Related Research Articles

Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation.

Nils Gabriel Sefström was a Swedish chemist. Sefström was a student of Berzelius and, when studying the brittleness of steel in 1830, he rediscovered a new chemical element, to which he gave the name vanadium.

Wallace Hume Carothers was an American chemist, inventor and the leader of organic chemistry at DuPont, who was credited with the invention of nylon.

Group 5 is a group of elements in the periodic table. Group 5 contains vanadium (V), niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta) and dubnium (Db). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.
Charles Benjamin Dudley was a U.S. chemist who was an early proponent of standardisation in industry.
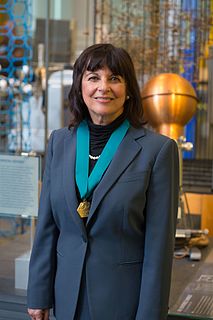
Jacqueline K. Barton, is an American chemist. She worked as a Professor of Chemistry at Hunter College (1980–82), and at Columbia University (1983–89) before joining the California Institute of Technology. In 1997 she became the Arthur and Marian Hanisch Memorial Professor of Chemistry and from 2009 to 2019, the Norman Davidson Leadership Chair of the Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Caltech. She currently is the John G. Kirkwood and Arthur A. Noyes Professor of Chemistry.

Andrés Manuel del Río y Fernández was a Spanish–Mexican scientist, naturalist and engineer who discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801. He proposed that the element be given the name panchromium, or later, erythronium, but his discovery was not credited at the time, and his names were not used.

Michael Stanley Whittingham is a British-American chemist. He is currently a professor of chemistry and director of both the Institute for Materials Research and the Materials Science and Engineering program at Binghamton University, State University of New York. He also serves as director of the Northeastern Center for Chemical Energy Storage (NECCES) of the U.S. Department of Energy at Binghamton. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2019 alongside Akira Yoshino and John B. Goodenough.
Norman Grant Gaylord was an American industrial chemist and research scientist. He was credited with playing a key role in the development of the gas-permeable rigid contact lens which allows oxygen to reach the wearer's cornea.
Clifford Cook Furnas was an American author, Olympic athlete, scientist, expert on guided missiles, university president, and public servant. He was first cousin of the author Evangeline Walton.
Ralph Franz Hirschmann was a German American chemist who led a team that was responsible for the first organic synthesis of an enzyme, a ribonuclease.

Martin Hill Ittner was a chemist working for Colgate, now known as Colgate-Palmolive. He is best known for his contributions to applied chemistry, including the development of toothpaste and detergent.

John Brown Francis Herreshoff was second winner of the Perkin Medal. He was also the president of The General Chemical Company.
John H. Sinfelt was an American chemical engineer whose research on catalytic reforming was responsible for the introduction of unleaded gasoline.
John Douglass Ferry was a Canadian-born American chemist and biochemist noted for development of surgical products from blood plasma and for studies of the chemistry of large molecules. Along with Williams and Landel, Ferry co-authored the work on time-temperature superposition in which the now famous WLF equation first appeared. The National Academy of Sciences called Ferry "a towering figure in polymer science". The University of Wisconsin said that he was "undoubtedly the most widely recognized research pioneer in the study of motional dynamics in macromolecular systems by viscoelastic techniques".
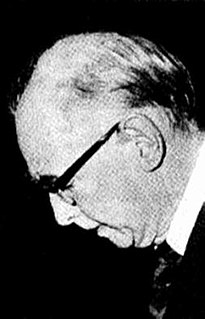
William Bleloch was a South African metallurgist noted for developing smelting techniques for the processing of chrome ores. At a 1975 ceremony when the University of the Witwatersrand conferred upon him an honorary doctorate of Science and Engineering, the citation read "William Bleloch can truly be called the father of our electrochemical and electrometallurgical industries".

William McMurtrie was an American chemist.
The Society of Chemical Industry or SCI America is an independent learned society inspired by the creation of the Society of Chemical Industry (SCI) in London in 1881. Originally known as the New York Section, it was formed in 1894 and officially renamed the America Section in 1919. The main activity of the America Section is the awarding of several prizes in chemistry: the Perkin Medal, the Chemical Industry Medal and the Gordon E. Moore Medal. The America Section also works with the American Chemical Society (ACS) and others to support scholars in chemistry and chemical engineering.
Nathaniel Howell Furman (1892–1965) was an American professor of analytical chemistry who helped develop the electrochemical uranium separation process as a member of the Manhattan Project.