
The Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of October 4, 1986Pub.L. 99–433,, made the most sweeping changes to the United States Department of Defense since the department was established in the National Security Act of 1947 by reworking the command structure of the U.S. military. It increased the powers of the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and implemented some of the suggestions from the Packard Commission, commissioned by President Reagan in 1985. Among other changes, Goldwater–Nichols streamlined the military chain of command, which now runs from the president through the secretary of defense directly to combatant commanders, bypassing the service chiefs. The service chiefs were assigned to an advisory role to the president and the secretary of defense, and given the responsibility for training and equipping personnel for the unified combatant commands.

United States Space Command is a unified combatant command of the United States Department of Defense, responsible for military operations in outer space, specifically all operations 100 kilometers above mean sea level. U.S. Space Command is responsible for the operational employment of space forces that are provided by the uniformed services of the Department of Defense.

The United States Army Space and Missile Defense Command (USASMDC) is an Army Service Component Command (ASCC) of the United States Army. The command was established in 1997. The current USASMDC commander is Lieutenant General Daniel L. Karbler with Senior Enlisted Advisor Command Sergeant Major Finis A. Dodson.

Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) is a major command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force (USAF). AFMC was created on July 1, 1992, through the amalgamation of the former Air Force Logistics Command (AFLC) and the former Air Force Systems Command (AFSC).

United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands in the United States Department of Defense. Headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska, USSTRATCOM is responsible for strategic nuclear deterrence, global strike, and operating the Defense Department's Global Information Grid. It also provides a host of capabilities to support the other combatant commands, including integrated missile defense; and global command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (C4ISR). This command exists to give national leadership a unified resource for greater understanding of specific threats around the world and the means to respond to those threats rapidly.

The United States Transportation Command (USTRANSCOM) is one of eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense. The command is located at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois, and was established in 1987.

The Combat Capabilities Development Command (CCDC) C5ISR Center, formerly the Communications-Electronics RD&E Center (CERDEC), is the United States Army information technologies and integrated systems center. CCDC C5ISR Center is headquartered at Aberdeen Proving Ground in Maryland, with activities at Fort Belvoir in Virginia and Joint Base McGuire-Dix-Lakehurst in New Jersey.

The Naval Information Warfare Systems Command (NAVWARSYSCOM), based in San Diego, is one of six SYSCOM Echelon II organizations within the United States Navy and is the Navy's technical authority and acquisition command for C4ISR, business information technology and space systems. Echelon II means that the organization reports to someone who, in turn, reports directly to the Chief of Naval Operations on the military side. From a civilian perspective, NAVWARSYSCOM reports to the Assistant Secretary of the Navy (RDA). The command was formerly known as SPAWAR, or the Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command and was renamed in June 2019 to better align its identity with its mission.

Located at Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico, the Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center is a direct reporting unit of Headquarters, United States Air Force. It is the Air Force independent test agency responsible for testing, under operationally realistic conditions, new systems being developed for Air Force and multi-service use.

Navy Expeditionary Combat Command (NECC) serves as the single functional command to centrally manage current and future readiness, resources, manning, training and equipping of the United States Navy's 21,000 expeditionary forces who are currently serving in every theater of operation. The NECC was established in January 2006. NECC is a subordinate command of the Navy's Fleet Forces Command.

The 1st Information Operations Command (Land), formerly the Land Information Warfare Activity Information Dominance Center (LIWA/IDC), is an information operations unit under the operational control of U.S. Army Cyber Command (ARCYBER) and headquartered at Fort Belvoir, Virginia.
The Operationally Responsive Space Office is a joint initiative of several agencies within the United States Department of Defense (DoD). The "stand up" of the office took place 21 May 2007 at Kirtland Air Force Base. The first director of the ORS Office was Col. Kevin McLaughlin, who was also dual-hatted as commander of the Space Development and Test Wing located at Kirtland. The ORS Office focuses on providing quick-response tactical space-based capabilities to the warfighter utilizing smaller satellites, such as the Tactical Satellite Program and smaller launch vehicles.

The Operational Test and Evaluation Force (OPTEVFOR) serves as an independent and objective agency within the United States Navy for the operational testing and evaluation (OT&E) of naval aviation, surface warfare, submarine warfare, C4I, cryptologic, and space systems in support Navy and U.S. Department of Defense acquisition programs.

The 32nd AAMDC or 32nd Army Air and Missile Defense Command is a theater level Army air and missile defense multi-component organization with a worldwide, 72-hour deployment mission. The 32nd AAMDC commands echelon above corps (EAC) ADA brigades and other assigned forces. Four such brigades, 11th Air Defense Artillery Brigade, 31st Air Defense Artillery Brigade, 69th Air Defense Artillery Brigade, and 108th Air Defense Artillery Brigade; by training, all stand ready to accomplish their mission of air defense against missile attack – 'anywhere, anytime' in support of the war-fighting combatant commander (CCDR).
A Joint Task Force for Elimination (JTF-E) headquarters was a concept for a military task force headquarters staffed by joint personnel for the purpose of conducting WMD Elimination operations through command and control of joint elimination enablers such as nuclear disablement teams, CBRN Response Teams, radiation assessment teams, and medical laboratories. A JTF-E headquarters may be formed per Joint Publication 3-40 one of two ways: 1) An existing headquarters designated by a Combatant Commander with Joint Elimination Coordination Element (JECE) augmentation and 2) Joint Forces Command (JFCOM) establishing a JTF-E by utilizing the JECE and another existing headquarters.
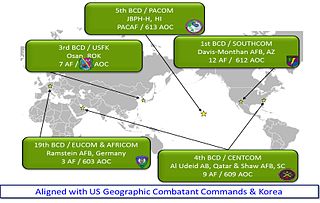
The Battlefield Coordination Detachment , or BCD, is the senior United States Army liaison element of the Army Air Ground System. The BCD serves as a bridge between the senior US Army headquarters element and the senior Air Force headquarters in each respective US combatant command or theater of operations. The BCD enables the coordination of Army-Air Force mission command, fire support, integrated air and missile defense, intelligence sharing, airspace management, and airlift. Additional space, cyber, and electronic warfare augmentation allow the BCD to further enable the designated Army force commander across the complete spectrum of warfare.

The Combined Force Space Component Command (CFSCC) is a U.S.–led multinational subordinate command of United States Space Command. It is responsible for tactical control of American and multinational space forces. The CFSCC's mission is to "plan, integrate, conduct, and assess global space operations in order to deliver combat relevant space capabilities to Combatant Commanders, Coalition partners, the Joint Force, and the Nation." It was established on 29 August 2019.

Space Operations Command (SpOC) is the United States Space Force's space operations, cyber operations, and intelligence field command. It is headquartered at Peterson Space Force Base, Colorado and serves as the U.S. Space Force's service component to United States Space Command. Space Operations Command consists of Space Operations Command West, its mission deltas, and garrison commands.
The Marine Air Command and Control System (MACCS) is the aviation command and control agencies of the United States Marine Corps that provide the Aviation Combat Element (ACE) commander with the means to monitor, supervise, and influence aviation operations in support of the Marine Air-Ground Task Force. The command and control agencies of the MACCS are provided by the squadrons and battalions of the Marine Air Control Groups that are present within each Marine Air Wing. The capabilities resident within the MACCS allow the MAGTF commander to safely conduct aviation operations, facilitate timely maneuver and prosecution of fires and ultimately retain full control of their entire area of operations. MACCS agencies are also responsible for coordinating Marine Corps aviation operations with joint, multinational and civil aviation.

The Space Rapid Capabilities Office is a Direct Reporting Unit of the United States Space Force which specializes in the expedited development and rapid production and deployment of space capabilities to fulfill short-term critical needs. The relatively small and unique office's work is directed by requirements for capabilities provided by the Commander of United States Space Command, and aims to provide capabilities responsive to a request within 1 to 5 years.

















