ages is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period.
In ancient Greece, the term ecumene (U.S.) or oecumene denoted the known, inhabited, or habitable world. In Greek antiquity, it referred to the portions of the world known to Hellenic geographers, subdivided into three continents: Africa, Europe, and Asia. Under the Roman Empire, it came to refer to civilization itself, as well as the secular and religious imperial administration.

Late antiquity is sometimes defined as spanning from the end of classical antiquity to the local start of the Middle Ages, from around the late 3rd century up to the 7th or 8th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin depending on location. The popularisation of this periodization in English has generally been credited to historian Peter Brown, who proposed a period between 150–750 AD. The Oxford Centre for Late Antiquity defines it as "the period between approximately 250 and 750 AD". Precise boundaries for the period are a continuing matter of debate. In the West, its end was earlier, with the start of the Early Middle Ages typically placed in the 6th century, or even earlier on the edges of the Western Roman Empire.
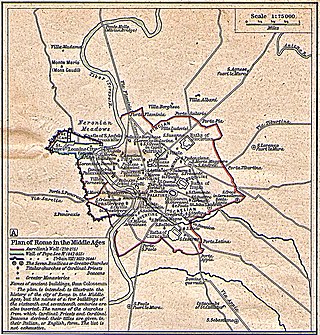
The Leonine City is the part of the city of Rome which, during the Middle Ages, was enclosed with the Leonine Wall, built by order of Pope Leo IV in the 9th century.

Liutprand was the king of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his multiple phases of law-giving, in fifteen separate sessions from 713 to 735 inclusive, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mostly successful, with most of Italy. He is often regarded as the most successful Lombard monarch, notable for the Donation of Sutri in 728, which was the first accolade of sovereign territory to the Papacy.

Liuvigild, Leuvigild, Leovigild, or Leovigildo, was a Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania from 568 to 586. Known for his Codex Revisus or Code of Leovigild, a law allowing equal rights between the Visigothic and Hispano-Roman population, his kingdom covered modern Portugal and most of modern Spain down to Toledo. Liuvigild ranks among the greatest Visigothic kings of the Arian period.

Sisebut was King of the Visigoths and ruler of Hispania and Septimania from 612 until his death in 621. His rule was marked by forced Christian conversion, anti-Judaic measures, Roman-like administration, and intellectual cosmopolitanism.

The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom was the mostly Germanic-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, especially after the kingship passed from Frankish kings to the Saxon Ottonian dynasty in 919. The king was elected, initially by the rulers of the stem duchies, who generally chose one of their own. After 962, when Otto I was crowned emperor, East Francia formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire, which also included the Kingdom of Italy and, after 1032, the Kingdom of Burgundy.

According to Roman Catholicism, the history of the papacy, the office held by the pope as head of the Catholic Church, spans from the time of Peter to the present day.
Peter John Heather is a British historian of late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Heather is Chair of the Medieval History Department and Professor of Medieval History at King's College London. He specialises in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Goths, on which he for decades has been considered the world's leading authority.
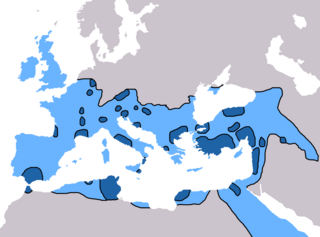
In 6th-century Christianity, Roman Emperor Justinian launched a military campaign in Constantinople to reclaim the western provinces from the Germans, starting with North Africa and proceeding to Italy. Though he was temporarily successful in recapturing much of the western Mediterranean he destroyed the urban centers and permanently ruined the economies in much of the West. Rome and other cities were abandoned. In the coming centuries the Western Church, as virtually the only surviving Roman institution in the West, became the only remaining link to Greek culture and civilization.

Christianity in late antiquity traces Christianity during the Christian Roman Empire — the period from the rise of Christianity under Emperor Constantine, until the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The end-date of this period varies because the transition to the sub-Roman period occurred gradually and at different times in different areas. One may generally date late ancient Christianity as lasting to the late 6th century and the re-conquests under Justinian of the Byzantine Empire, though a more traditional end-date is 476, the year in which Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustus, traditionally considered the last western emperor.
Tiberius was the second son of Byzantine Emperor Maurice and his wife Constantina. His father intended him to inherit Italy and the western islands, centered in Rome; however, this did not come to fruition as his father was overthrown by the new Emperor Phocas, who had him and his father executed, along with his younger brothers, in the Harbor of Eutropius, Chalcedon.

European science in the Middle Ages comprised the study of nature, mathematics and natural philosophy in medieval Europe. Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the decline in knowledge of Greek, Christian Western Europe was cut off from an important source of ancient learning. Although a range of Christian clerics and scholars from Isidore and Bede to Jean Buridan and Nicole Oresme maintained the spirit of rational inquiry, Western Europe would see a period of scientific decline during the Early Middle Ages. However, by the time of the High Middle Ages, the region had rallied and was on its way to once more taking the lead in scientific discovery. Scholarship and scientific discoveries of the Late Middle Ages laid the groundwork for the Scientific Revolution of the Early Modern Period.

Renovatio imperii Romanorum was a formula declaring an intention to restore or revive the Roman Empire. The formula was used by several emperors of the Carolingian and Ottonian dynasties, but the idea was common during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages.














