Related Research Articles

Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2. Generating electricity from fusion power remains the focus of international research.

Tritium or hydrogen-3 is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life ~12.3 years. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (protium) contains one proton and zero neutrons, and that of a non-radioactive hydrogen-2 (deuterium) contains one proton and one neutron.
Nuclear engineering is the engineering discipline concerned with designing and applying systems that utilize the energy released by nuclear processes. The most prominent application of nuclear engineering is the generation of electricity. Worldwide, some 440 nuclear reactors in 32 countries generate 10 percent of the world's energy through nuclear fission. In the future, it is expected that nuclear fusion will add another nuclear means of generating energy. Both reactions make use of the nuclear binding energy released when atomic nucleons are either separated (fission) or brought together (fusion). The energy available is given by the binding energy curve, and the amount generated is much greater than that generated through chemical reactions. Fission of 1 gram of uranium yields as much energy as burning 3 tons of coal or 600 gallons of fuel oil, without adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
Livermorium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Lv and atomic number 116. It is an extremely radioactive element that has only been created in a laboratory setting and has not been observed in nature. The element is named after the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the United States, which collaborated with the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Russia, to discover livermorium during experiments conducted between 2000 and 2006. The name of the laboratory refers to the city of Livermore, California, where it is located, which in turn was named after the rancher and landowner Robert Livermore. The name was adopted by IUPAC on May 30, 2012. Five isotopes of livermorium are known, with mass numbers of 288 and 290–293 inclusive; the longest-lived among them is livermorium-293 with a half-life of about 60 milliseconds. A sixth possible isotope with mass number 294 has been reported but not yet confirmed.
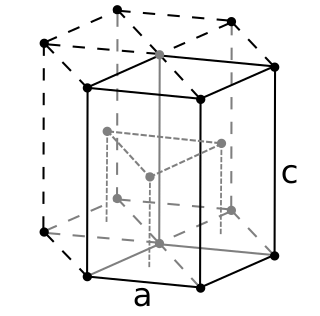
Nihonium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Nh and atomic number 113. It is extremely radioactive: its most stable known isotope, nihonium-286, has a half-life of about 10 seconds. In the periodic table, nihonium is a transactinide element in the p-block. It is a member of period 7 and group 13.

Nuclear weapon designs are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three existing basic design types:

Neutron activation is the process in which neutron radiation induces radioactivity in materials, and occurs when atomic nuclei capture free neutrons, becoming heavier and entering excited states. The excited nucleus decays immediately by emitting gamma rays, or particles such as beta particles, alpha particles, fission products, and neutrons. Thus, the process of neutron capture, even after any intermediate decay, often results in the formation of an unstable activation product. Such radioactive nuclei can exhibit half-lives ranging from small fractions of a second to many years.

In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus.
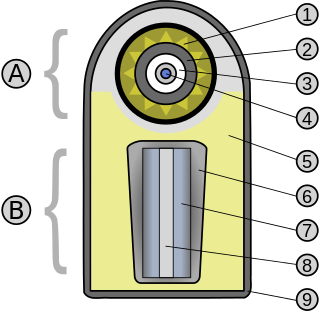
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass, or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239. The first full-scale thermonuclear test was carried out by the United States in 1952 and the concept has since been employed by most of the world's nuclear powers in the design of their weapons.
Caesium (55Cs) has 41 known isotopes, the atomic masses of these isotopes range from 112 to 152. Only one isotope, 133Cs, is stable. The longest-lived radioisotopes are 135Cs with a half-life of 1.33 million years, 137
Cs
with a half-life of 30.1671 years and 134Cs with a half-life of 2.0652 years. All other isotopes have half-lives less than 2 weeks, most under an hour.
Seaborgium (106Sg) is a synthetic element and so has no stable isotopes. A standard atomic weight cannot be given. The first isotope to be synthesized was 263Sg in 1974. There are 13 known radioisotopes from 258Sg to 271Sg and 4 known isomers. The longest-lived isotope is 269Sg with a half-life of 14 minutes.
Bohrium (107Bh) is an artificial element. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes, and a standard atomic weight cannot be given. The first isotope to be synthesized was 262Bh in 1981. There are 11 known isotopes ranging from 260Bh to 274Bh, and 1 isomer, 262mBh. The longest-lived isotope is 270Bh with a half-life of 2.4 minutes, although the unconfirmed 278Bh may have an even longer half-life of about 690 seconds.
Hassium (108Hs) is a synthetic element, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all synthetic elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 265Hs in 1984. There are 13 known isotopes from 263Hs to 277Hs and 1–4 isomers. The most stable isotope of hassium cannot be determined based on existing data due to uncertainty that arises from the low number of measurements. The half-lives of 269Hs and 271Hs are about 12 seconds, whereas that of 270Hs is about 7.6 seconds. It is also possible that 277mHs is more stable than these, with its half-life likely being 130±100 seconds, but only one event of decay of this isotope has been registered as of 2016.
Darmstadtium (110Ds) is a synthetic element, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all synthetic elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 269Ds in 1994. There are 11 known radioisotopes from 267Ds to 281Ds and 2 or 3 known isomers. The longest-lived isotope is 281Ds with a half-life of 14 seconds.
Roentgenium (111Rg) is a synthetic element, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all synthetic elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 272Rg in 1994, which is also the only directly synthesized isotope; all others are decay products of heavier elements. There are seven known radioisotopes, having mass numbers of 272, 274, and 278–282. The longest-lived isotope is 282Rg with a half-life of about 2 minutes, although the unconfirmed 283Rg and 286Rg may have longer half-lives of about 5.1 minutes and 10.7 minutes respectively.
Copernicium (112Cn) is a synthetic element, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all synthetic elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 277Cn in 1996. There are 6 known radioisotopes ; the longest-lived isotope is 285Cn with a half-life of 30 seconds.
Zero power critical is a condition of nuclear fission reactors that is useful for characterizing the reactor core. A reactor is in the zero power critical state if it is sustaining a stable fission chain reaction with no significant growth or decay in the reaction rate, and at a low enough level that thermal considerations are not important to the reaction. For example, a reactor that can produce gigawatts of heat might be considered zero-power critical when producing 100 watts of heat through a fission chain reaction.

The explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy released such as blast, thermal, and nuclear radiation, when that particular nuclear weapon is detonated, usually expressed as a TNT equivalent (the standardized equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene which, if detonated, would produce the same energy discharge), either in kilotonnes (kt—thousands of tonnes of TNT), in megatonnes (Mt—millions of tonnes of TNT), or sometimes in terajoules (TJ). An explosive yield of one terajoule is equal to 0.239 kilotonnes of TNT. Because the accuracy of any measurement of the energy released by TNT has always been problematic, the conventional definition is that one kilotonne of TNT is held simply to be equivalent to 1012 calories.
Nuclear data represents measured probabilities of various physical interactions involving the nuclei of atoms. It is used to understand the nature of such interactions by providing the fundamental input to many models and simulations, such as fission and fusion reactor calculations, shielding and radiation protection calculations, criticality safety, nuclear weapons, nuclear physics research, medical radiotherapy, radioisotope therapy and diagnostics, particle accelerator design and operations, geological and environmental work, radioactive waste disposal calculations, and space travel calculations.
Krypton-85 (85Kr) is a radioisotope of krypton.
References
- ↑ "Joint Evaluated Fission and Fusion (JEFF) Nuclear Data Week 2021". Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA). Retrieved 2024-03-18.