Related Research Articles

The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an independent International research institute located in Laxenburg, near Vienna in Austria, founded as an East-West scientific cooperation initiative during the Cold War. Through its research programs and initiatives, the institute conducts policy-oriented interdisciplinary research into issues too large or complex to be solved by a single country or academic discipline. These include climate change, energy security, population aging, and sustainable development. The results of IIASA research and the expertise of its researchers are made available to policymakers worldwide to help them make informed and evidence-based policies.
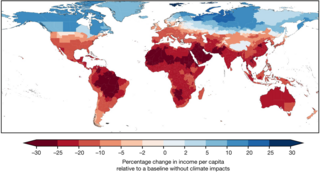
Economic analysis of climate change is using economic tools and models to calculate the magnitude and distribution of damages caused by climate change. It can also give guidance for the best policies for mitigation and adaptation to climate change from an economic perspective. There are many economic models and frameworks. For example, in a cost–benefit analysis, the trade offs between climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation are made explicit. For this kind of analysis, integrated assessment models (IAMs) are useful. Those models link main features of society and economy with the biosphere and atmosphere into one modelling framework. The total economic impacts from climate change are difficult to estimate. In general, they increase the more the global surface temperature increases.

Resources for the Future (RFF) is an American nonprofit organization, founded in 1952, that conducts independent research into environmental, energy, and natural resource issues, primarily via economics and other social sciences. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., RFF performs research around the world.

Mark Diesendorf is an Australian academic and environmentalist, known for his work in sustainable development and renewable energy. He currently researches at the University of New South Wales, Australia. He was formerly professor of environmental science and founding director of the Institute for Sustainable Futures at the University of Technology, Sydney and before that a principal research scientist with CSIRO, where he was involved in early research on integrating wind power into electricity grids. His most recent books are The Path to a Sustainable Civilisation (2023) and Sustainable Energy Solutions for Climate Change (2014).

Mark Kenneth Jaccard is a Canadian energy economist and author. He develops and applies models that assess sustainability policies for energy and material. Jaccard is a professor of sustainable energy in the School of Resource and Environmental Management (REM) at Simon Fraser University.
Integrated assessment modelling (IAM) or integrated modelling (IM) is a term used for a type of scientific modelling that tries to link main features of society and economy with the biosphere and atmosphere into one modelling framework. The goal of integrated assessment modelling is to accommodate informed policy-making, usually in the context of climate change though also in other areas of human and social development. While the detail and extent of integrated disciplines varies strongly per model, all climatic integrated assessment modelling includes economic processes as well as processes producing greenhouse gases. Other integrated assessment models also integrate other aspects of human development such as education, health, infrastructure, and governance.
The Energy Modeling Forum (EMF) is a structured forum for discussing important issues in energy and the environment. The EMF was established in 1976 at Stanford University. The EMF works through a series of ad hoc working groups, each focussing on a particular corporate or policy decision. The EMF provides a non-partisan platform that ensures objective consideration of opposing views. Participation is by invitation.
Kenneth Caldeira is an American atmospheric scientist. His areas of research include ocean acidification, climate effects of trees, intentional climate modification, interactions in the global carbon cycle/climate system, and sustainable energy.

The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research is a German government-funded research institute addressing crucial scientific questions in the fields of global change, climate impacts, and sustainable development. Ranked among the top environmental think tanks worldwide, it is one of the leading research institutions and part of a global network of scientific and academic institutions working on questions of global environmental change. It is a member of the Leibniz Association, whose institutions perform research on subjects of high relevance to society.

An Appeal to Reason: A Cool Look at Global Warming is a 2008 book by Nigel Lawson. In it, Lawson claims that, although global warming is happening, the science is far from settled. He opposes the scientific consensus as summarized by the IPCC. He also argues that warming will bring both benefits and negative consequences, and that the impact of these changes will be relatively moderate rather than apocalyptic. The book has been rejected by climatologists, including IPCC authors Jean Palutikof and Robert Watson as unscientific.

Mark Zachary Jacobson is a professor of civil and environmental engineering at Stanford University and director of its Atmosphere/Energy Program. He is also a co-founder of the non-profit, Solutions Project.

Ottmar Georg Edenhofer is a German economist who is regarded as one of the world's leading experts on climate change policy, environmental and energy policy, and energy economics. His work has been heavily cited. Edenhofer currently holds the professorship of the Economics of Climate Change at Technische Universität Berlin. Together with Earth scientist Johan Rockström, economist Ottmar Edenhofer is scientific director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), representing the interdisciplinary and solutions-oriented approach of the institute. Furthermore, he is director of the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC). From 2008 to 2015 he served as one of the co-chairs of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Working Group III "Mitigation of Climate Change".
David W. Keith is a professor in the Department of the Geophysical Sciences at the University of Chicago. He joined the University of Chicago in April 2023. Keith previously served as the Gordon McKay Professor of Applied Physics for Harvard University's Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and professor of public policy for the Harvard Kennedy School at Harvard University. Early contributions include development of the first atom interferometer and a Fourier-transform spectrometer used by NASA to measure atmospheric temperature and radiation transfer from space.

Carlo Carraro is the chancellor of the University of Venice for the three-year period 2009–2012, with a two-year extension of his mandate in accordance to the Gelmini University Law bringing it up to summer 2014. He is also professor of environmental economics at the same university. He is director of the Sustainable Development Programme of the Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei and director of the Climate Impacts and Policy Division of the Euro-Mediterranean Center for Climate Change (CMCC). In 2008, Carraro was elected vice-chair of the Working Group III and member of the bureau of the Nobel Laureate Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Christopher B. Field is an American scientist and researcher, who has contributed to the field of climate change. The author of more than 200 scientific publications, Field's research emphasizes impacts of climate change, from the molecular to the global scale. His work includes major field experiments on responses of California grassland to multi-factor global change, integrative studies on the global carbon cycle, and assessments of impacts of climate change on agriculture. Field's work with models includes studies on the global distribution of carbon sources and sinks, and studies on environmental consequences of expanding biomass energy.

The contributions of women in climate change have received increasing attention in the early 21st century. Feedback from women and the issues faced by women have been described as "imperative" by the United Nations and "critical" by the Population Reference Bureau. A report by the World Health Organization concluded that incorporating gender-based analysis would "provide more effective climate change mitigation and adaptation."

Sir James Ferguson "Jim" Skea CBE FRSE is a British academic. He is currently Chair of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for its seventh assessment cycle, and a Professor of Sustainable Energy at Imperial College London. Before being elected as Chair, Skea was Co-Chair of Working Group III of the IPCC. He was a founding member of the UK Government's Committee on Climate Change and currently chairs Scotland's Just Transition Commission. He was a co-author of the IPCC 2018 Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C. In July 2023, Skea was elected as Chair of the IPCC.
Energy modeling or energy system modeling is the process of building computer models of energy systems in order to analyze them. Such models often employ scenario analysis to investigate different assumptions about the technical and economic conditions at play. Outputs may include the system feasibility, greenhouse gas emissions, cumulative financial costs, natural resource use, and energy efficiency of the system under investigation. A wide range of techniques are employed, ranging from broadly economic to broadly engineering. Mathematical optimization is often used to determine the least-cost in some sense. Models can be international, regional, national, municipal, or stand-alone in scope. Governments maintain national energy models for energy policy development.
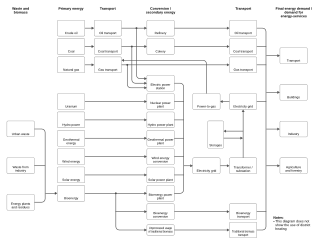
An energy system is a system primarily designed to supply energy-services to end-users. The intent behind energy systems is to minimise energy losses to a negligible level, as well as to ensure the efficient use of energy. The IPCC Fifth Assessment Report defines an energy system as "all components related to the production, conversion, delivery, and use of energy".
Gilbert E. Metcalf is the John DiBiaggio Professor of Citizenship and Public Service, emeritus, at Tufts University, where he was a professor of economics. Currently, he is a visiting professor at the MIT Sloan School as well as a research associate at the National Bureau of Economic Research and a University Fellow at Resources For The Future. Under the Obama administration, he served as the deputy assistant secretary for environment and energy at the U.S. Department of Treasury where he was the founding U.S. Board Member for the UN based Green Climate Fund. His research interests are in the areas of energy, environmental, and climate policy.
References
- ↑ "John Weyant | Management Science and Engineering". Stanford Management Science and Engineering. Retrieved 2019-06-17.
- ↑ "Introducing Renewed Energy: Insights for Clean Energy's Future, a Groundbreaking New Book from KF Press". Kauffman Fellows. Summer 2018.
- ↑ Golden, Mark (24 August 2018). "Proscriptions and prescriptions for the next wave of cleantech investments, new Stanford-led analysis finds". Stanford.