The economy of Djibouti is derived in large part from its strategic location on the Red Sea. Djibouti is mostly barren, with little development in the agricultural and industrial sectors. The country has a harsh climate, a largely unskilled labour force, and limited natural resources. The country's most important economic asset is its strategic location, connecting the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. As such, Djibouti's economy is commanded by the services sector, providing services as both a transit port for the region and as an international transshipment and refueling centre.

The economy of Georgia is an emerging free market economy. Its gross domestic product fell sharply following the dissolution of the Soviet Union but recovered in the mid-2000s, growing in double digits thanks to the economic and democratic reforms brought by the peaceful Rose Revolution. Georgia continued its economic progress since, "moving from a near-failed state in 2003 to a relatively well-functioning market economy in 2014". In 2007, the World Bank named Georgia the World's number one economic reformer.

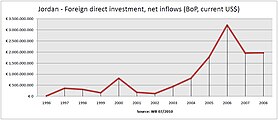
The economy of Jordan is classified as a lower middle income economy. Jordan's GDP per capita rose by 351% in the 1970s, declined 30% in the 1980s, and rose 36% in the 1990s. After King Abdullah II's accession to the throne in 1999, liberal economic policies were introduced. Jordan's economy had been growing at an annual rate of 8% between 1999 and 2008. However, growth has slowed to 2% after the Arab Spring in 2011. The substantial increase of the population, coupled with slowed economic growth and rising public debt led to a worsening of poverty and unemployment in the country. As of 2023, Jordan has a GDP of US$50.85 billion, ranking it 89th worldwide.

The economy of Kazakhstan is the largest in Central Asia in both absolute and per capita terms. In 2021, Kazakhstan attracted more than US$370 billion of foreign investments since becoming an independent republic after the dissolution of the former Soviet Union.

The economy of Mauritius is a mixed developing economy based on agriculture, exports, financial services, and tourism. Since the 1980s, the government of Mauritius has sought to diversify the country's economy beyond its dependence on just agriculture, particularly sugar production.

The United Arab Emirates is a high-income developing market economy. The UAE's economy is the 4th largest in the Middle East, with a gross domestic product (GDP) of US$415 billion in 2021-2023.
A free-trade zone (FTZ) is a class of special economic zone. It is a geographic area where goods may be imported, stored, handled, manufactured, or reconfigured and re-exported under specific customs regulation and generally not subject to customs duty. Free trade zones are generally organized around major seaports, international airports, and national frontiers—areas with many geographic advantages for trade.
The Licence Raj or Permit Raj is a pejorative for the system of strict government control and regulation of the Indian economy that was in place from the 1950s to the early 1990s. Under this system, businesses in India were required to obtain licences from the government in order to operate, and these licences were often difficult to obtain.

Foreign direct investment in Iran (FDI) has been hindered by unfavorable or complex operating requirements and by international sanctions, although in the early 2000s the Iranian government liberalized investment regulations. Iran ranks 62nd in the World Economic Forum's 2011 analysis of the global competitiveness of 142 countries. In 2010, Iran ranked sixth globally in attracting foreign investments.
The Federal Ministry of Budget and Economic Planning is one of the Federal Ministries of Nigeria.
Board of Investment (BOI) (Urdu: ہیئتِ پاکستان برائے سرمایہ کاری) is the premier investment promotion agency of Pakistan working under the administrative control of the Prime Minister’s Office and is mandated to promote and facilitate both local & foreign investment. The Board of Investment is a member of the World Association of Investment Promotion Agencies (WAIPA).

Invest KOREA (IK), Korea's national investment promotion agency, was established as part of the Korea Trade-Investment Promotion Agency (KOTRA) to promote foreign direct investment (FDI) to Korea. It provides comprehensive services for all investment stages of Korea, including investment feasibility study, investment execution, and grievance resolution.
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) is a central government department under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry in India. It is responsible for formulation and implementation of promotional and developmental measures for growth of the industrial sector, keeping in view the national priorities and socio-economic objectives. While individual administrative ministries look after the production, distribution, development and planning aspects of specific industries allocated to them, DPIIT is responsible for the overall industrial policy. It is also responsible for facilitating and increasing the foreign direct investment (FDI) flows to the country.
The Vanuatu Foreign Investment Promotion Agency (VFIPA), is Vanuatu's National investment promotion agency. It was established by the foreign investment act [cap 248] in 1998 and operating as a unit under the department of Trades and Industry with a mandate to "promote and facilitate foreign investments into Vanuatu."

Mawarid Finance is a private joint stock company in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, providing Shari'a-compliant financial services. It was founded in 2006 with a paid-up capital of AED 1 billion. All of its products are based on Islamic financial principles such as Ijarah, Istisnaa, Murabaha, Mudharaba, Musharaka, Kafalah and Wakala and its practices are governed by a full Sharia board.
The Investment Development Authority of Lebanon (IDAL) is the national investment promotion agency of Lebanon. IDAL was established in 1994 with the aim of promoting Lebanon as a key investment destination, and attracting facilitating, and retaining investments in the country. In 2001, Investment Law No.360 was enacted to reinforce the organisation's mission, providing a framework for regulating investment activities in Lebanon, and providing local and foreign investors alike with a range of incentives and business support services. In addition to its role as an investment promotion agency, IDAL is entrusted with the active promotion and marketing of Lebanese exports including but not limited to agricultural and agro-industrial products. IDAL enjoys financial and administrative autonomy and reports to the President of the Council of Ministers who exercises a tutorial authority over it.

Dubai Airport Freezone is a designated free economic zone in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, providing company formation and business setup services in Dubai. DAFZ is home to more than 2,000 registered businesses from over 20+ sectors and various industries, with 20,000+ professionals.

United Arab Emirates corporate law regulates the governance, finance and power of corporations in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) through UAE law. Every emirate has its own basic corporate code.
Hasan Abdullah Ismaik is a Jordanian businessman and Chairman of Hasan Abdullah Mohammed Group, a UAE-based group of investment companies founded by Ismaik in 2006. He owns Marya Development & Real Estate Investment LLC, a private investment company in the United Arab Emirates with a diversified investment portfolio that includes projects worth US$4 billion. He is the Chairman of Al-Ashmal Real-Estate Investment Co. in Jordan; and Chairman of publicly listed Masaken for Land and Industrial Development Projects. In 2014, Forbes Magazine listed Ismaik as the first Jordanian billionaire and the third-youngest billionaire in the Middle East.
Designated Freezones in the United Arab Emirates are special areas in the United Arab Emirates that are subject to special rules for supplies of goods within the region for VAT purposes. They are instrumental components of the country's economic landscape, contributing significantly to its development and global standing. Established to diversify the economy away from oil dependence, these zones serve as pivotal entities fostering international trade, foreign investment and economic growth.